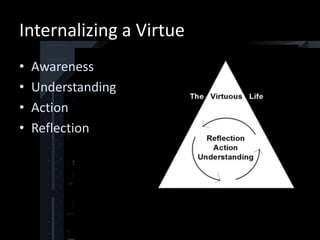
This document discusses the Catholic virtue of integrity. It defines integrity as consistently acting in accordance with one's values and moral principles. It notes that integrity requires allowing faith to shape all aspects of life, both public and private. Some societal pressures that challenge integrity, such as lying and compromising beliefs, are mentioned. The document then provides seven habits for maintaining integrity online, such as refreshing one's values, seeking accountability, and practicing humble authenticity. It concludes by suggesting a technology examination of conscience.