This document discusses positive thinking and how to develop more positive habits and thought patterns. It covers:
1) The benefits of positive thinking like optimism and focusing on what's good, and the downsides of negative thinking like pessimism.
2) Six habits to adopt like focusing on the good, choosing positive words, and limiting complaints.
3) How positive thinking is linked to better health while negative thinking can delay healing. It also discusses cognitive distortions and irrational beliefs.
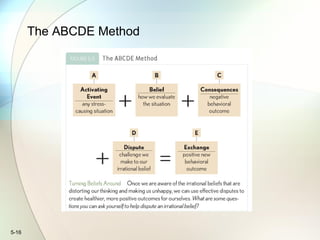
4) The ABCDE method for overcoming irrational beliefs by disputing negative thoughts and replacing them with positive outcomes.