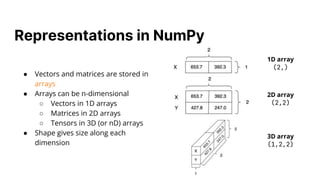
The document discusses optimizing code using linear algebra concepts, particularly focusing on vector and matrix operations to improve K-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithms. Key topics include distance metrics, matrix subtraction, and the importance of vectorization to reduce computation time. The document also provides code improvements from loop-based to vectorized solutions for calculating distances and determining nearest neighbors.













![Our first code improvement
def calculate_manhattan_distance(a: list, b: list, p: int) -> float:
"""Calculates the Manhattan distance between two vectors, X and Y."""
i = len(a)
diffs = []
for element in range(0, i):
diffs.append(abs(a[element] - b[element]))
return sum(diffs)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoriseallthethings-noname-230310100646-ae2f7ca1/85/Vectorise-all-the-things-15-320.jpg)
![Our first code improvement
def calculate_manhattan_distance(a: list, a: list, p: int) -> float:
"""Calculates the Manhattan distance between two vectors, X and Y."""
i = len(a)
diffs = []
for element in range(0, i):
diffs.append(abs(a[element] - b[element]))
return sum(diffs)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoriseallthethings-noname-230310100646-ae2f7ca1/85/Vectorise-all-the-things-16-320.jpg)





![Our second code improvement
def apply_manhattan_distance(vectors_1: list, vectors_2: list, p: int
) -> list:
"""Calculates the pairwise difference between two lists of vectors."""
distances = []
for train_obs in vectors_1:
tmp_distances = []
for test_obs in vectors_2:
tmp_distances.append(calculate_manhattan_distance(train_obs, test_obs, p))
distances.append(tmp_distances)
return [list(x) for x in zip(*distances)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoriseallthethings-noname-230310100646-ae2f7ca1/85/Vectorise-all-the-things-22-320.jpg)








![Our final code improvements
def calculate_nearest_neighbour(distances: list, labels: list, k: int
) -> str:
"""
Calculates the k-nearest neighbours for a test point,
using k selected neighbours.
"""
sorted_distances = sorted(zip(distances, labels), key=itemgetter(0))[1:]
top_n_labels = [label for dist, label in sorted_distances][:k]
return max(set(top_n_labels), key=top_n_labels.count)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoriseallthethings-noname-230310100646-ae2f7ca1/85/Vectorise-all-the-things-31-320.jpg)
![Our final code improvements
def calculate_nearest_neighbour(distances: list, labels: list, k: int
) -> str:
"""
Calculates the k-nearest neighbours for a test point,
using k selected neighbours.
"""
sorted_distances = sorted(zip(distances, labels), key=itemgetter(0))[1:]
top_n_labels = [label for dist, label in sorted_distances][:k]
return max(set(top_n_labels), key=top_n_labels.count)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vectoriseallthethings-noname-230310100646-ae2f7ca1/85/Vectorise-all-the-things-32-320.jpg)

