This document discusses networking and programming interfaces in Windows. It is divided into two parts:
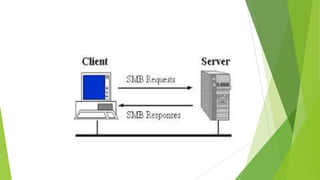
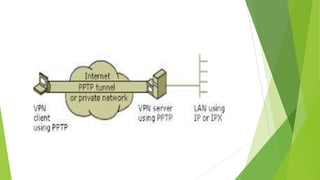
Part I covers networking topics like network interfaces, protocols (SMB, TCP/IP, HTTP), domains, and Active Directory.
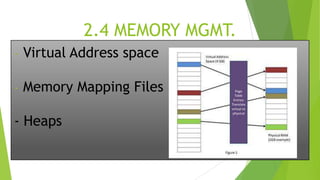
Part II discusses the Win32 and .NET programming interfaces, covering access to kernel objects, sharing objects between processes, process management (priority classes and levels), and memory management (virtual address space, memory mapping, heaps).