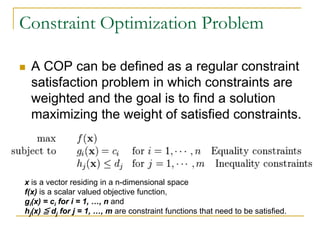
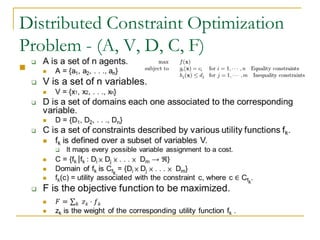
This document discusses modeling word sense disambiguation as a distributed constraint optimization problem. It provides background on word sense disambiguation, constraint optimization problems, and distributed constraint optimization problems. It then describes representing word sense disambiguation as a distributed constraint optimization problem by defining agents, variables, domains, and constraints. The document outlines experiments using this approach on Senseval data and compares results to other methods. It concludes that this framework can effectively encode information from various knowledge sources to perform word sense disambiguation.