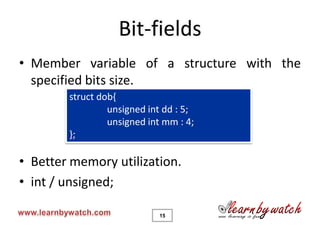
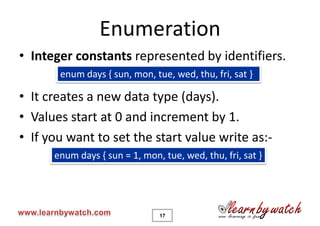
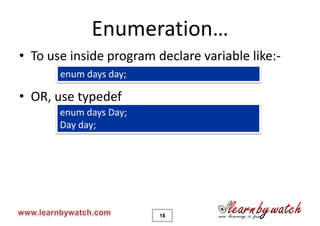
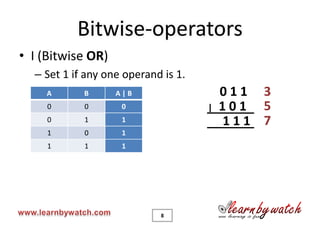
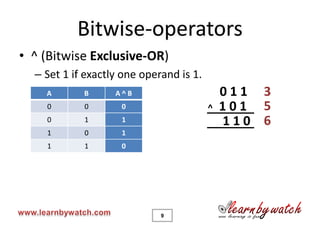
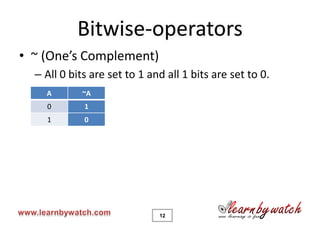
This document is a tutorial on C programming language concepts including unions, bitwise operators, bit-fields, and enumerations. It contains code examples and explanations of each concept over 19 pages. Key points covered include how unions allow variables of different types to share the same memory space, how bitwise operators manipulate bits, how bit-fields optimize memory usage, and how enums create integer constants represented by identifiers. The document encourages solving quizzes and contacting the author for any questions.









![Operator Associativity Type
() [] . -> left to right Highest
+ - ++ -- ! & * ~ sizeof (type) right to left Unary
* / % left to right multiplicative
+ - left to right additive
<< >> left to right shifting
< <= > >= left to right relational
== != left to right equality
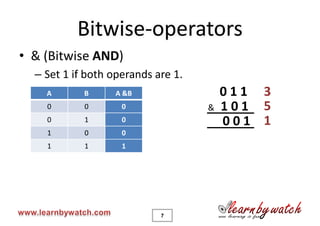
& left to right bitwise AND
^ left to right bitwise OR
| left to right bitwise OR
&& left to right logical AND
|| left to right logical OR
?: right to left conditional
= += -= *= /= &= |= ^= <<= >>= %= right to left assignment
, left to right comma
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unions-100427070235-phpapp02/85/Unions-14-320.jpg)