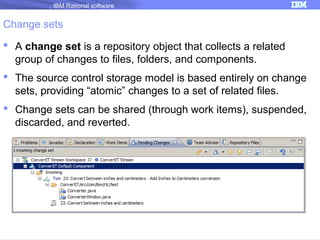
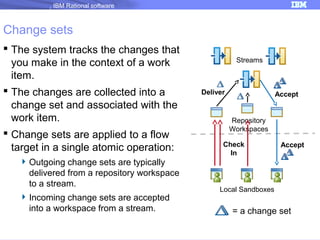
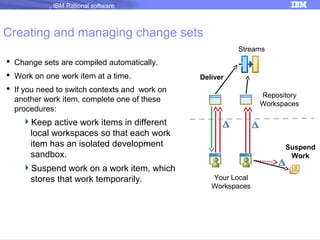
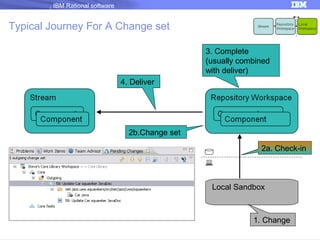
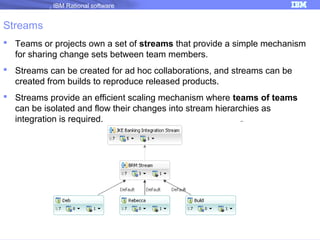
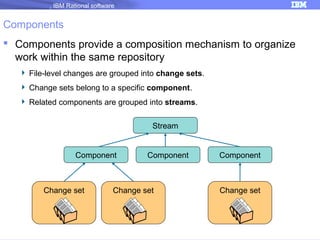
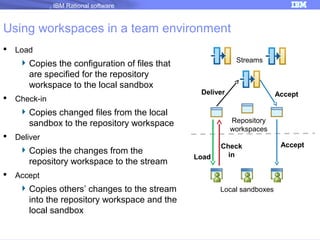
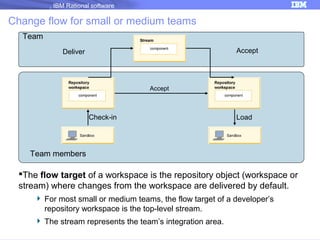
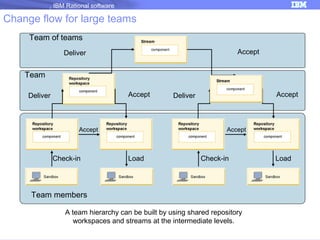
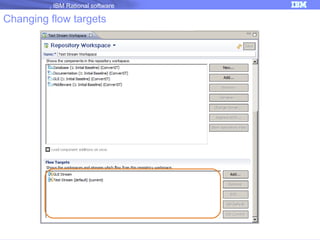
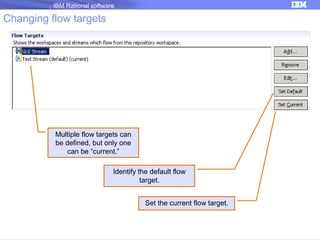
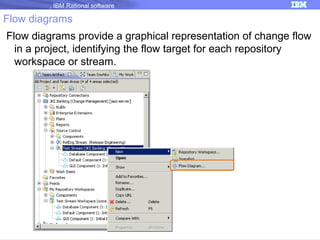
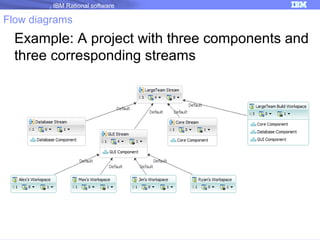
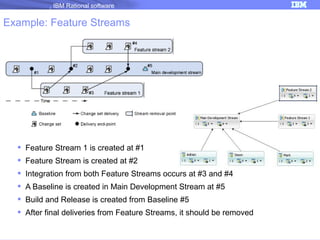
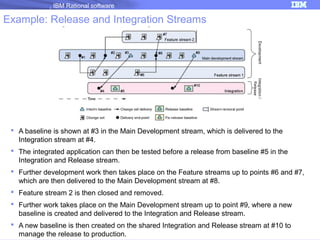
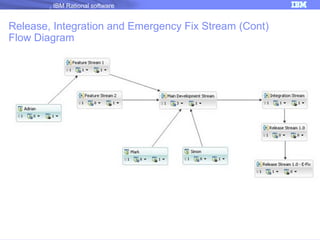
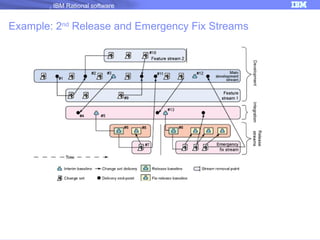
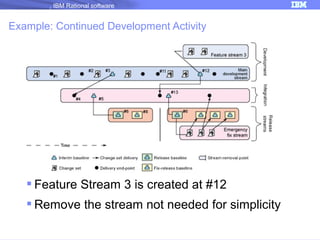
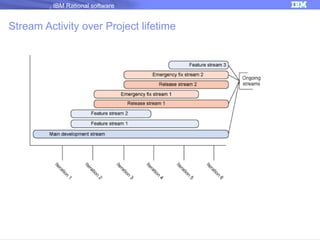
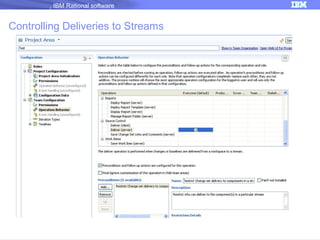
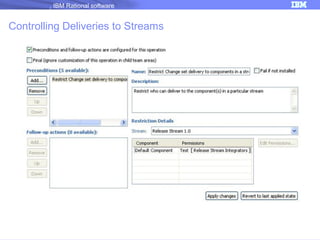
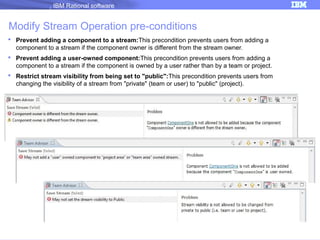
The document discusses IBM Rational Software's capabilities for parallel development using Jazz source control, focusing on elements like change sets, streams, and components. It explains the processes for creating and managing change sets, the role of streams in team collaboration, and the importance of isolation in development environments. Additionally, it covers workflows for various team sizes and includes diagrams illustrating change flows in projects.