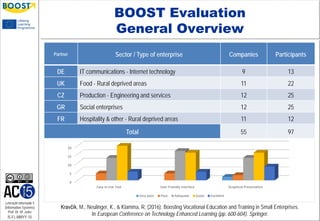
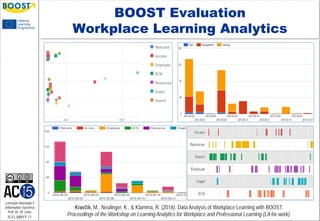
The document discusses the use of web-based personal learning environments (PLEs) to enhance workplace learning in small enterprises, where traditional training methods are often inadequate. The BOOST methodology is introduced, focusing on employee skills training to improve business performance, and emphasizes tailored learning solutions for specific business needs. Evaluation results and feedback indicate that the BOOST approach is well-received for its flexibility and adaptability in supporting employee development.


![Lehrstuhl Informatik 5
(Information Systems)
Prof. Dr. M. Jarke
I5-FL-MMYY-4
Related Work
Lack of internal capacity and motivation to provide
learning opportunities for employees [Johnson 2002]
In SME learning takes place through work processes,
is multi episodic, often informal, problem based, takes
place on a just in time basis [Attwell 2012]
Training provided through government courses is
typically perceived by managers as lacking value in
improving business performance [Jones 2013]
SRL skills are important and can be supported by
properly designed PLEs [Nussbaumer 2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boost-icwl-161028150303/85/Using-Personal-Learning-Environments-to-Support-Workplace-Learning-in-Small-Companies-4-320.jpg)