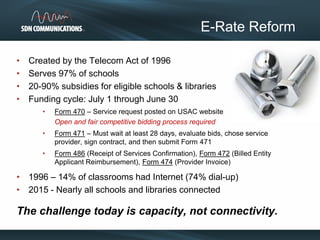
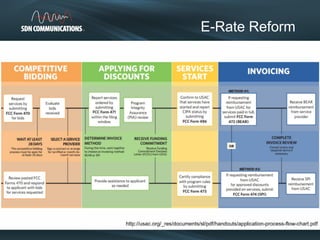
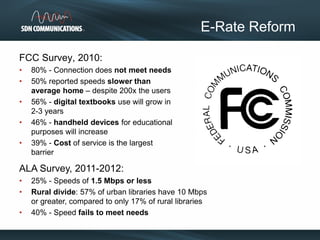
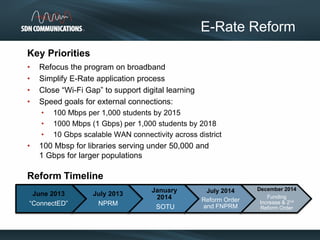
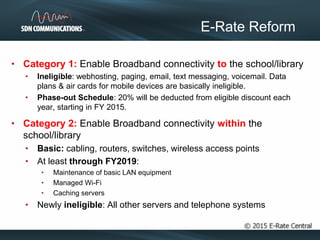
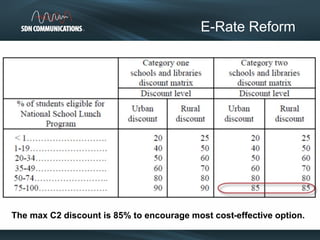
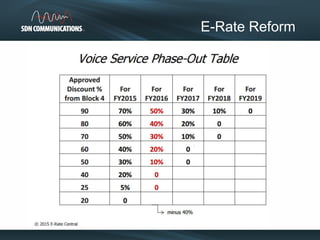
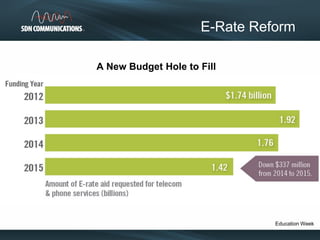
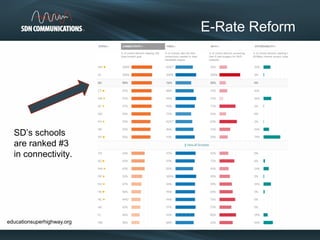
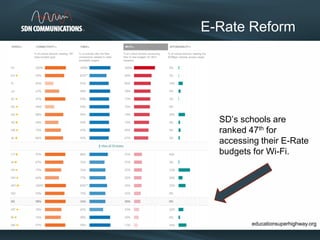
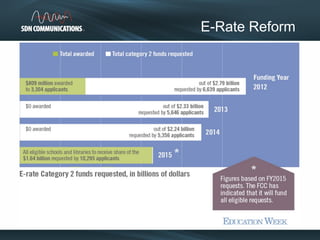
SDN provides internet and networking services across South Dakota, connecting over 300 communities with a focus on enhancing digital resources for schools and libraries through e-rate reform. Recent changes aim to increase broadband access and funding allocations for schools, pushing for higher connectivity speeds and addressing capacity challenges. The reforms also simplify the application process and enhance support for digital learning initiatives.