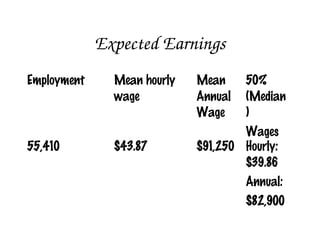
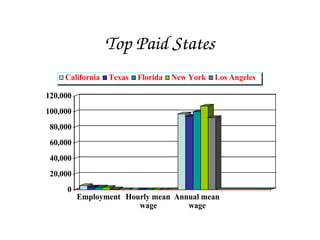
Veterinarians care for the health and well-being of animals through diagnosis, treatment, and research of medical conditions affecting pets, livestock, and zoo animals. Their duties include examining animals, performing surgery, collecting samples, prescribing medication, and educating the public on zoonotic diseases. An advanced degree and state licensure is required to become a veterinarian.