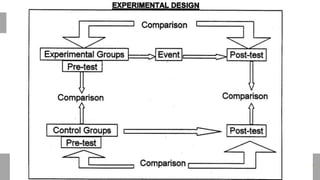
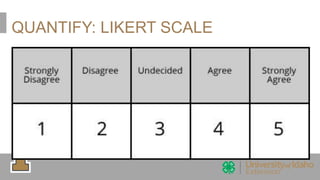
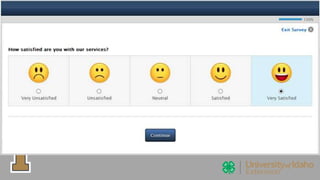
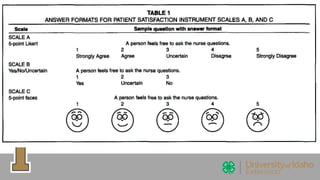
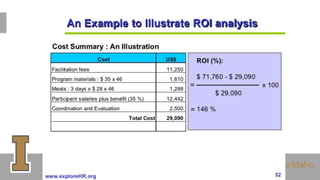
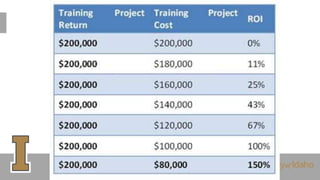
The document outlines the evaluation of training programs based on Kirkpatrick's five levels: reaction, knowledge, behavior, society, and ROI, emphasizing the complexity of measuring each level. It highlights the importance of behavior change, the difficulties in achieving and measuring success, and the necessity of planning and commitment. Additionally, it covers various experimental designs, methods of evaluation, and the costs and benefits associated with evaluating training programs.