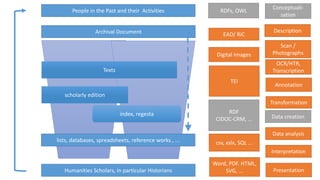
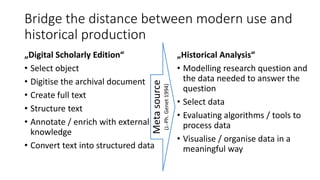
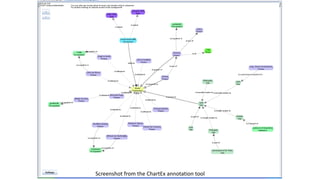
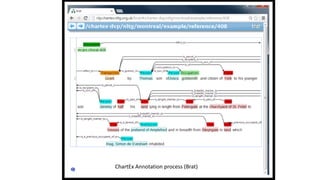
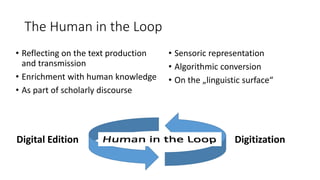
The document discusses the process of creating digital scholarly editions of historical documents, emphasizing the integration of modern technologies with traditional archival practices. It outlines the steps involved in digitization, data structuring, annotation, and the use of computational methods for historical analysis. The concept of the 'assertive edition' is introduced, which includes formal representations of historical assertions linked to digital documents, highlighting the importance of both human interpretation and machine assistance in scholarly discourse.