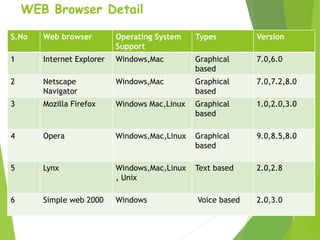
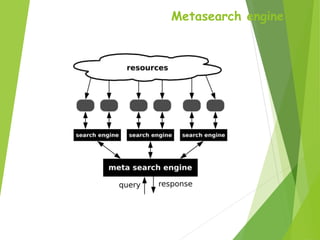
A web browser allows users to view and interact with web pages on the World Wide Web. It formats HTML content for display. Popular browsers include Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Safari, and Opera. A search engine is a program that helps users locate information on the web. It has three main components: web crawlers that gather page data, a database to store this indexed data, and a search interface for users. Popular search engines are Google, Yahoo, and Bing. A meta-search engine sends search requests to multiple other search engines and aggregates the results into a single list.