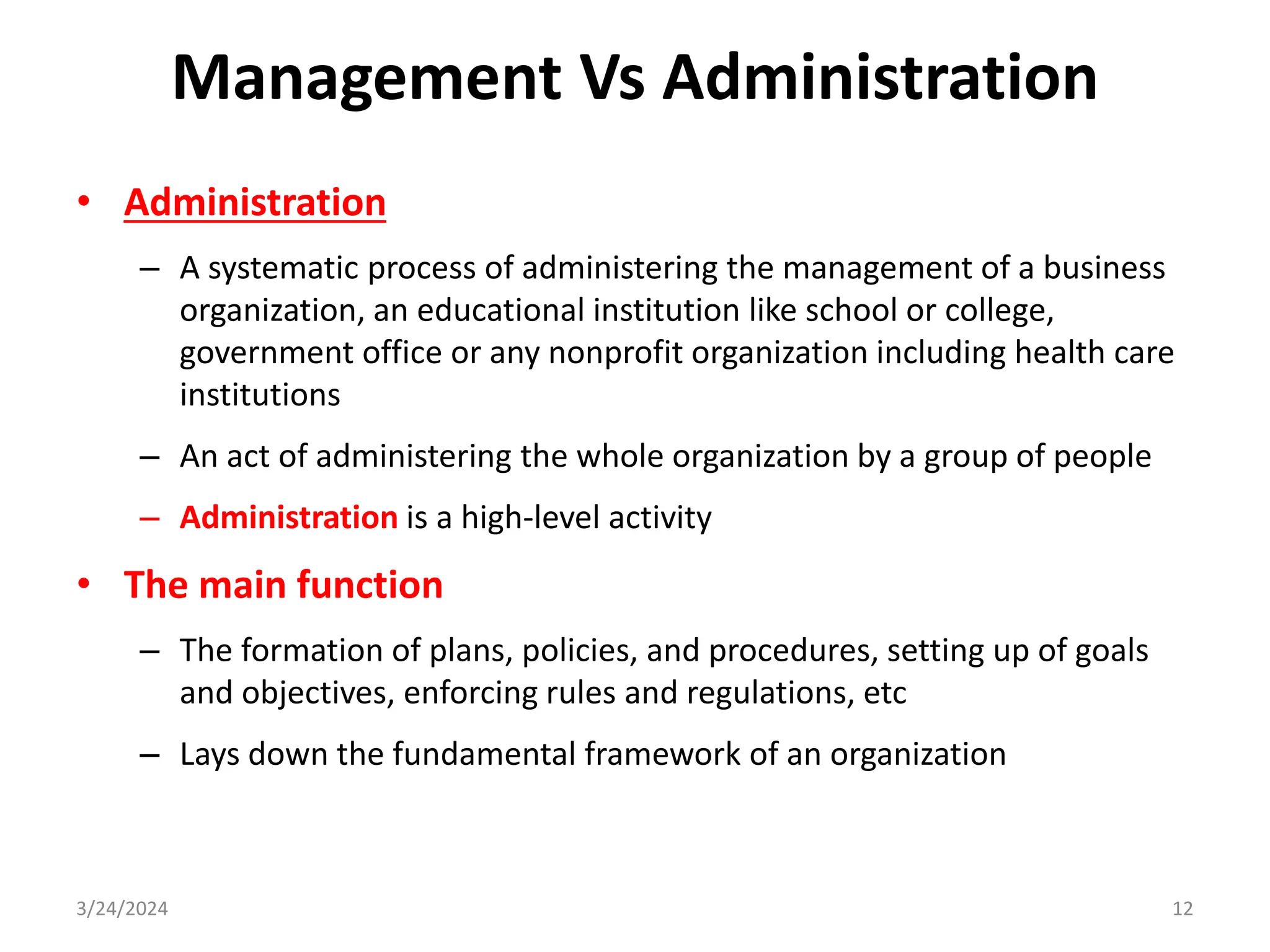
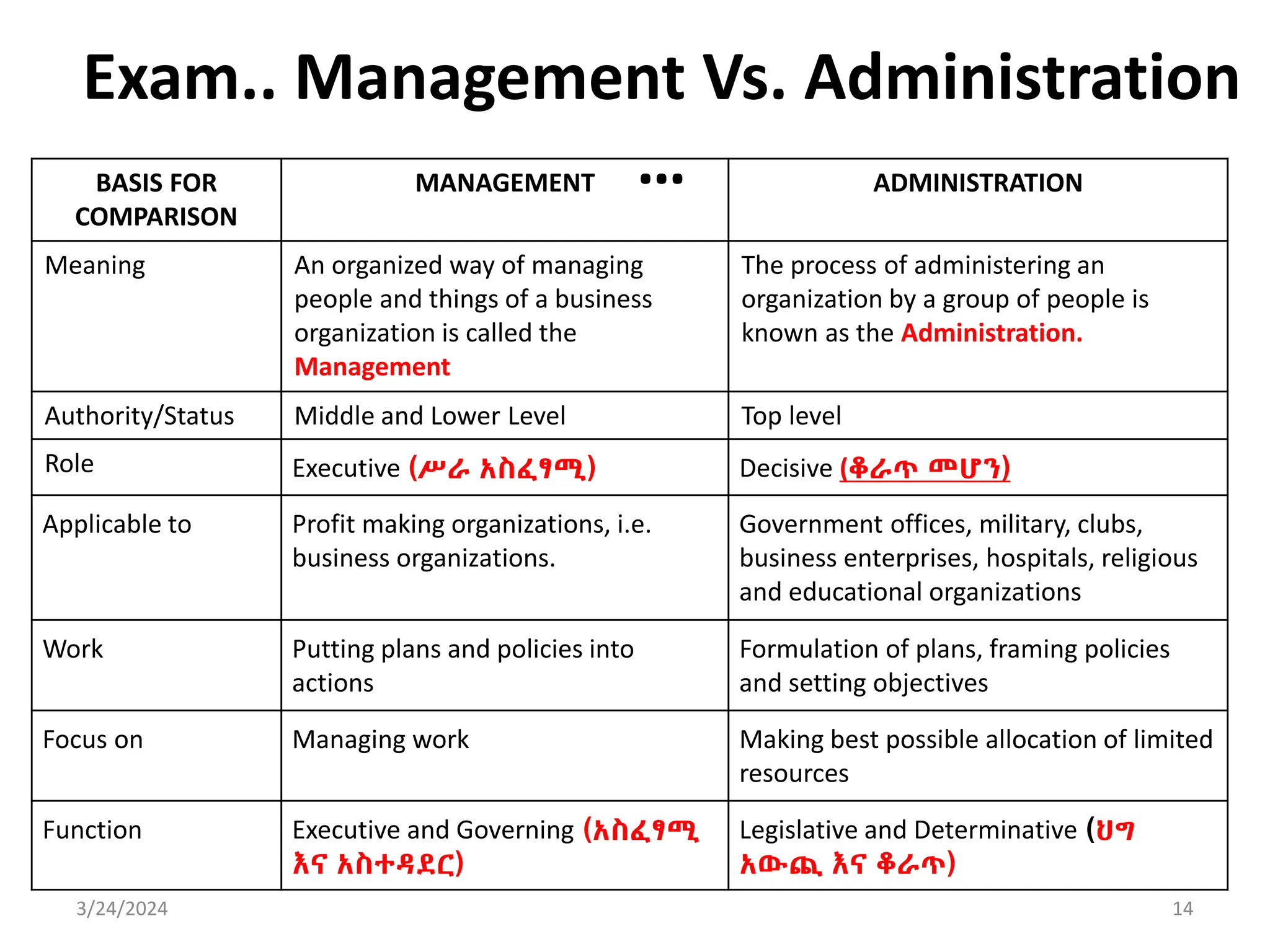
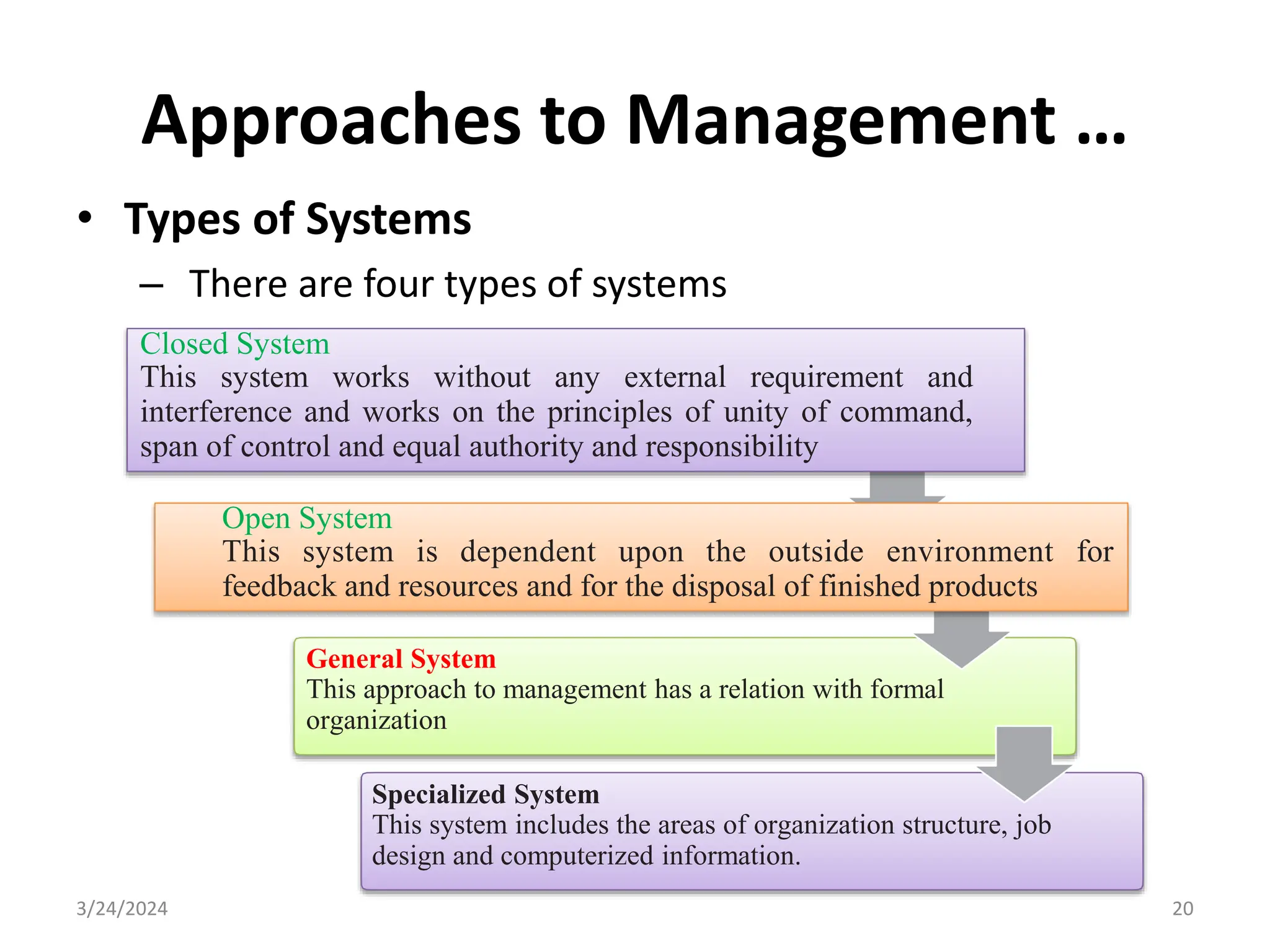
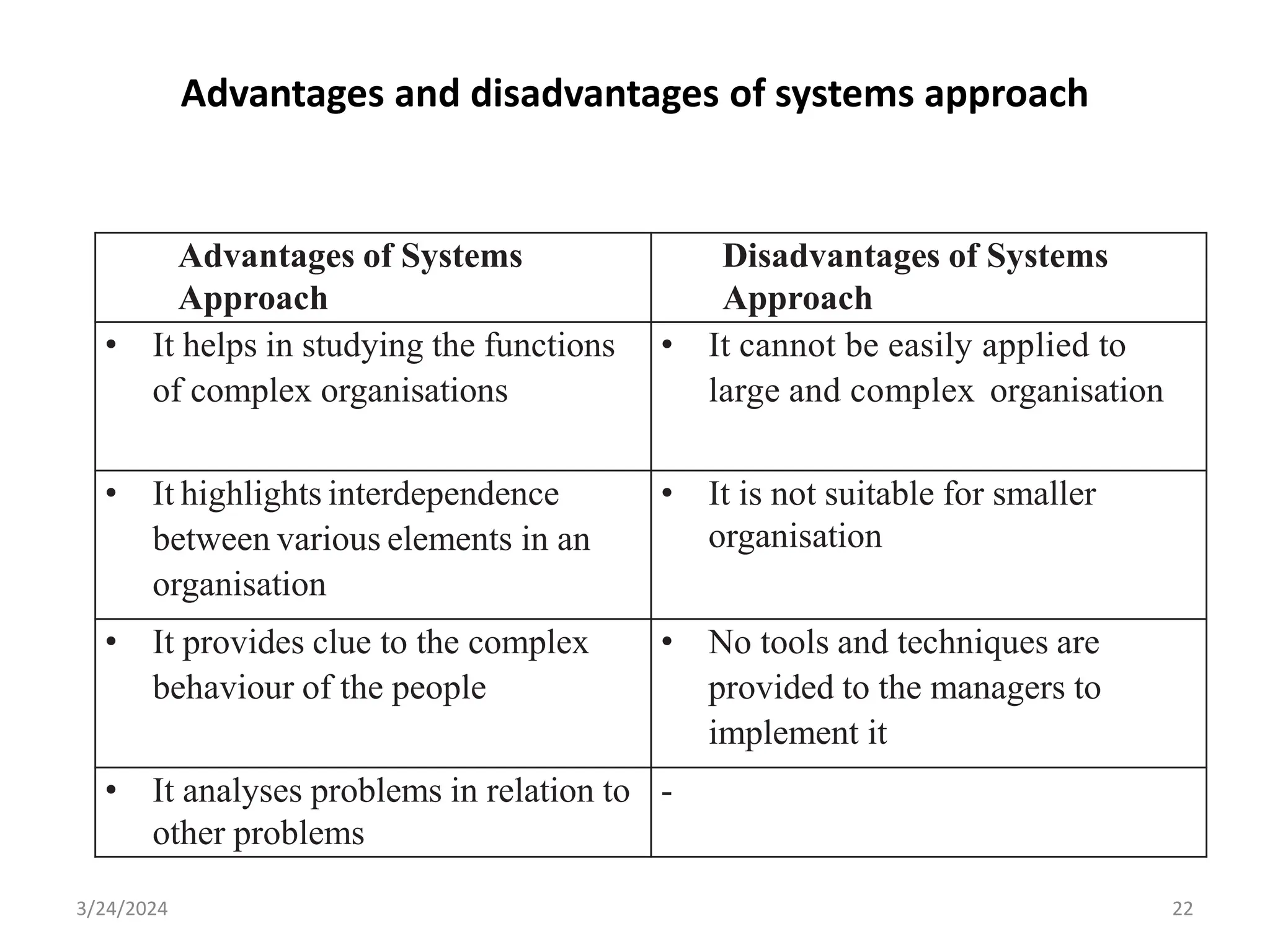
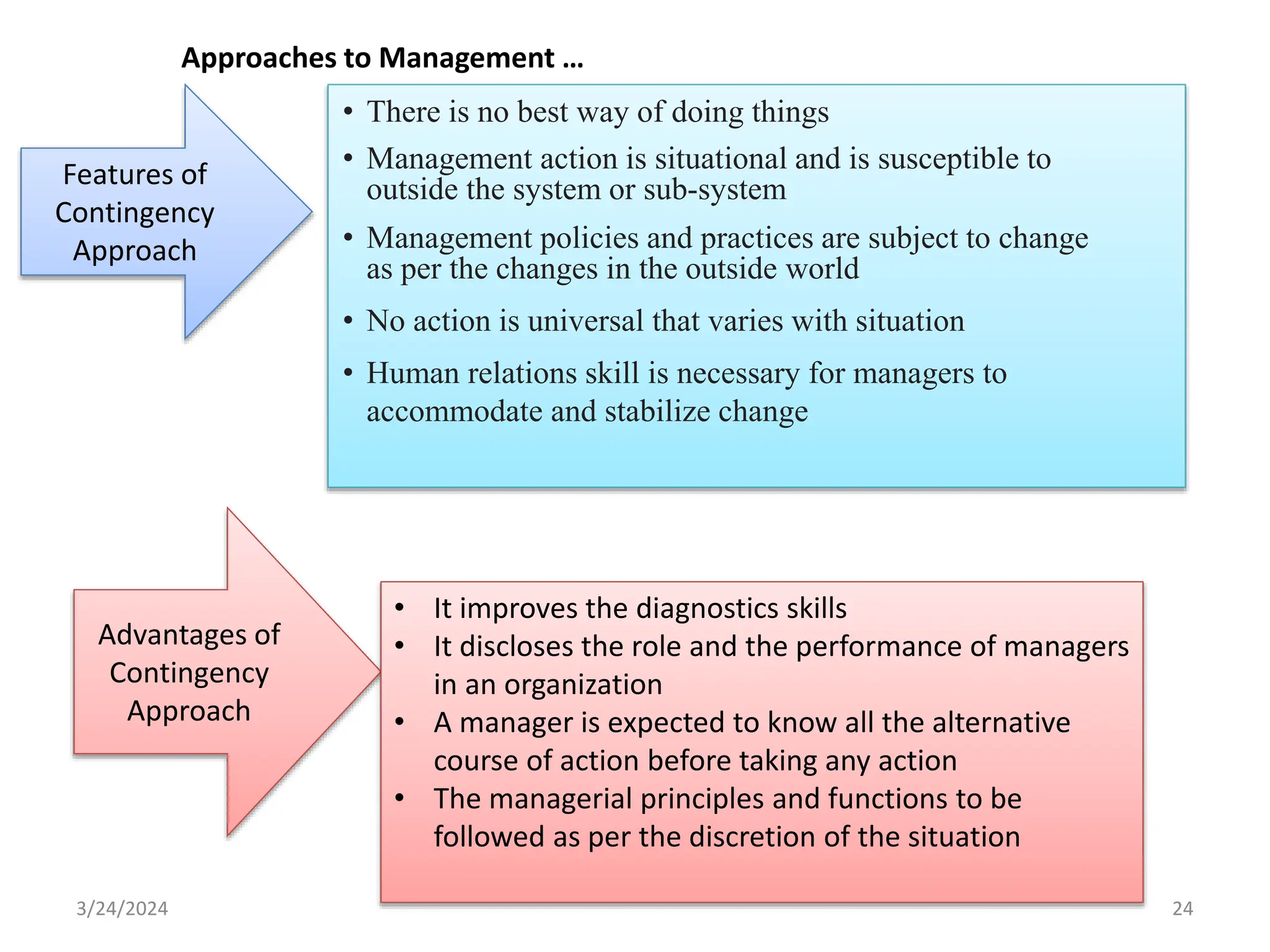
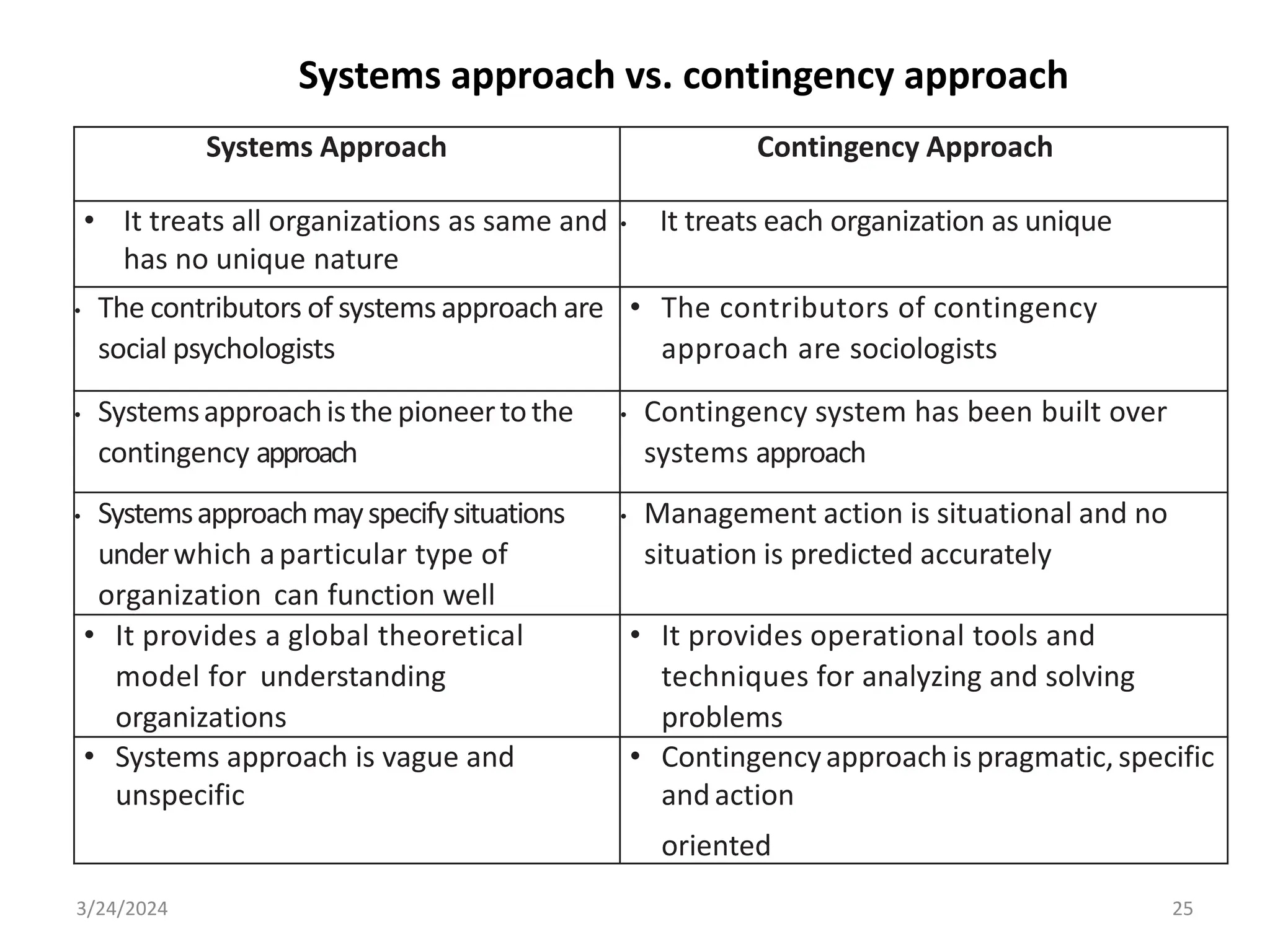
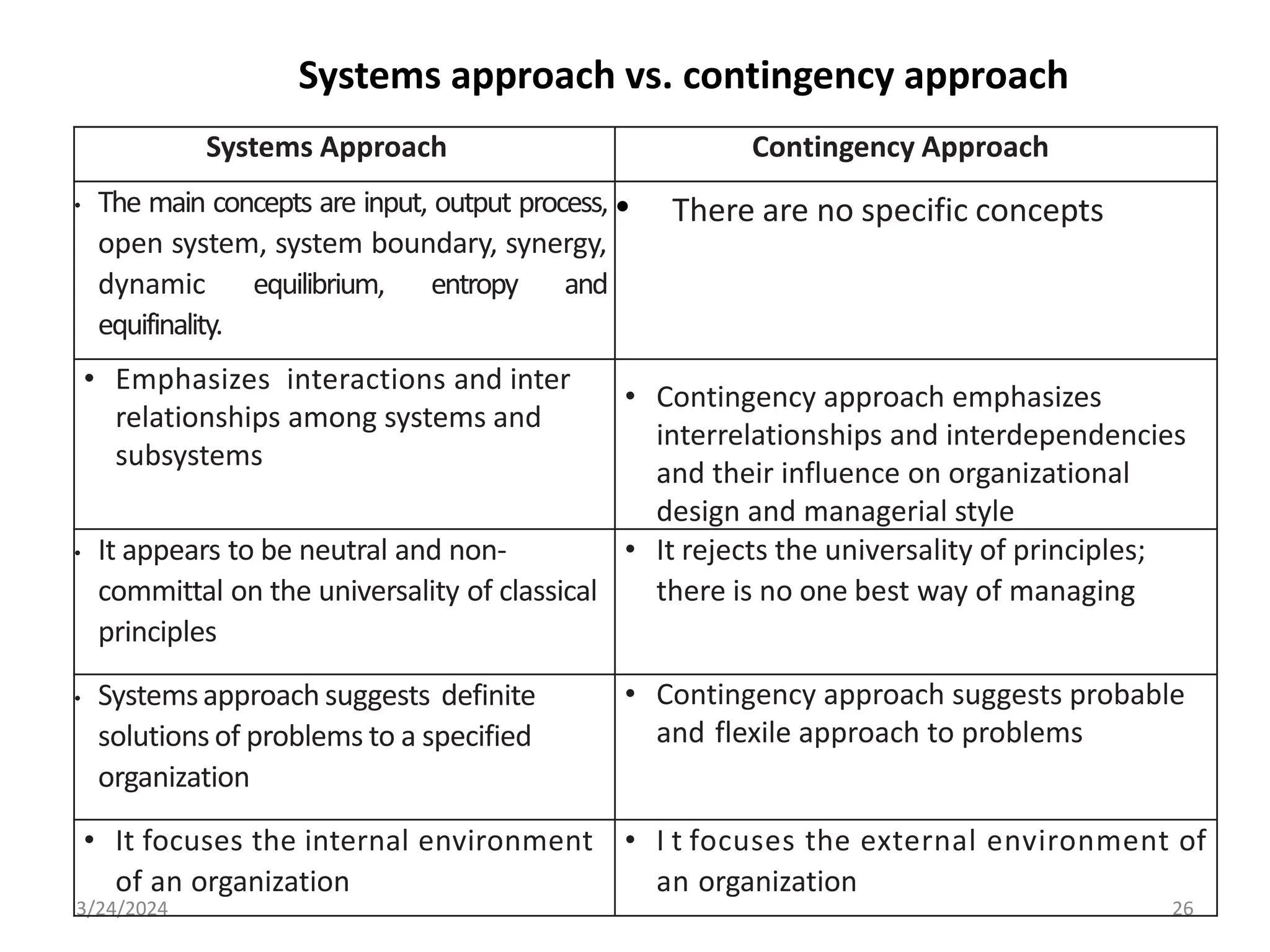
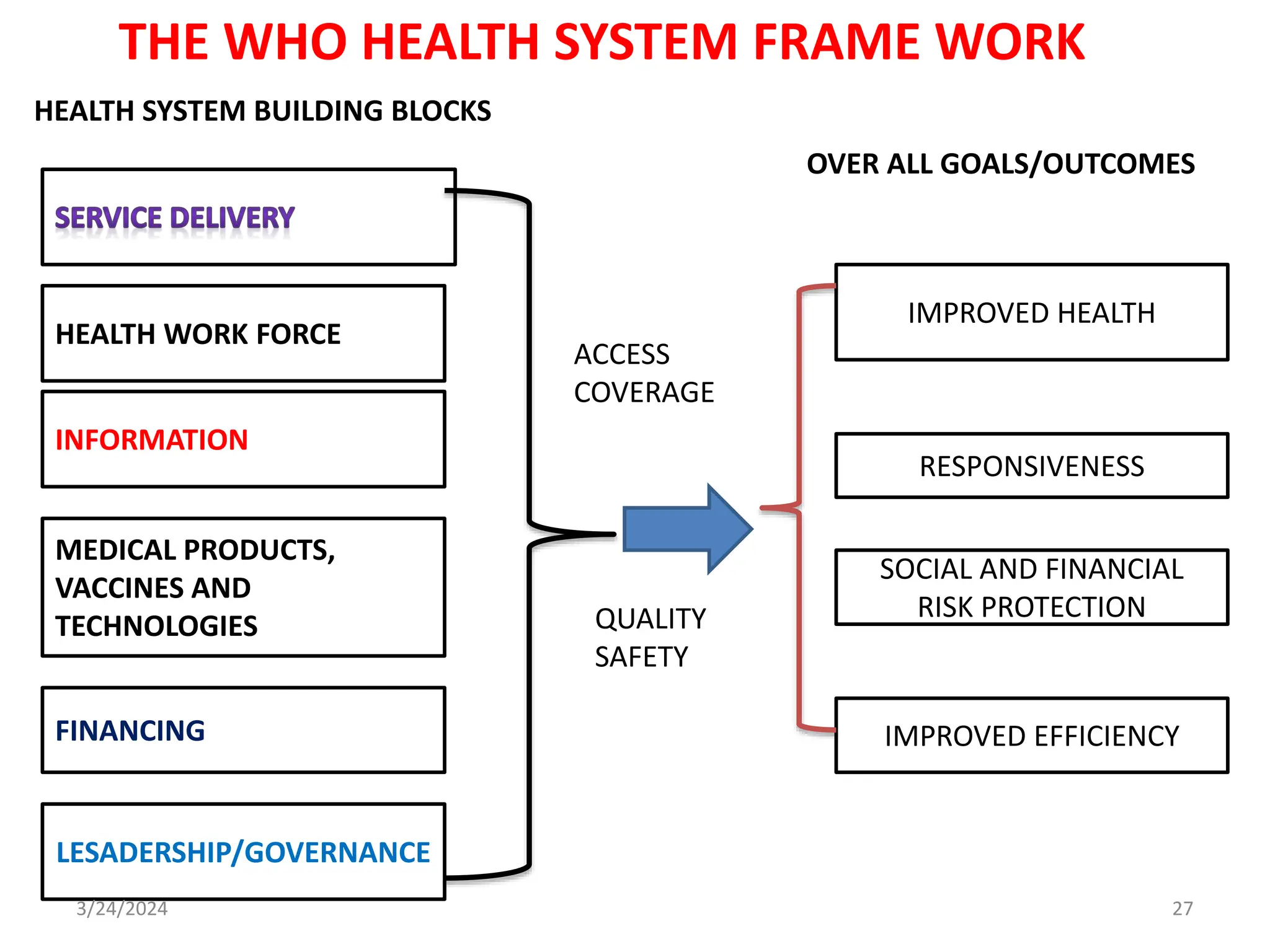
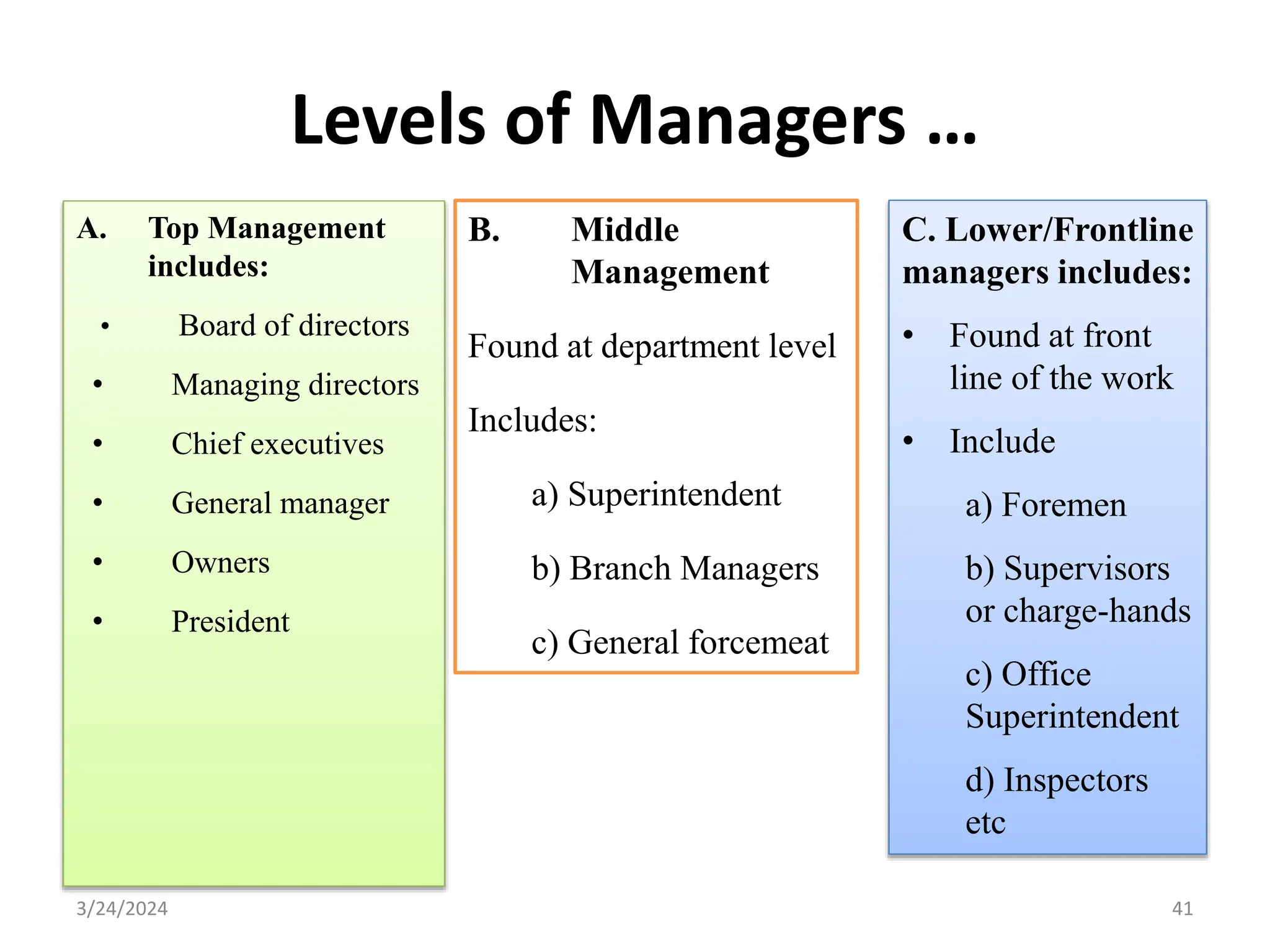
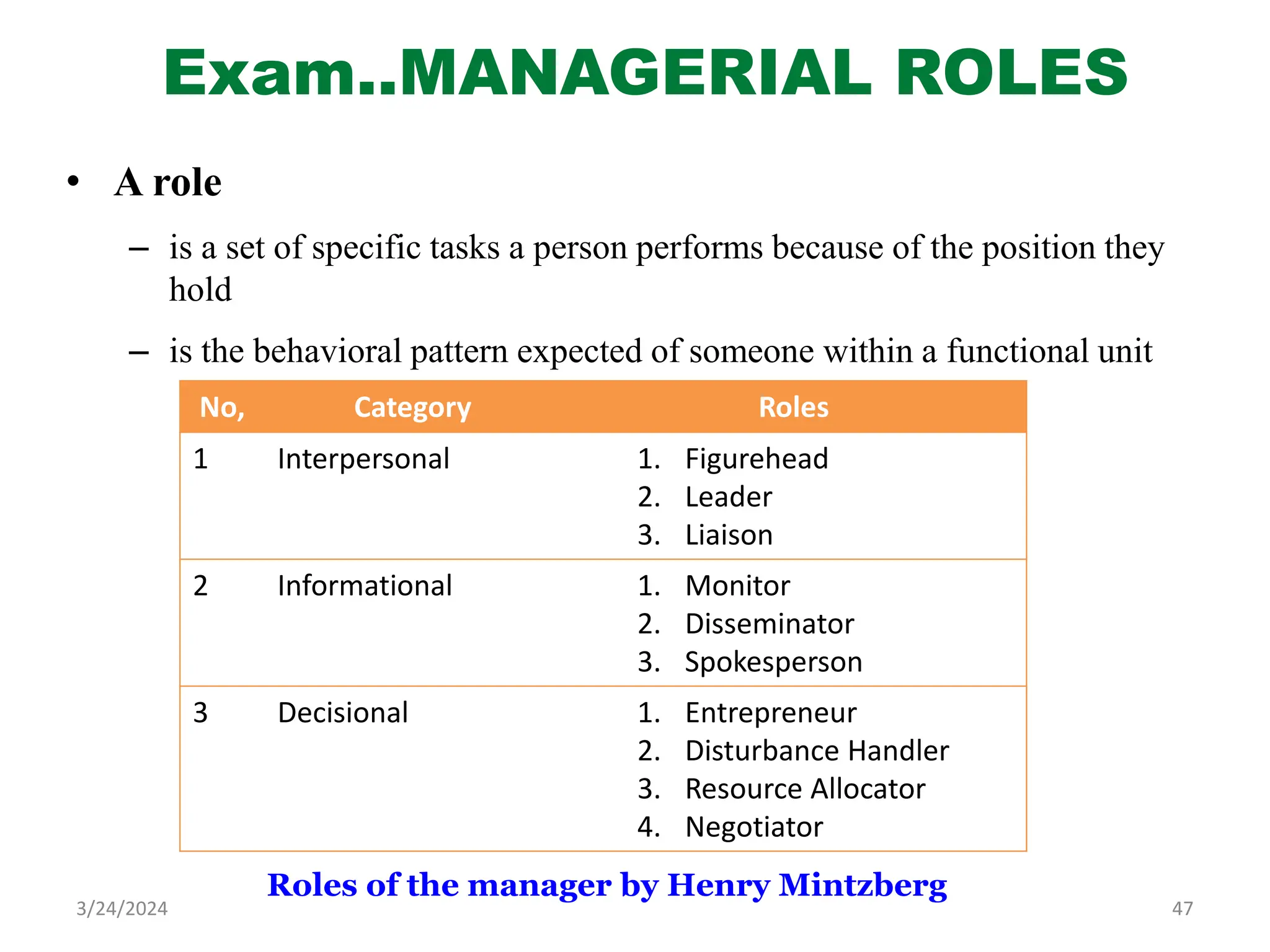
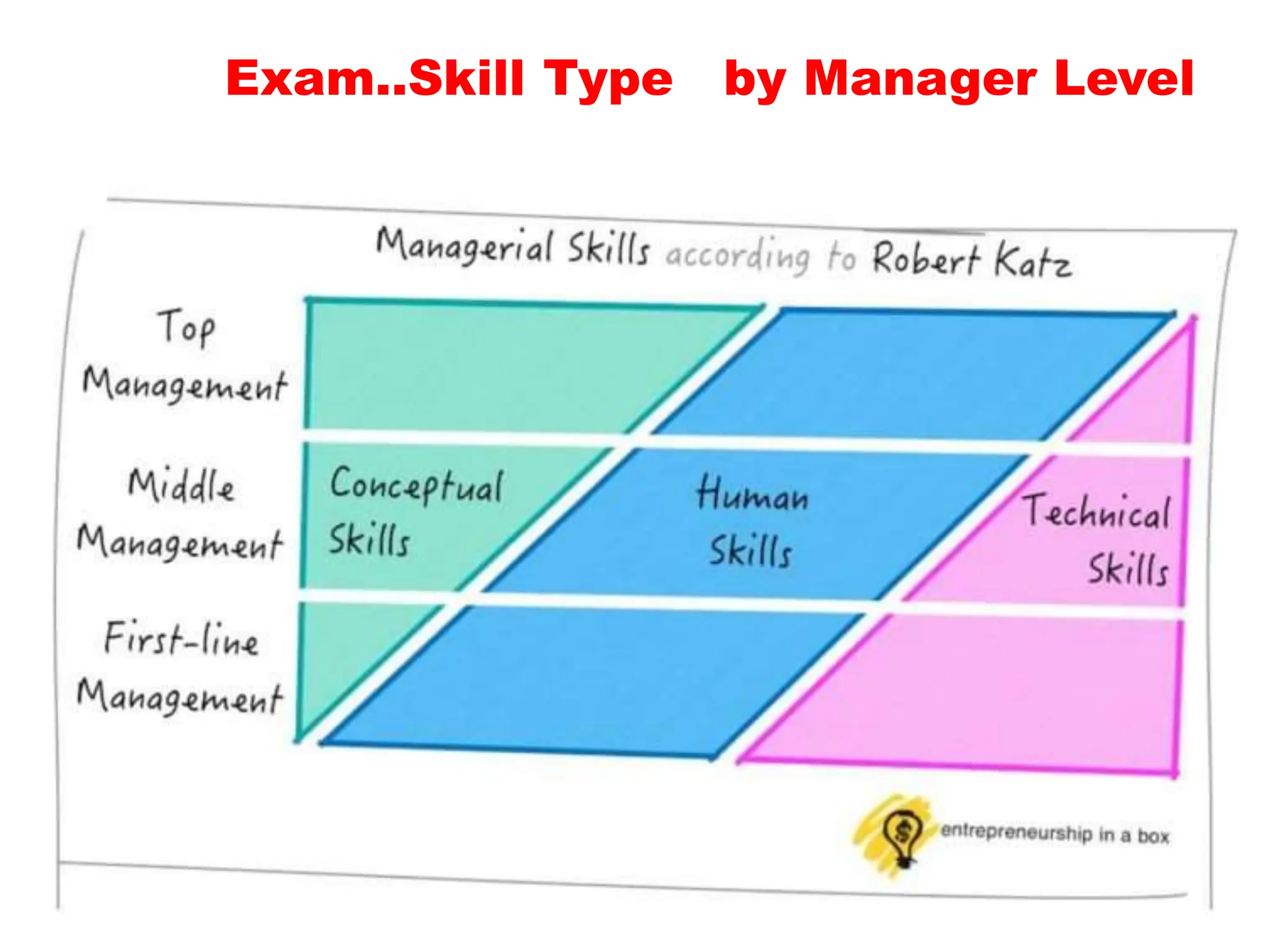
The document is a comprehensive guide on health service management authored by Ebrahim Mohammed, outlining key concepts, definitions, and functions of management. It distinguishes between management and administration, discusses various approaches to management such as systems and contingency approaches, and emphasizes the importance of effective resource utilization, managerial roles, and the principles of management. Additionally, the document covers the hierarchical levels of managers and their respective functions within organizations.