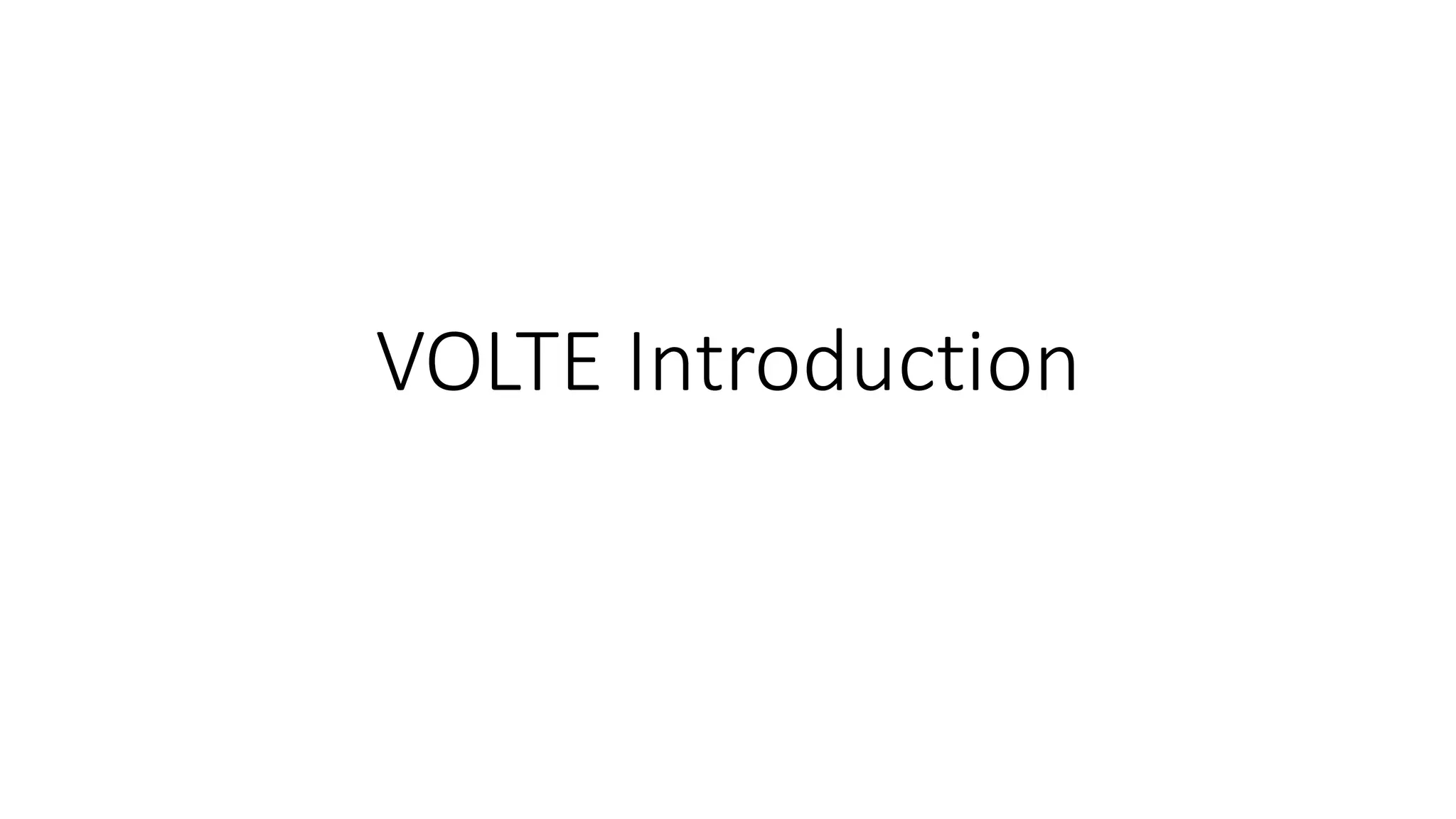
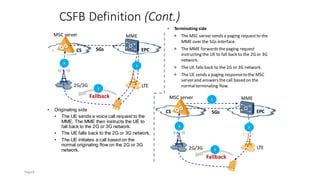
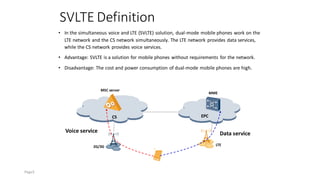
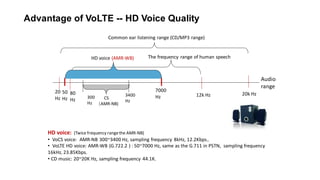
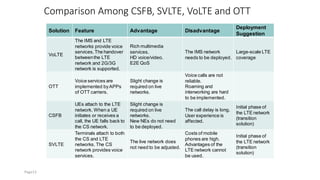
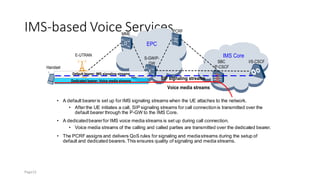
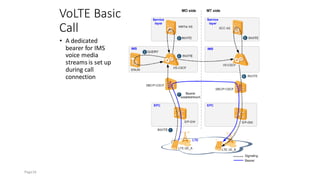
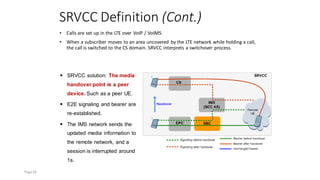
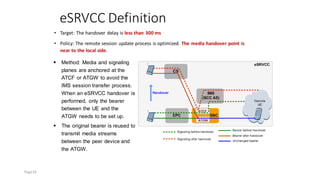
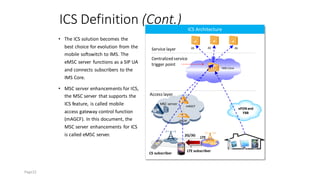
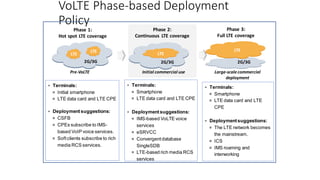
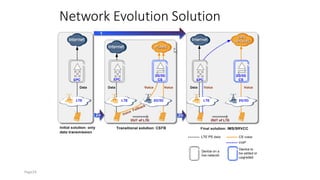
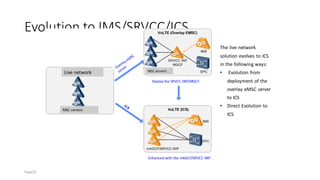
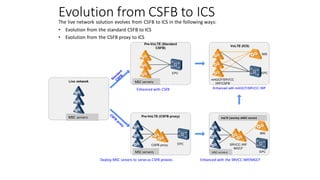
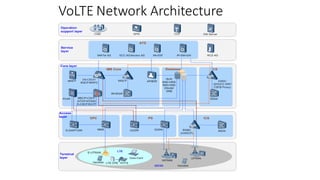
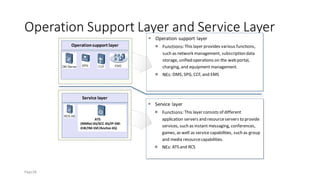
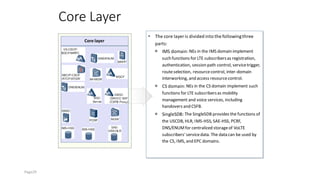
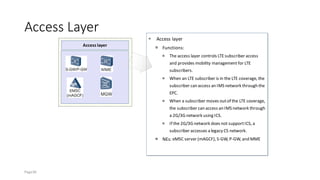
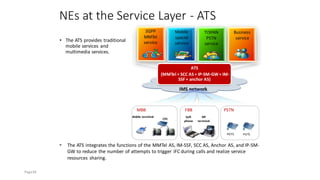
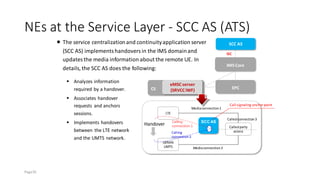
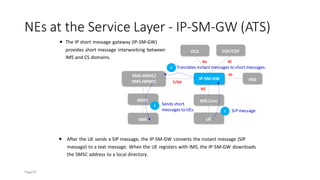
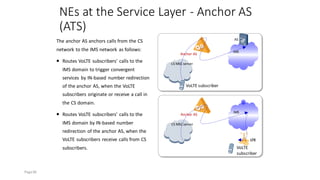
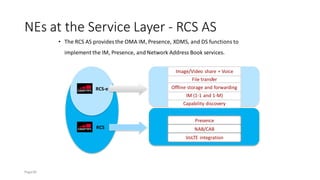
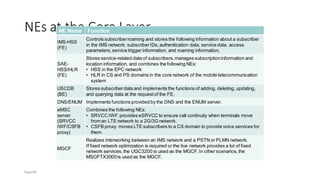
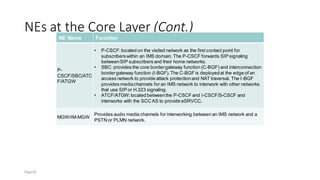
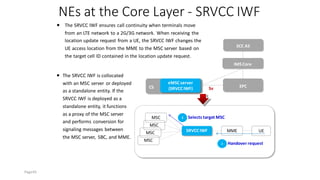
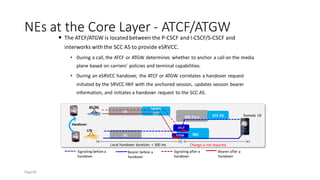
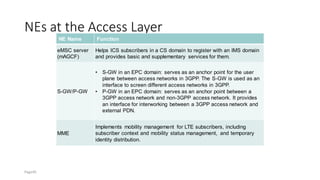
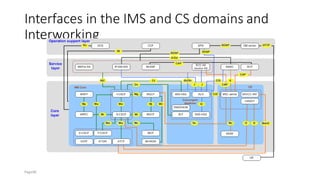
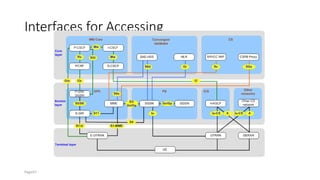
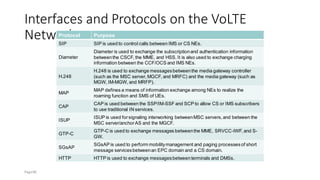
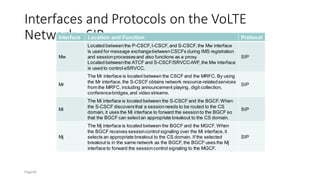
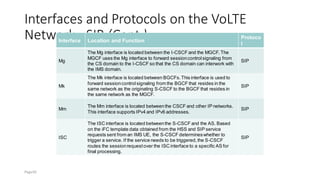
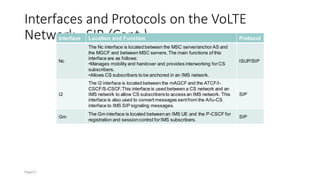
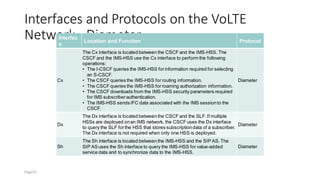
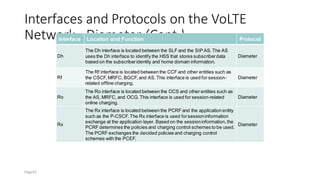
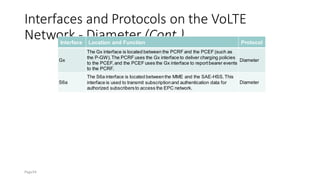
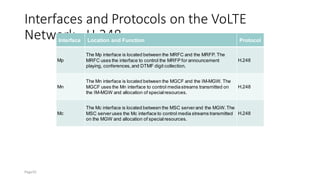
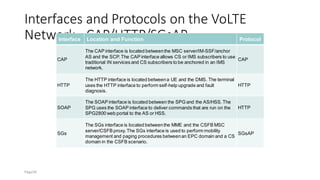
The document discusses various voice solutions for LTE networks, focusing on Circuit Switched Fallback (CSFB), Simultaneous Voice and LTE (SVLTE), Over-The-Top (OTT), and Voice over LTE (VoLTE). It highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, particularly emphasizing the benefits of VoLTE, such as enhanced voice quality, richer multimedia services, and guaranteed end-to-end Quality of Service (QoS). Additionally, it outlines the evolution and deployment strategies for IMS-based voice services.