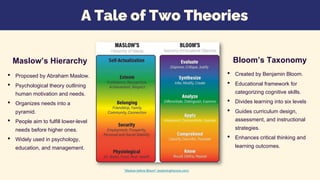
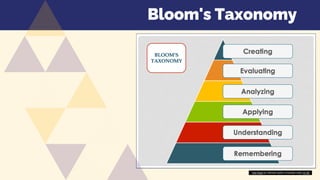
The document outlines a session on integrating Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Bloom's taxonomy into course design, emphasizing the importance of addressing student needs in educational settings. It discusses strategies for creating supportive learning environments and enhancing critical thinking through structured learning objectives. Additionally, it includes reflection prompts for educators to evaluate their course designs and recognizes the relevance of both frameworks in improving teaching and learning outcomes.