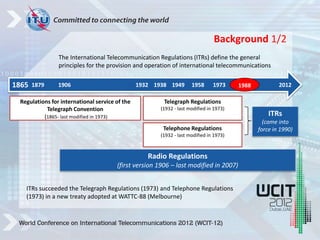
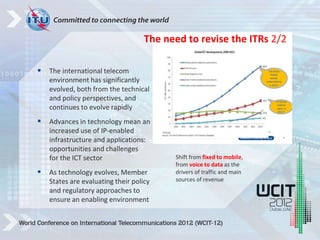
The International Telecommunication Regulations (ITRs) define principles for international telecommunications and are being revised. The ITRs were last updated in 1988 but the telecom environment has significantly changed with advances in technology, increased liberalization, and a shift to mobile and data. Member states and industry stakeholders provided over 100 proposals on issues like mobile roaming, taxation, security, and economic regulations. The conference WCIT-12 aims to update the ITRs to address current concerns and enable efficient international telecom services to support social and economic development.