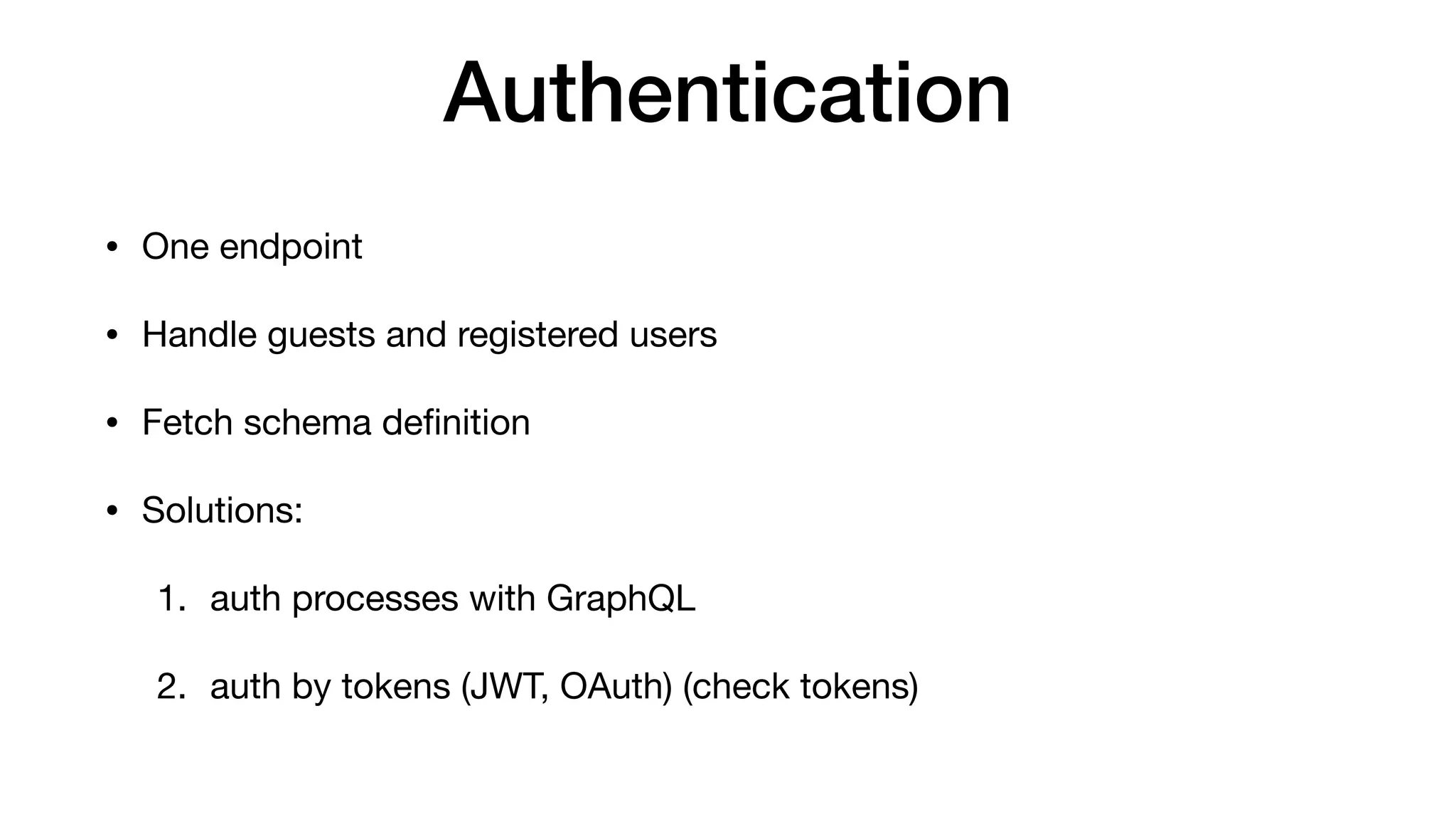
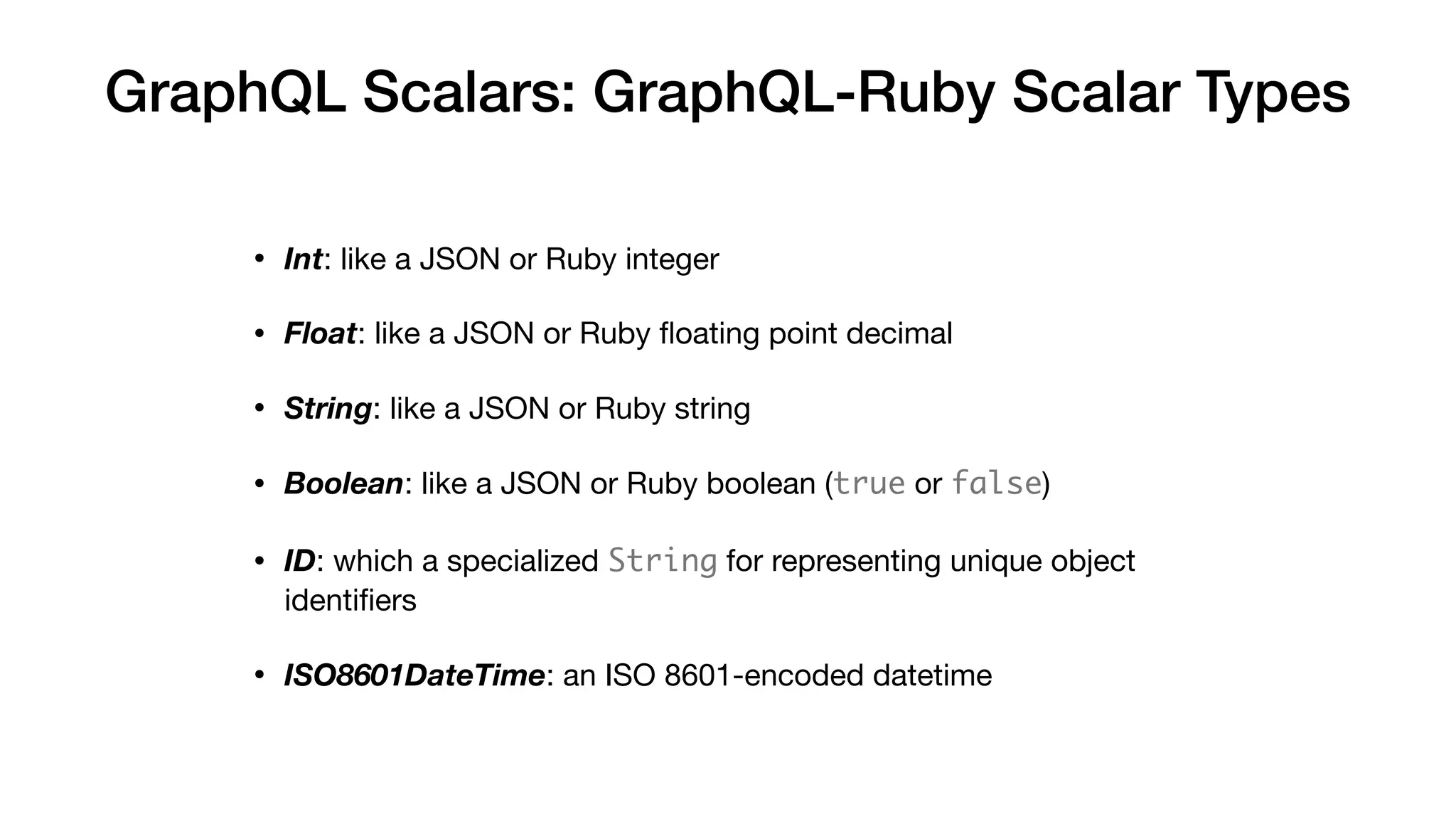
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to GraphQL, its schema definition language (SDL), and its execution process. Key concepts covered include types, queries, fields, arguments, and various GraphQL constructs such as enums, input objects, and directives. The material also highlights common pitfalls and describes how GraphQL operates over transport protocols like HTTP.

![query {
me {
firstName
lastName
company
position
socialLinks {
name
url
}
}
}
{
"data": {
"me": {
"firstName": "Valentyn",
"lastName": "Ostakh",
"company": "RubyGarage",
"position": "Ruby/JS developer",
"socialLinks": [
{
"name": "facebook",
"url": "https://facebook.com/valikos"
},
{
"name": "twitter",
"url": "https://twitter.com/valikos_ost"
},
{
"name": "github",
"url": "https://github.com/valikos"
}
]
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-2-2048.jpg)








![GraphQL Object Type
{
"data": {
"character": {
"firstName": "Peter",
"lastName": "Griffin",
"friends": [
{
"firstName": "Brian",
"lastName": null
},
{
"firstName": "Homer",
"lastName": "Simpson"
}
]
}
}
}
query {
character {
firstName
lastName
friends {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-11-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Object Type
{
"data": {
"character": {
"firstName": "Peter",
"lastName": "Griffin",
"friends": [
{
"firstName": "Brian",
"lastName": null
},
{
"firstName": "Homer",
"lastName": "Simpson"
}
]
}
}
}
query {
character {
firstName
lastName
friends {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-12-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Object Type
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName: String
friends: [Character!]
}
module Types
class CharacterType < BaseObject
field :first_name, String, null: false
field :last_name, String, null: true
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType], null: true
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-13-2048.jpg)

![GraphQL Fields
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName: String
friends: [Character!]
}
module Types
class CharacterType < BaseObject
field :first_name, String, null: false
field :last_name, String, null: true
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType], null: true
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-15-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Fields
{
"data": {
"character": {
"firstName": "Peter",
"lastName": "Griffin",
"friends": [
{
"firstName": "Brian",
"lastName": null
},
{
"firstName": "Homer",
"lastName": "Simpson"
}
]
}
}
}
query {
character {
firstName
lastName
friends {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-16-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Fields
{
"data": {
"character": {
"firstName": "Peter",
"lastName": "Griffin",
"friends": [
{
"firstName": "Brian",
"lastName": null
},
{
"firstName": "Homer",
"lastName": "Simpson"
}
]
}
}
}
query {
character {
firstName
lastName
friends {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-17-2048.jpg)

![GraphQL Fields: Arguments
{
"data": {
"character": {
"firstName": "Jon",
"lastName": "wonS",
"friends": [
{
"firstName": "Samwell",
"lastName": "Tarly"
}
]
}
}
}
query {
character {
firstName
lastName(reverse: true)
friends(last: 1) {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-19-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Fields: Arguments
{
"data": {
"character": {
"firstName": "Jon",
"lastName": "wonS",
"friends": [
{
"firstName": "Samwell",
"lastName": "Tarly"
}
]
}
}
}
query {
character {
firstName
lastName(reverse: true)
friends(last: 1) {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-20-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Fields: Arguments
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName(reverse: Boolean): String
friends(last: Int): [Character!]
}
module Types
class CharacterType < BaseObject
field :first_name, String, null: false
field :last_name, String, null: true do
argument :reverse, Boolean, required: false
end
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType], null: true do
argument :last, Integer, required: false
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-21-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Fields: Arguments
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName(reverse: Boolean): String
friends(last: Int): [Character!]
}
module Types
class CharacterType < BaseObject
field :first_name, String, null: false
field :last_name, String, null: true do
argument :reverse, Boolean, required: false
end
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType], null: true do
argument :last, Integer, required: false
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-22-2048.jpg)

![GraphQL Fields: Resolvers
module Types
class CharacterType < BaseObject
field :first_name, String, null: false
field :last_name, String, null: true
field :full_name, String, null: false
def full_name
[object.full_name, object.last_name].join(' ')
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-24-2048.jpg)









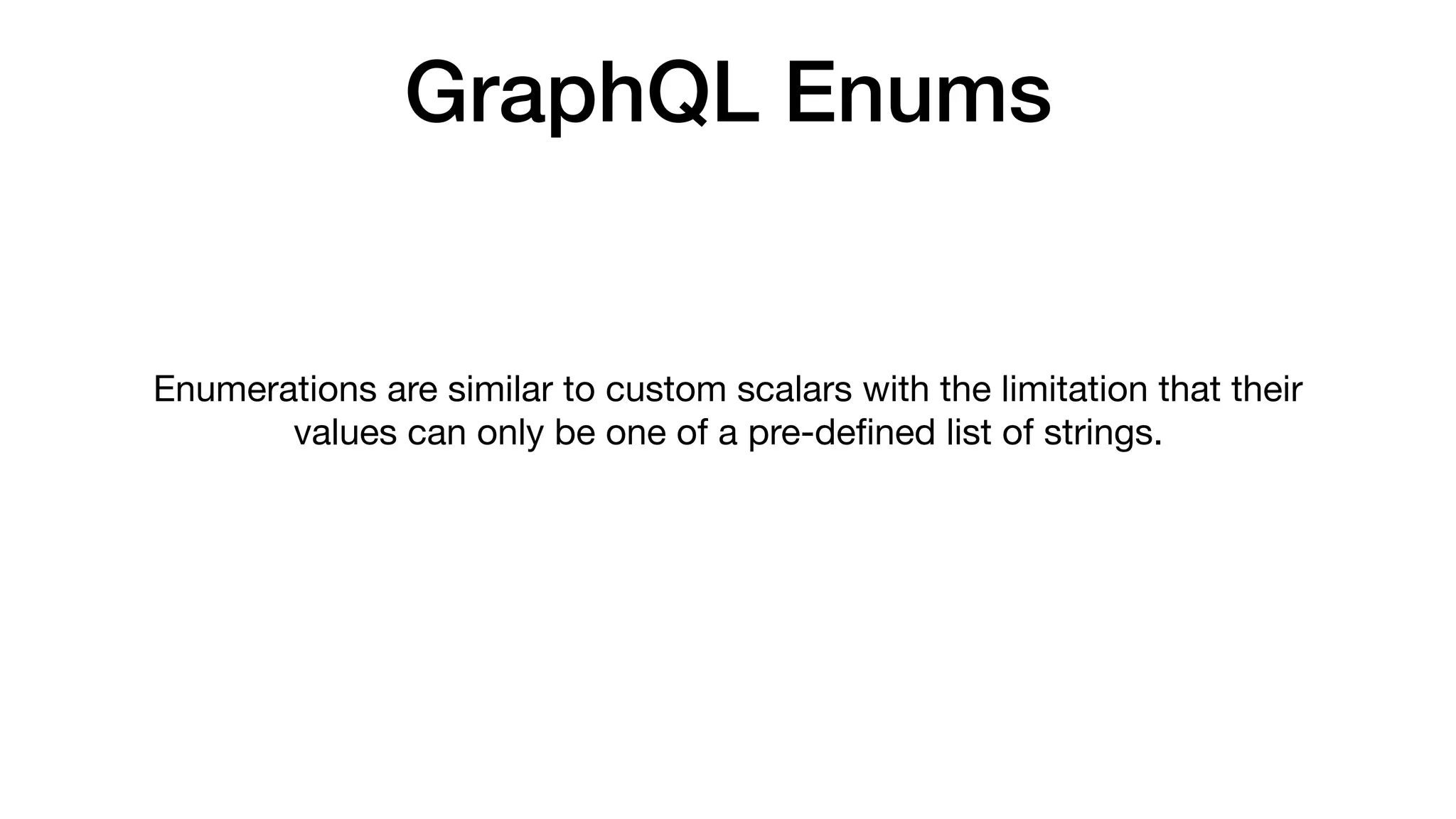
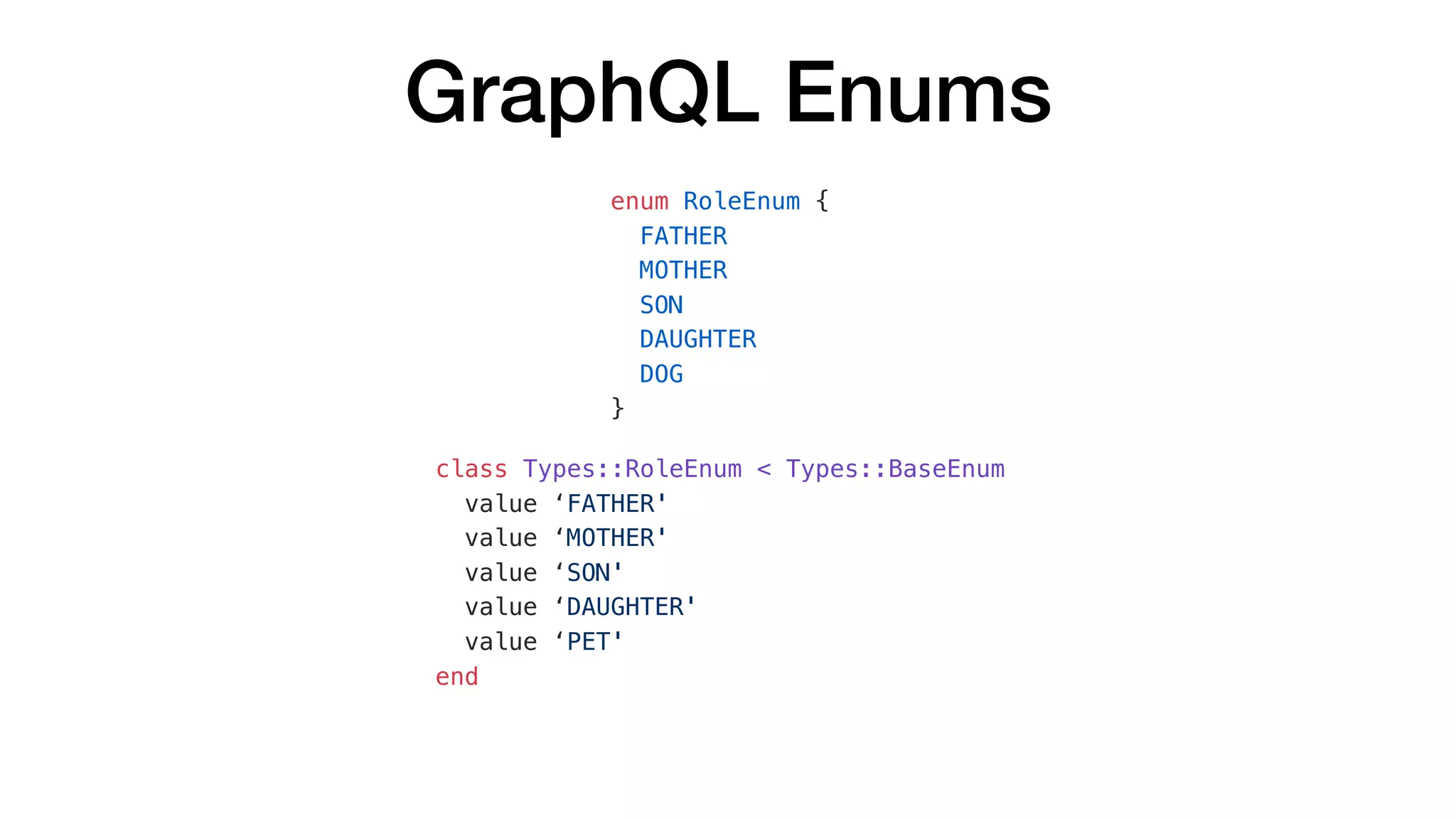
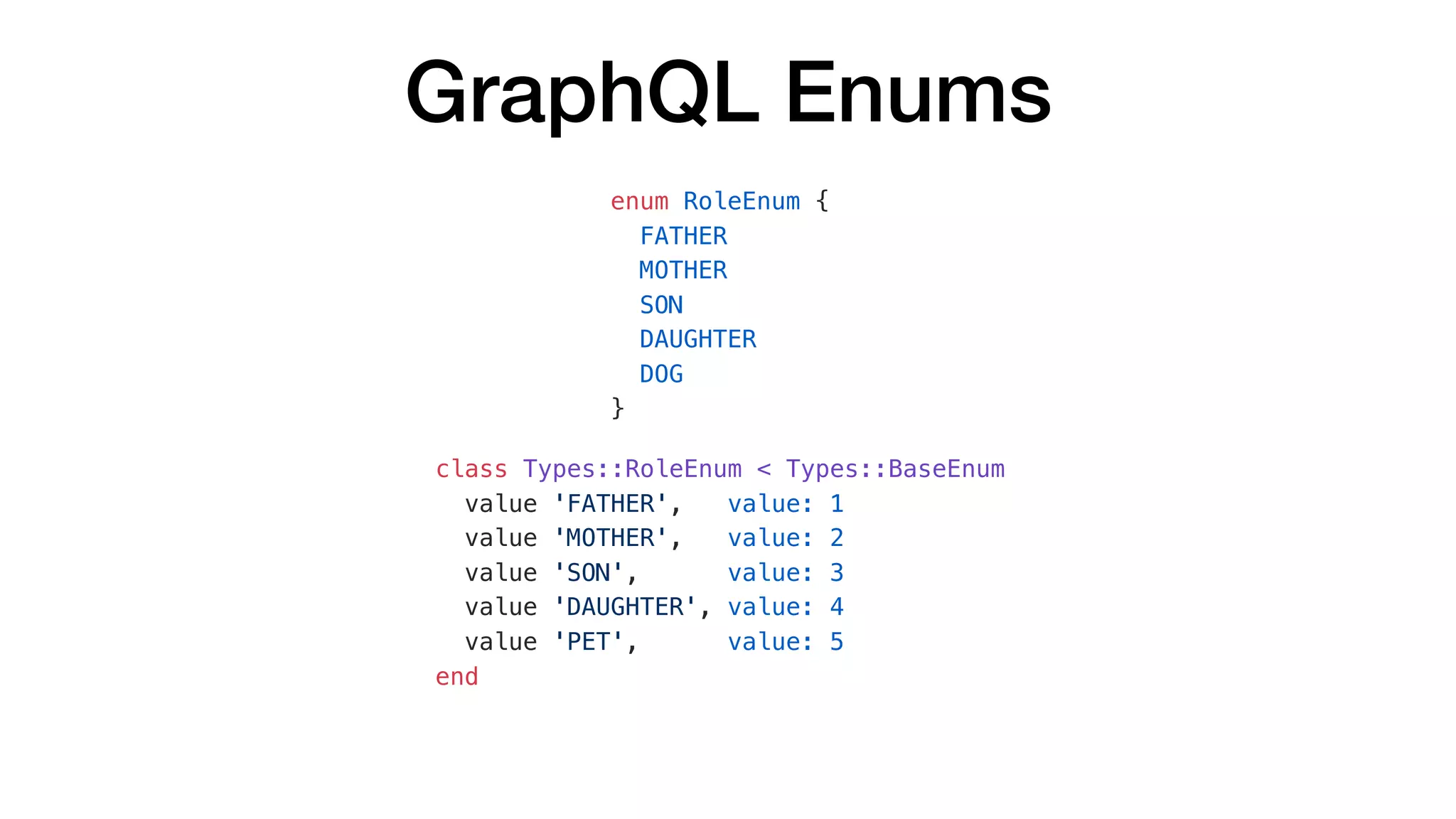
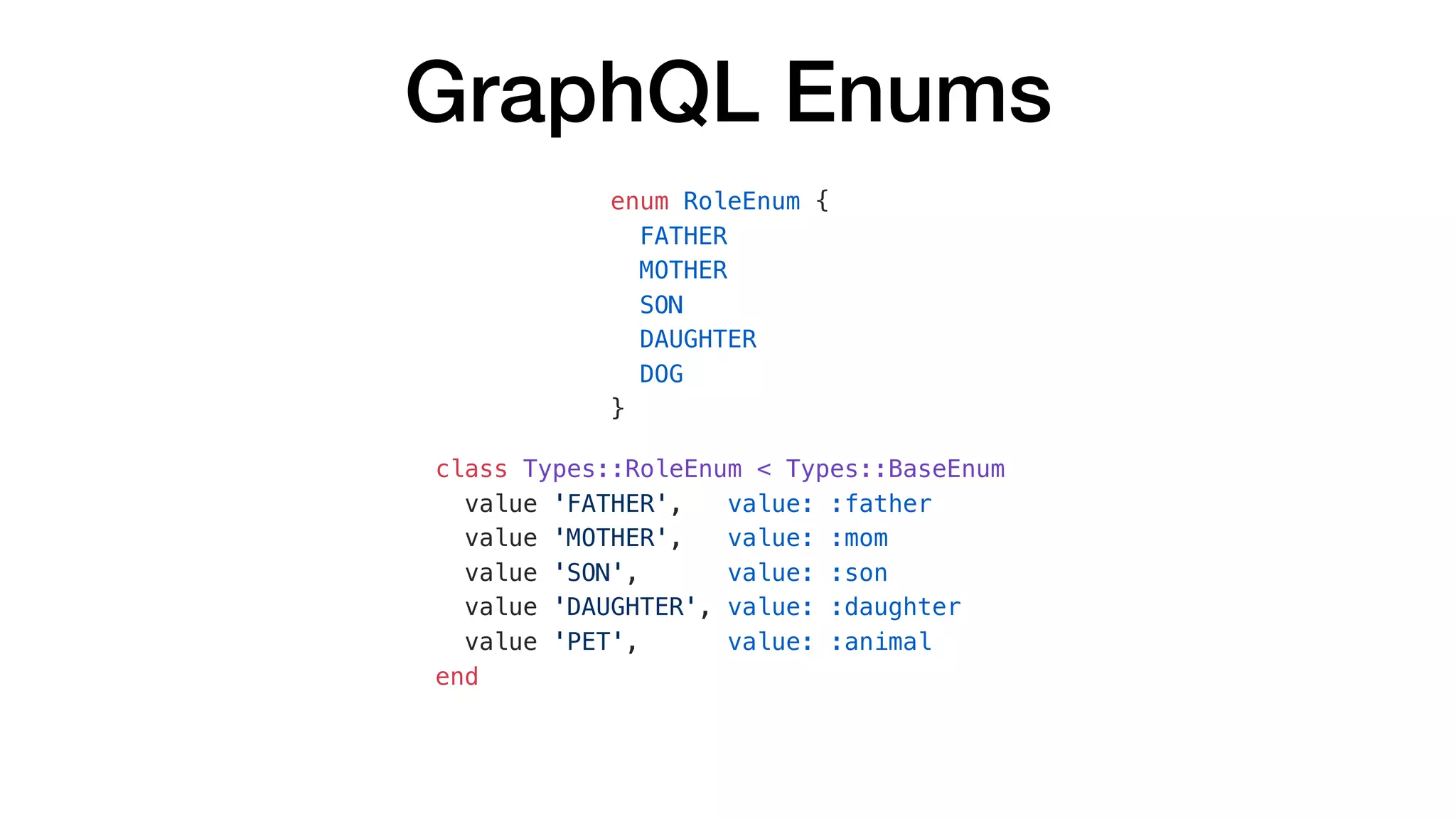
![GraphQL Enums
{
"data": {
"character": {
"firstName": "Peter",
"role": "FATHER",
"friends": [
{
"firstName": "Brian",
"role": "PET"
},
{
"firstName": "Stewie",
"role": "SON"
}
]
}
}
}
query {
character {
firstName
role
friends {
firstName
role
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-36-2048.jpg)

![GraphQL Lists
{
"data": {
"character": {
"firstName": "Peter",
"lastName": "Griffin",
"friends": [
{
"firstName": "Brian",
"lastName": null
},
{
"firstName": "Homer",
"lastName": "Simpson"
}
]
}
}
}
query {
character {
firstName
lastName
friends {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-41-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Lists
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName: String
friends: [Character!]
}
module Types
class CharacterType < BaseObject
field :first_name, String, null: false
field :last_name, String, null: true
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType], null: true
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-42-2048.jpg)

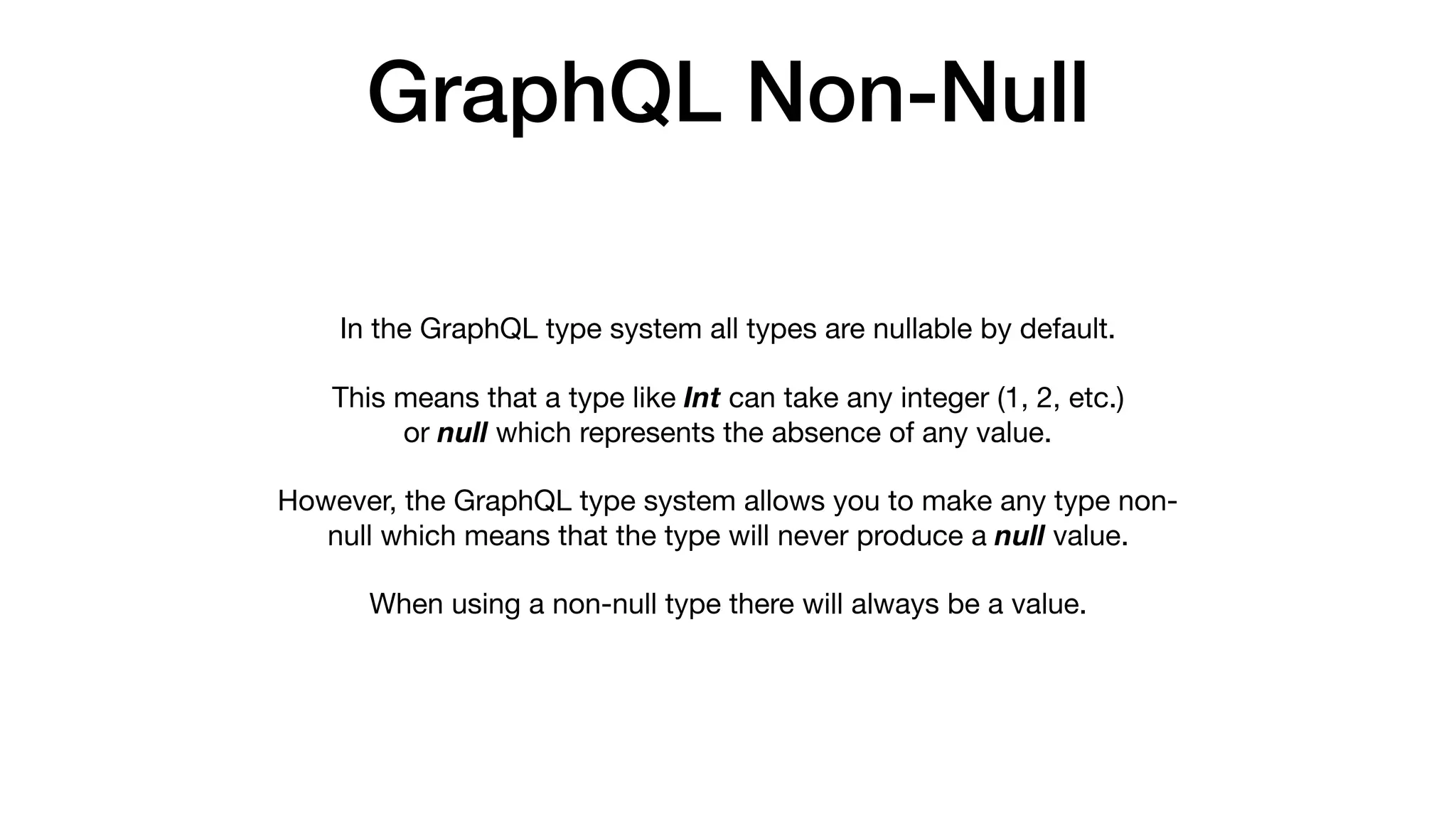
![GraphQL Non-Null
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName: String
friends: [Character!]!
}
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName: String
friends: [Character]!
}
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName: String
friends: [Character!]
}
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName: String
friends: [Character]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-45-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Non-Null
module Types
class CharacterType < BaseObject
field :first_name, String, null: false
field :last_name, String, null: true
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType, null: true], null: true
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType, null: true], null: false
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType, null: false], null: true
field :friends, [Types::CharacterType, null: false], null: false
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-46-2048.jpg)

![GraphQL Unions
{
search(in: "Adventure Time") {
__typename
... on Character {
firstName
}
... on land {
name
}
... on Building {
type
}
}
}
{
"data": {
"search": [
{
"__typename": "Character",
"firstName": "Finn"
},
{
"__typename": "Land",
"name": "Land of Ooo"
},
{
"__typename": "Building",
"type": "Fort"
}
]
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-48-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Unions
union Result = Character | Land | Building
type Character {
firstName: String!
}
type Building {
type: String!
}
type Land {
name: String!
}
type Query {
search: [Result]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-49-2048.jpg)
![GraphQL Unions
union Result = Character | Land | Building
type Character {
firstName: String!
}
type Building {
type: String!
}
type Land {
name: String!
}
type Query {
search: [Result]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-50-2048.jpg)







![GraphQL Directives
query {
character {
firstName
lastName
friends @skip(if: $isAlone){
firstName
lastName
}
}
}
type Character {
firstName: String!
lastName: String
surname: String @deprecated(reason: "Use lastName. Will be removed...")
friends: [Character!]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-62-2048.jpg)














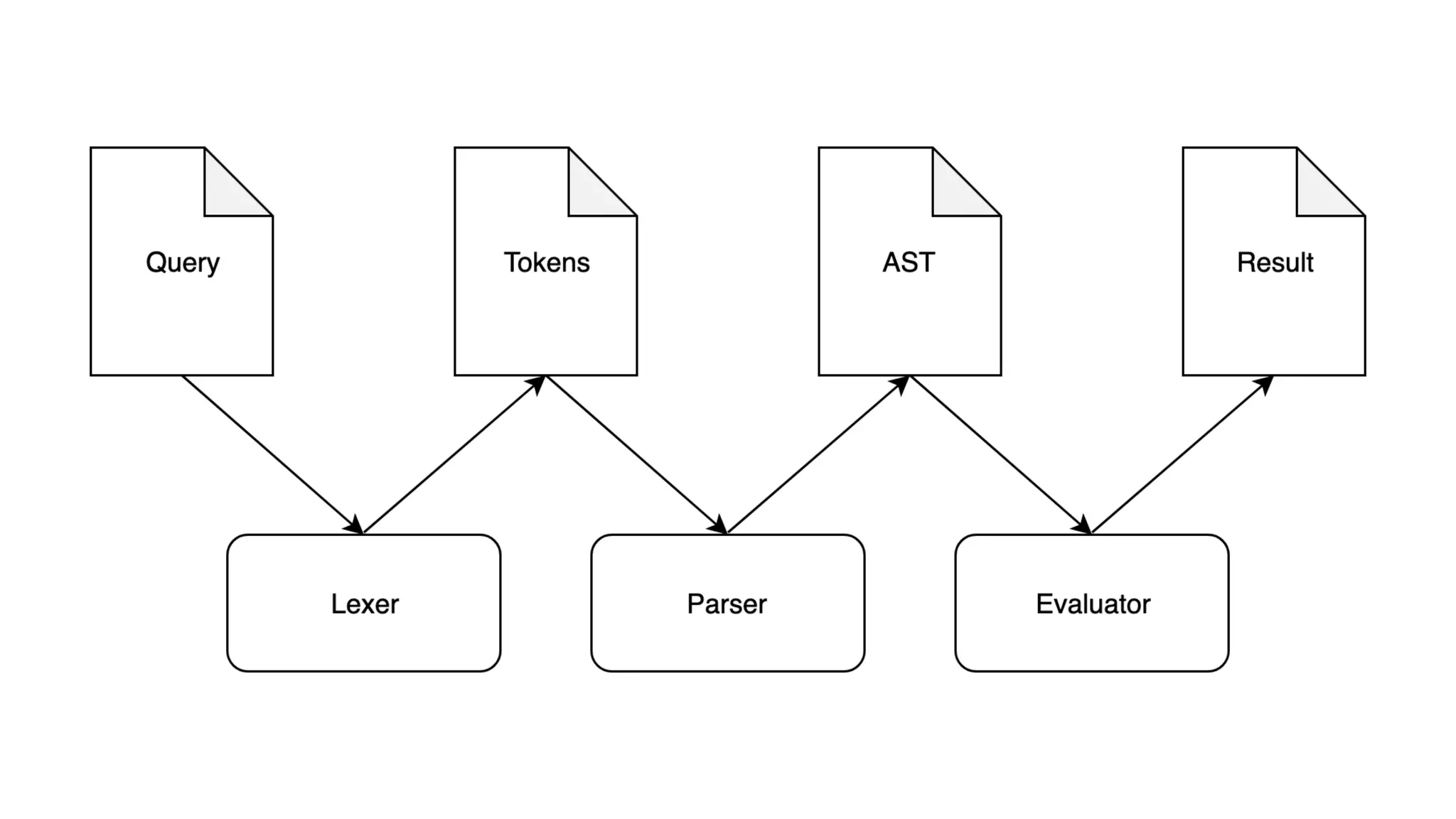


![Lexer
query {
character {
firstName
lastName
friends {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}
GraphQL.scan(query) =>
[
(QUERY "query" [2:1]),
(LCURLY "{" [2:7]),
(IDENTIFIER "character" [3:3]),
(LCURLY "{" [3:13]),
(IDENTIFIER "firstName" [4:5]),
(IDENTIFIER "lastName" [5:5]),
(IDENTIFIER "friends" [6:5]),
(LCURLY "{" [6:13]),
(IDENTIFIER "firstName" [7:7]),
(IDENTIFIER "lastName" [8:7]),
(RCURLY "}" [9:5]),
(RCURLY "}" [10:3]),
(RCURLY "}" [11:1])
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-83-2048.jpg)
![Parser
query {
character {
firstName
lastName
friends {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}
GraphQL.parse(query) =>
#<GraphQL::Language::Nodes::Document:0x00007fbd8ae3dec0
@definitions=
[#<GraphQL::Language::Nodes::OperationDefinition:…
@col=1,
@directives=[],
@filename=nil,
@line=2,
@name=nil,
@operation_type="query",
@selections=
[#<GraphQL::Language::Nodes::Field:…
@alias=nil,
@arguments=[],
@col=3,
@directives=[],
@filename=nil,
@line=3,
@name="character"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whathowtodowithgraphql-valentynostakh-190524125840/75/What-How-to-do-with-GraphQL-Valentyn-Ostakh-ENG-Ruby-Meditation-27-84-2048.jpg)