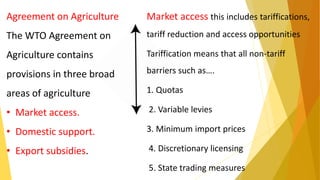
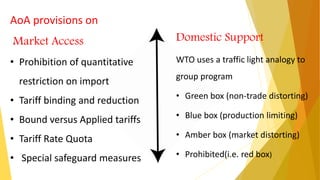
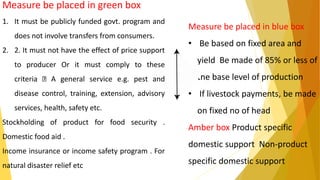
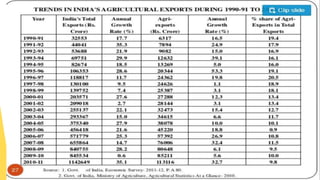
WTO was formed on January 1, 1995 to oversee international trade and replaced the previous GATT agreement. It aims to implement multilateral trade agreements and promote free trade. Key organs of the WTO include the Ministerial Conference and councils overseeing trade in goods, services, intellectual property, and dispute settlement. The WTO agreements cover trade in goods, services, intellectual property rights, agriculture, textiles, investment measures, and dispute resolution. India has benefited from WTO membership but still faces challenges in agriculture and other sectors.
![WHAT IS WTO
• WTO was formed on 1st Jan , 1995 .
• It took over GATT (general agreement on tariffs and
trade).
• In 8th round of GATT, popularly known as Uruguay round,
members nation of GATT decided to set up a new
organization, ‘World Trade Organization’ in place of GATT.
[World Trade Organization]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wto-191221122949/85/Wto-1-320.jpg)