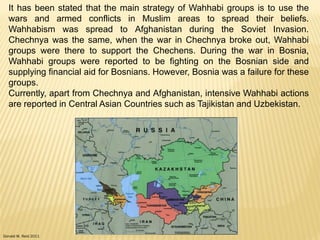
Wahhabism is a branch of Sunni Islam named after Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, an 18th century preacher from Saudi Arabia. Central to Wahhabism is the belief in tawhid (the oneness of God) and the rejection of shirk (polytheism) which is applied literally and includes prohibiting prayers to saints and visiting graves. Wahhabism spread with the expansion of the Saud family in the Arabian Peninsula in the 18th century and is now the dominant form of Islam in Saudi Arabia. Critics argue Wahhabism has been spread more recently through funding from Saudi oil wealth and by associating with conflicts in places like Afghanistan, Bosnia, and Central