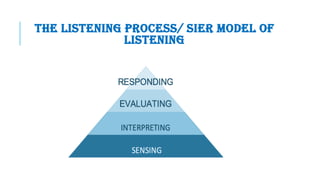
The document discusses active listening and its importance in organizations. Active listening requires listening attentively, understanding what is said, responding appropriately, and retaining information. It helps with personal and professional growth, decision making, relationships, and productivity. True listening is active and involves hearing, paying attention, understanding, and giving feedback, while hearing is a passive process. Barriers to listening include physical, psychological, linguistic, and cultural factors. Effective listening involves limiting interruptions, paying attention, allowing silence, encouraging others to contribute, restating ideas accurately, and demonstrating a receptive attitude. Feedback is also discussed, including its importance in organizations, types of feedback, and how to give and receive it effectively.