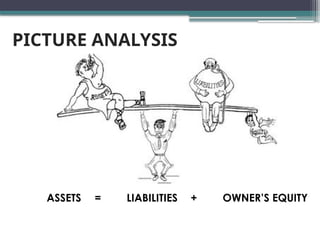
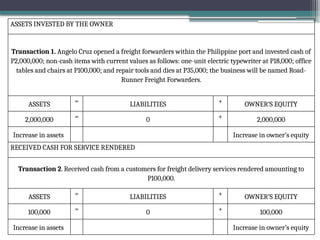
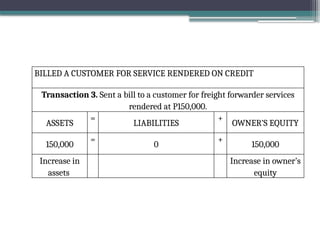
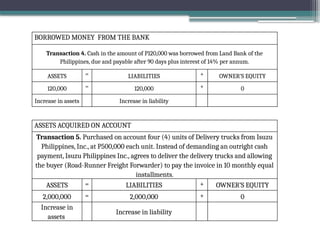
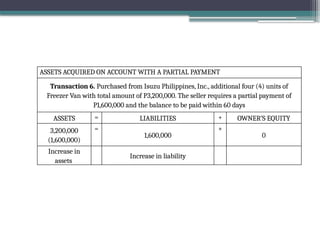
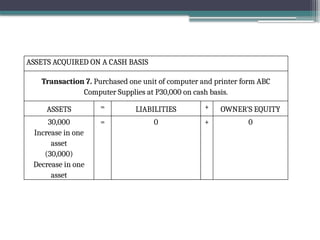
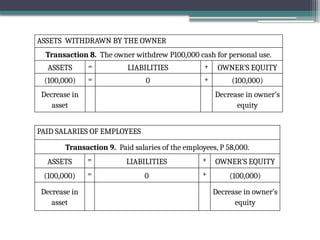
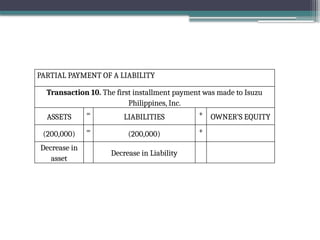
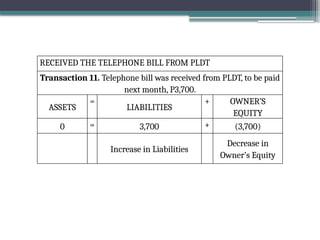
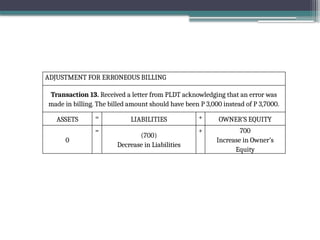
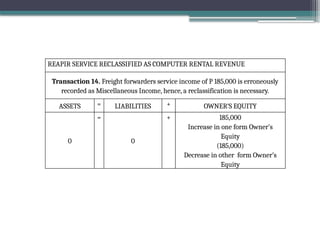
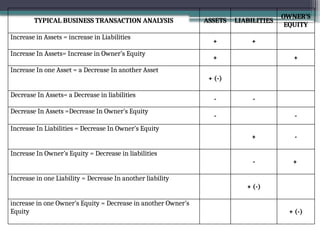
accounting is governed by a basic but fundamental equation: Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity. This formula represents the financial balance of any organization. Assets are things owned, such as cash, equipment, or property. Liabilities are obligations like loans or accounts payable. The owner's equity reflects what belongs to the owner after liabilities are subtracted. Every financial transaction in accounting affects this equation, ensuring records remain balanced and accurate.