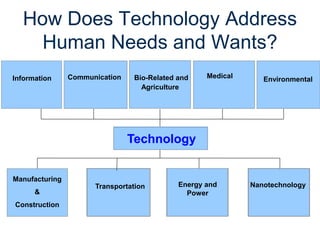
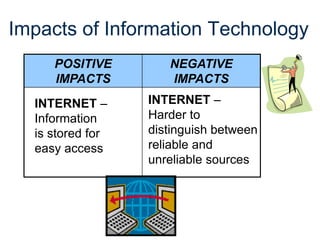
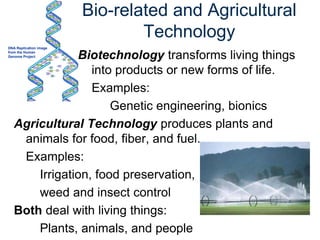
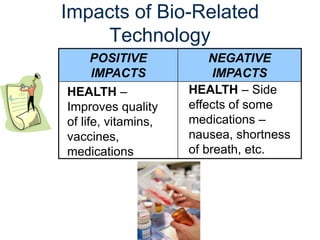
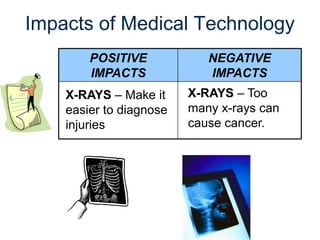
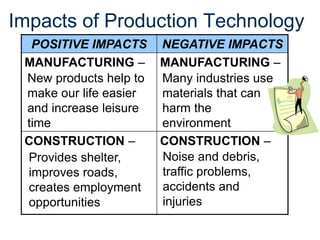
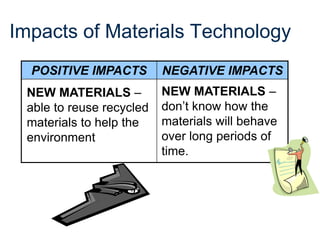
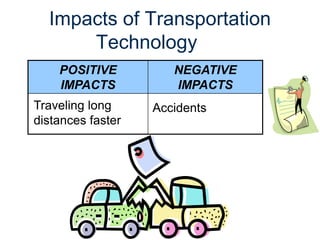
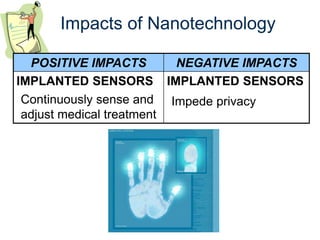
The document provides an overview of technology, defining it as products and processes created to meet human needs, and discusses its various types including information, communication, medical, and transportation technologies. It outlines how these technologies influence society positively and negatively, highlighting examples and their impacts on health, the environment, and communication. Each section discusses specific technologies, their applications, and the associated benefits and drawbacks.