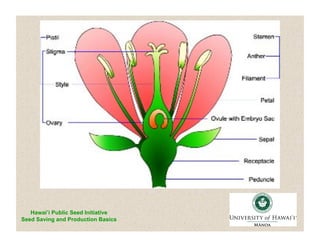
This document discusses guidelines for growing seed crops and maintaining genetic diversity. It addresses reasons for self-seed production such as heirloom varieties and sustainability. Key points covered include selecting self-pollinated annual crops and open-pollinated varieties, maintaining an adequate number of plants to limit genetic drift, implementing selection and rouging procedures to ensure seed purity, properly labeling and controlling pollen flow. The document also discusses isolation distances which vary based on the crop and pollination method.