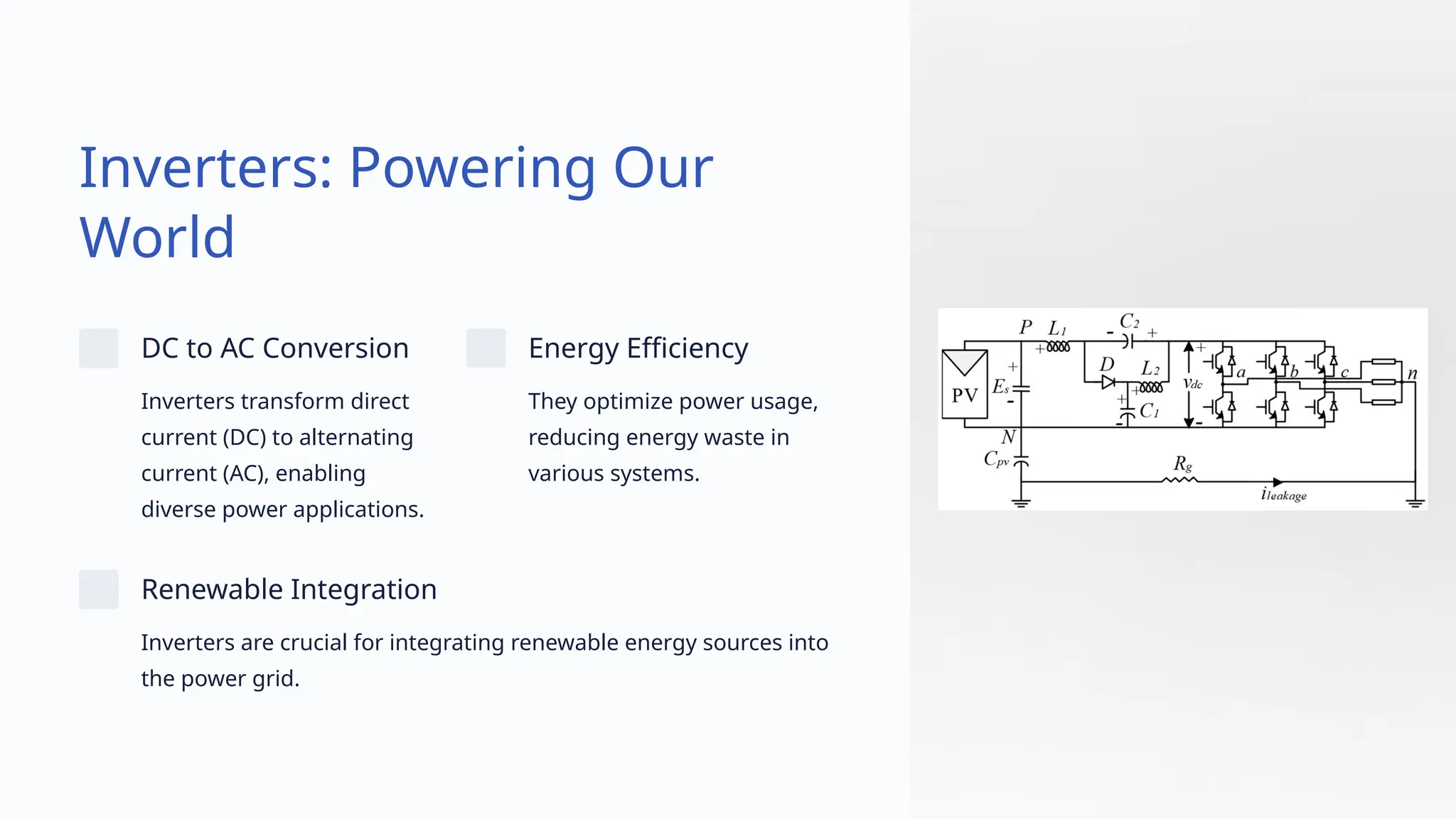
The document provides an overview of inverter technology, focusing on design principles, applications, and innovations. It outlines the critical role in converting DC to AC power and highlights challenges such as efficiency, heat management, and cost optimization. Key trends and advancements, including AI integration and modular design, are also discussed, emphasizing the importance of efficiency and reliability in inverter design.