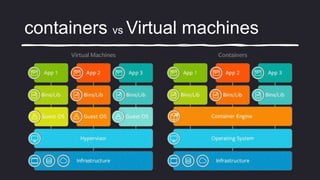
The document discusses key concepts in software development, including version control systems (VCS), containerization, and low-code development. It explains VCS as tools for managing file revisions with benefits like history tracking and collaboration, while containerization allows application management in isolated environments. Low-code development is presented as a method that accelerates application creation through user-friendly components and templates.