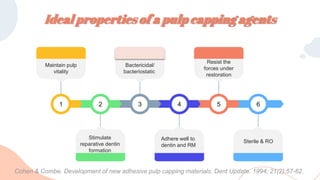
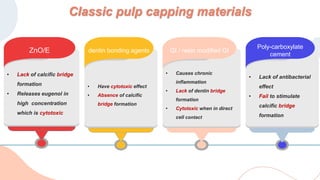
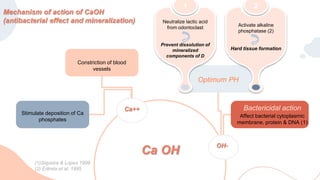
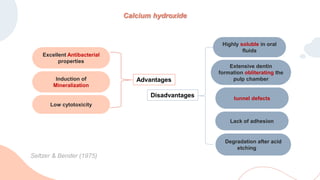
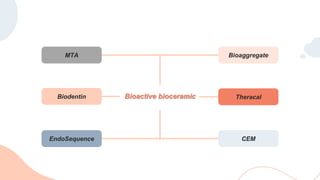
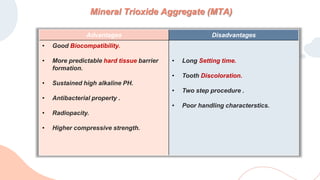
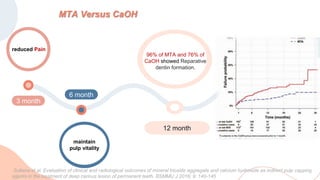
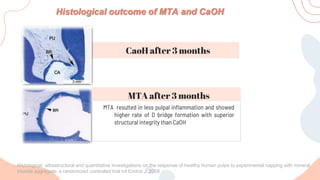
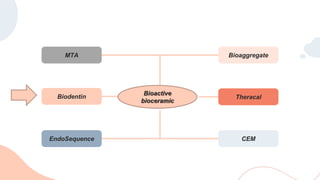
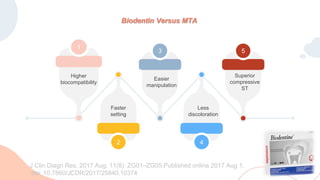
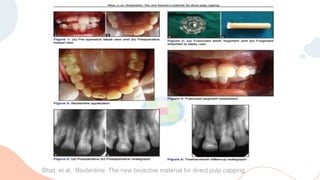
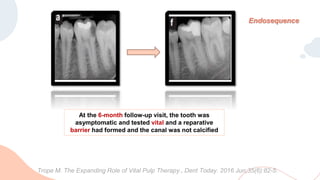
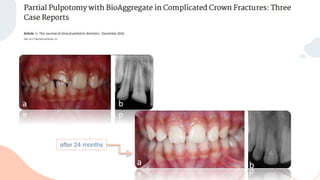
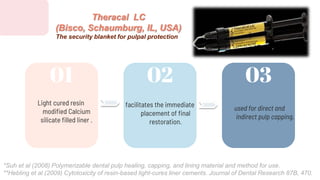
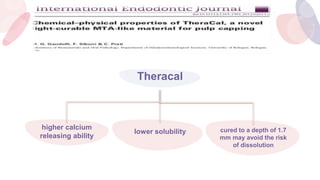
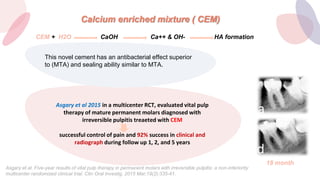
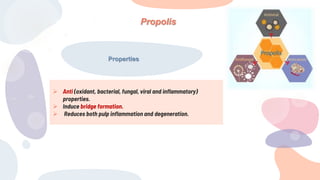
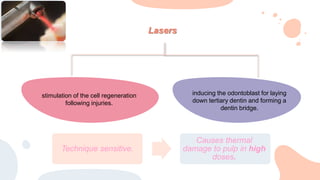
This document discusses various materials used for vital pulp therapy (VPT). It begins by outlining the ideal properties of a pulp capping agent, such as maintaining pulp vitality and stimulating reparative dentin formation. Classic materials like calcium hydroxide, zinc oxide-eugenol, and polycarboxylate cement are described along with their disadvantages. More recent bioactive bioceramic materials like mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and Endosequence are then discussed and compared to calcium hydroxide, with studies showing higher success rates for reparative dentin formation and less inflammation with bioceramics. The document concludes by mentioning recent advances in VPT including the