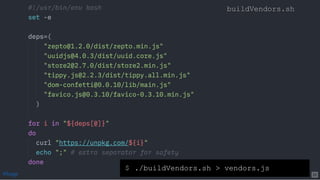
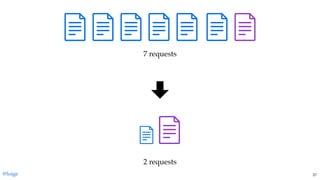
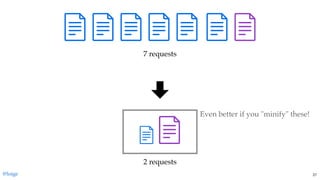
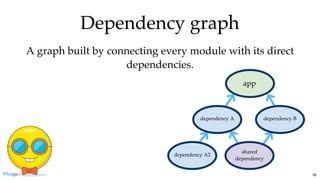
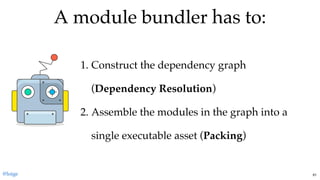
The document discusses the complexities of JavaScript module bundling, highlighting the necessity of modules for structuring applications and the importance of information hiding. It covers various JavaScript module systems such as CommonJS, AMD, and ES2015 modules, explaining their features and differences. Additionally, it introduces tools like 'lumpy' for efficient asset management and emphasizes the need for standardized module formats in development.










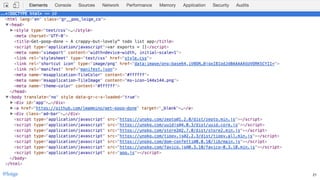



























![const myModule = (() => {
const privateFoo = () => { /* ... */ }
const privateBar = [ /* ... */ ]
const exported = {
publicFoo: () => { /* ... */ },
publicBar: [ /* ... */ ]
};
return exported
})()
myModule.publicFoo()
myModule.publicBar[0]
myModule.privateFoo // undefined
myModule.privateBar // undefined
privateFoo // undefined
privateBar // undefined @loige42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-60-320.jpg)
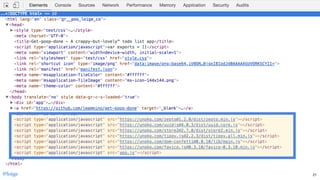
![const myModule = (() => {
const privateFoo = () => { /* ... */ }
const privateBar = [ /* ... */ ]
const exported = {
publicFoo: () => { /* ... */ },
publicBar: [ /* ... */ ]
};
return exported
})() A module
myModule.publicFoo()
myModule.publicBar[0]
myModule.privateFoo // undefined
myModule.privateBar // undefined
privateFoo // undefined
privateBar // undefined @loige42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-61-320.jpg)
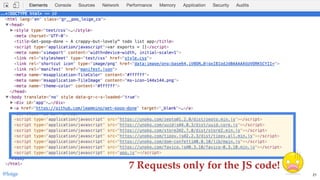
![const myModule = (() => {
const privateFoo = () => { /* ... */ }
const privateBar = [ /* ... */ ]
const exported = {
publicFoo: () => { /* ... */ },
publicBar: [ /* ... */ ]
};
return exported
})() A module
myModule.publicFoo()
myModule.publicBar[0]
myModule.privateFoo // undefined
myModule.privateBar // undefined
privateFoo // undefined
privateBar // undefined
IIFE
Creates an isolated scope
and executes it
@loige42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-62-320.jpg)
![const myModule = (() => {
const privateFoo = () => { /* ... */ }
const privateBar = [ /* ... */ ]
const exported = {
publicFoo: () => { /* ... */ },
publicBar: [ /* ... */ ]
};
return exported
})() A module
myModule.publicFoo()
myModule.publicBar[0]
myModule.privateFoo // undefined
myModule.privateBar // undefined
privateFoo // undefined
privateBar // undefined
information hiding
non-exposed functionality
@loige42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-63-320.jpg)
![const myModule = (() => {
const privateFoo = () => { /* ... */ }
const privateBar = [ /* ... */ ]
const exported = {
publicFoo: () => { /* ... */ },
publicBar: [ /* ... */ ]
};
return exported
})() A module
myModule.publicFoo()
myModule.publicBar[0]
myModule.privateFoo // undefined
myModule.privateBar // undefined
privateFoo // undefined
privateBar // undefined
defines exported
functionalities
@loige42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-64-320.jpg)
![const myModule = (() => {
const privateFoo = () => { /* ... */ }
const privateBar = [ /* ... */ ]
const exported = {
publicFoo: () => { /* ... */ },
publicBar: [ /* ... */ ]
};
return exported
})() A module
myModule.publicFoo()
myModule.publicBar[0]
myModule.privateFoo // undefined
myModule.privateBar // undefined
privateFoo // undefined
privateBar // undefined
propagates the exports
to the outer scope (assigning it to myModule)
@loige42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-65-320.jpg)
![const myModule = (() => {
const privateFoo = () => { /* ... */ }
const privateBar = [ /* ... */ ]
const exported = {
publicFoo: () => { /* ... */ },
publicBar: [ /* ... */ ]
};
return exported
})() A module
myModule.publicFoo()
myModule.publicBar[0]
myModule.privateFoo // undefined
myModule.privateBar // undefined
privateFoo // undefined
privateBar // undefined
Can access exported
functionalities
@loige42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-66-320.jpg)
![const myModule = (() => {
const privateFoo = () => { /* ... */ }
const privateBar = [ /* ... */ ]
const exported = {
publicFoo: () => { /* ... */ },
publicBar: [ /* ... */ ]
};
return exported
})() A module
myModule.publicFoo()
myModule.publicBar[0]
myModule.privateFoo // undefined
myModule.privateBar // undefined
privateFoo // undefined
privateBar // undefined
No visibility for the
non-exported ones
@loige42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-67-320.jpg)




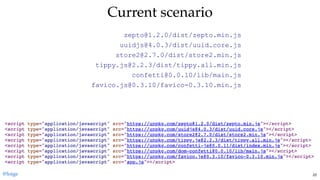
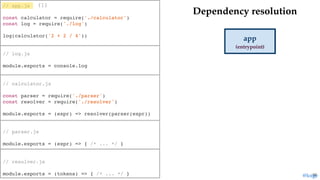
![// or import single functionality
const { concat } = require('./loDash')
concat([1], [2], [3])
// app.js
// import full module
const _ = require('./loDash')
_.concat([1], [2], [3])
// loDash.js
const loDash = {
/* ... */
}
module.exports = loDash
CommonJSCommonJS
@loige 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-74-320.jpg)
![// or import single functionality
const { concat } = require('./loDash')
concat([1], [2], [3])
// app.js
// import full module
const _ = require('./loDash')
_.concat([1], [2], [3])
// loDash.js
const loDash = {
/* ... */
}
module.exports = loDash
CommonJSCommonJS
module
@loige 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-75-320.jpg)
![// or import single functionality
const { concat } = require('./loDash')
concat([1], [2], [3])
// app.js
// import full module
const _ = require('./loDash')
_.concat([1], [2], [3])
// loDash.js
const loDash = {
/* ... */
}
module.exports = loDash
CommonJSCommonJS
module
app using module
@loige 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-76-320.jpg)
![// or import single functionality
const { concat } = require('./loDash')
concat([1], [2], [3])
// app.js
// import full module
const _ = require('./loDash')
_.concat([1], [2], [3])
// loDash.js
const loDash = {
/* ... */
}
module.exports = loDash
CommonJSCommonJS
module
app using module
@loige 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-77-320.jpg)
![// or import single functionality
const { concat } = require('./loDash')
concat([1], [2], [3])
// app.js
// import full module
const _ = require('./loDash')
_.concat([1], [2], [3])
// loDash.js
const loDash = {
/* ... */
}
module.exports = loDash
CommonJSCommonJS
module
app using module
@loige 48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-78-320.jpg)

![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// jquery-1.9.0.js
define(
'jquery',
['sizzle', 'jqueryUI'],
function (sizzle, jqueryUI) {
// Returns the exported value
return function () {
// ...
}
}
)
@loige 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-80-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// jquery-1.9.0.js
define(
'jquery',
['sizzle', 'jqueryUI'],
function (sizzle, jqueryUI) {
// Returns the exported value
return function () {
// ...
}
}
)
module
@loige 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-81-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// jquery-1.9.0.js
define(
'jquery',
['sizzle', 'jqueryUI'],
function (sizzle, jqueryUI) {
// Returns the exported value
return function () {
// ...
}
}
)
module
module name
@loige 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-82-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// jquery-1.9.0.js
define(
'jquery',
['sizzle', 'jqueryUI'],
function (sizzle, jqueryUI) {
// Returns the exported value
return function () {
// ...
}
}
)
module
dependencies
@loige 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-83-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// jquery-1.9.0.js
define(
'jquery',
['sizzle', 'jqueryUI'],
function (sizzle, jqueryUI) {
// Returns the exported value
return function () {
// ...
}
}
)
module
factory function used to construct the
module,
receives the dependencies as arguments
@loige 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-84-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// jquery-1.9.0.js
define(
'jquery',
['sizzle', 'jqueryUI'],
function (sizzle, jqueryUI) {
// Returns the exported value
return function () {
// ...
}
}
)
module
exported value
@loige 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-85-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// app.js
// define paths
requirejs.config({
baseUrl: 'js/lib',
paths: {
jquery: 'jquery-1.9.0'
}
})
define(['jquery'], function ($) {
// this is executed only when jquery
// and its deps are loaded
});
@loige 51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-86-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// app.js
// define paths
requirejs.config({
baseUrl: 'js/lib',
paths: {
jquery: 'jquery-1.9.0'
}
})
define(['jquery'], function ($) {
// this is executed only when jquery
// and its deps are loaded
}); app
@loige 51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-87-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// app.js
// define paths
requirejs.config({
baseUrl: 'js/lib',
paths: {
jquery: 'jquery-1.9.0'
}
})
define(['jquery'], function ($) {
// this is executed only when jquery
// and its deps are loaded
}); app
Require.js config
jquery will be loaded from
://<currentDomain>/js/lib/jquery-1.9.0.js
@loige 51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-88-320.jpg)
![AMD (AMD ( ))
Asynchronous Module DefinitionAsynchronous Module Definition
Require.jsRequire.js
// app.js
// define paths
requirejs.config({
baseUrl: 'js/lib',
paths: {
jquery: 'jquery-1.9.0'
}
})
define(['jquery'], function ($) {
// this is executed only when jquery
// and its deps are loaded
}); app
app main function
Has jquery as dependency
@loige 51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-89-320.jpg)


![(function (root, factory) {
if (typeof exports === 'object') {
// CommonJS
module.exports = factory(require('dep'))
} else if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
// AMD
define(['dep'], function (dep) {
return (root.returnExportsGlobal = factory(dep))
})
} else {
// Global Variables
root.myModule = factory(root.dep)
}
}(this, function (dep) {
// Your actual module
return {}
}))
loige.link/umd@loige 53 . 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-92-320.jpg)
![(function (root, factory) {
if (typeof exports === 'object') {
// CommonJS
module.exports = factory(require('dep'))
} else if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
// AMD
define(['dep'], function (dep) {
return (root.returnExportsGlobal = factory(dep))
})
} else {
// Global Variables
root.myModule = factory(root.dep)
}
}(this, function (dep) {
// Your actual module
return {}
}))
loige.link/umd
IIFE with arguments:
- Current scope (this) and the module
factory function.
- "dep" is a sample dependency of the
module.
@loige 53 . 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-93-320.jpg)
![(function (root, factory) {
if (typeof exports === 'object') {
// CommonJS
module.exports = factory(require('dep'))
} else if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
// AMD
define(['dep'], function (dep) {
return (root.returnExportsGlobal = factory(dep))
})
} else {
// Global Variables
root.myModule = factory(root.dep)
}
}(this, function (dep) {
// Your actual module
return {}
}))
loige.link/umd@loige 53 . 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-94-320.jpg)
![(function (root, factory) {
if (typeof exports === 'object') {
// CommonJS
module.exports = factory(require('dep'))
} else if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
// AMD
define(['dep'], function (dep) {
return (root.returnExportsGlobal = factory(dep))
})
} else {
// Global Variables
root.myModule = factory(root.dep)
}
}(this, function (dep) {
// Your actual module
return {}
}))
loige.link/umd@loige 53 . 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-95-320.jpg)
![(function (root, factory) {
if (typeof exports === 'object') {
// CommonJS
module.exports = factory(require('dep'))
} else if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd) {
// AMD
define(['dep'], function (dep) {
return (root.returnExportsGlobal = factory(dep))
})
} else {
// Global Variables
root.myModule = factory(root.dep)
}
}(this, function (dep) {
// Your actual module
return {}
}))
loige.link/umd@loige 53 . 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-96-320.jpg)













![const $ = require('zepto')
const tippy = require('tippy.js')
const UUID = require('uuidjs')
const { confetti } = require('dom-confetti/src/main')
const store = require('store2')
const Favico = require('favico.js')
!(function () {
const colors = ['#a864fd', '#29cdff', '#78ff44', '#ff718d', '#fdff6a']
const todoApp = (rootEl, opt = {}) => {
const todos = opt.todos || []
let completedTasks = opt.completedTasks || 0
const onChange = opt.onChange || (() => {})
const list = rootEl.find('.todo-list')
const footer = rootEl.find('.footer')
const todoCount = footer.find('.todo-count')
const insertInput = rootEl.find('.add-todo-box input')
const insertBtn = rootEl.find('.add-todo-box button')
const render = () => {
let tips
list.html('')
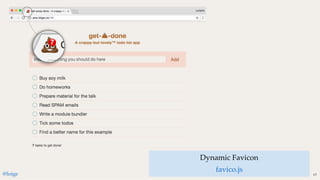
The browser doesn't know how
to process require.
It doesn't support CommonJS!
@loige 58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-110-320.jpg)


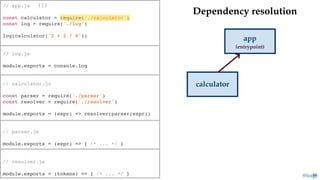
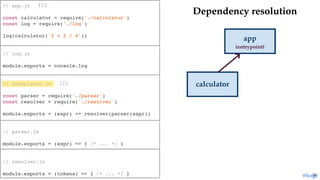
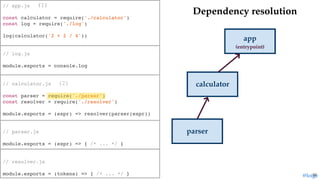
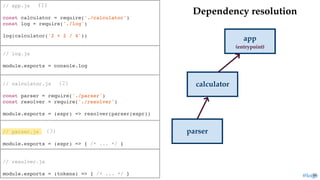
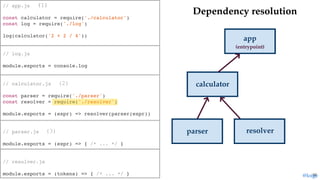
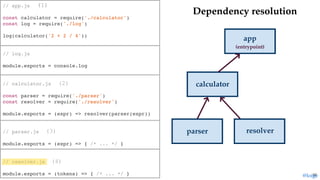
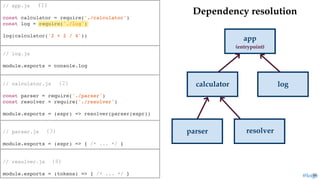
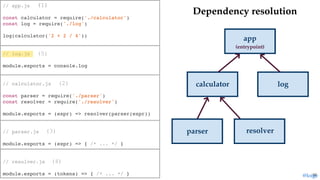



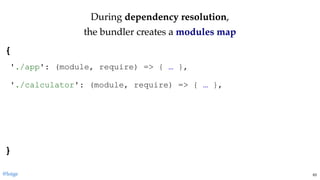
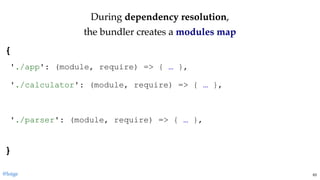
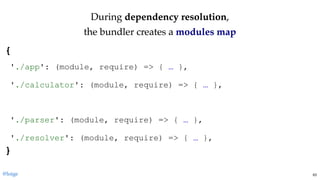
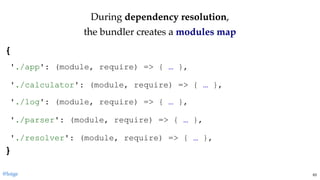
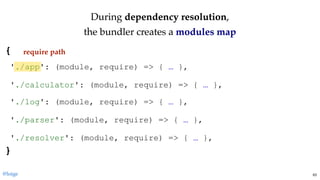
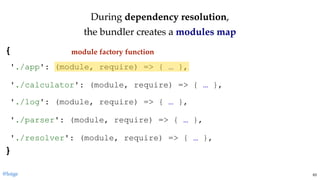
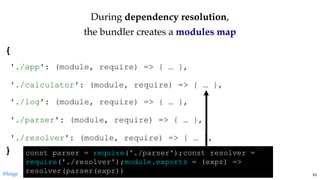
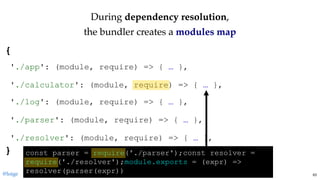
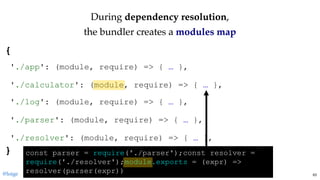

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
) 65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-139-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
)
IIFE passing the modules map as
argument
65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-140-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
)
Custom require function:
it will load the modules by
evaluating the code from the
modules map
65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-141-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
)
A reference to a module with an
empty module.exports.
This will be filled at evaluation
time
65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-142-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
)
Invoking the factory function for
the given module name.
(Service locator pattern)
65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-143-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
)
The current reference module is
passed, the factory function will
modify this object by adding the
proper exported values.
65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-144-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
)
The custom require function is
passed so, modules can
recursively require other modules
65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-145-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
)
The resulting module.exports is
returned
65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-146-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
)
The entrypoint module is
required, triggering the actual
execution of the business logic
65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-147-320.jpg)

return module.exports
}
require('./app')
})(
{
'./app': (module, require) => { … },
'./calculator': (module, require) => { … },
'./log': (module, require) => { … },
'./parser': (module, require) => { … },
'./resolver': (module, require) => { … }
}
) 65
@loige](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-148-320.jpg)






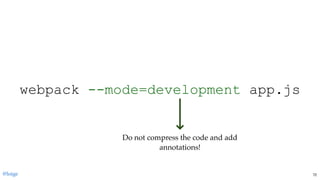
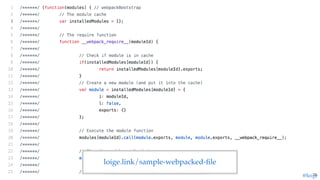

![const { resolve, join } = require('path')
const CompressionPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
entry: './app.js',
output: {
path: resolve(join(__dirname, 'build')),
filename: 'app.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.js$/,
exclude: /(node_modules|bower_components)/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
['@babel/preset-env']
]
}
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new CompressionPlugin()
]
}
Webpack.config.js
@loige75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-158-320.jpg)
![const { resolve, join } = require('path')
const CompressionPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
entry: './app.js',
output: {
path: resolve(join(__dirname, 'build')),
filename: 'app.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.js$/,
exclude: /(node_modules|bower_components)/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
['@babel/preset-env']
]
}
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new CompressionPlugin()
]
}
Webpack.config.js
Entrypoint
Build the dependency graph starting from ./app.js
@loige75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-159-320.jpg)
![const { resolve, join } = require('path')
const CompressionPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
entry: './app.js',
output: {
path: resolve(join(__dirname, 'build')),
filename: 'app.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.js$/,
exclude: /(node_modules|bower_components)/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
['@babel/preset-env']
]
}
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new CompressionPlugin()
]
}
Webpack.config.js
Output
Save the resulting bundled file in ./build/app.js
@loige75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-160-320.jpg)
![const { resolve, join } = require('path')
const CompressionPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
entry: './app.js',
output: {
path: resolve(join(__dirname, 'build')),
filename: 'app.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.js$/,
exclude: /(node_modules|bower_components)/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
['@babel/preset-env']
]
}
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new CompressionPlugin()
]
}
Webpack.config.js
Loaders
All the files matching "*.js" are processed with babel
and converted to ES5 Javascript
@loige75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-161-320.jpg)
![const { resolve, join } = require('path')
const CompressionPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
entry: './app.js',
output: {
path: resolve(join(__dirname, 'build')),
filename: 'app.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.js$/,
exclude: /(node_modules|bower_components)/,
use: {
loader: 'babel-loader',
options: {
presets: [
['@babel/preset-env']
]
}
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new CompressionPlugin()
]
}
Webpack.config.js
Plugins
Uses a plugin that generates a gzipped copy of every
emitted file.
@loige75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-162-320.jpg)





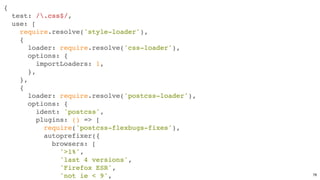
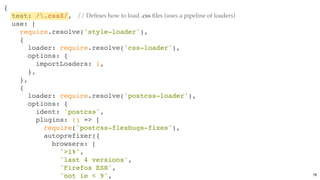






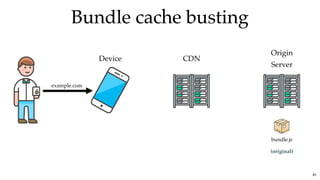
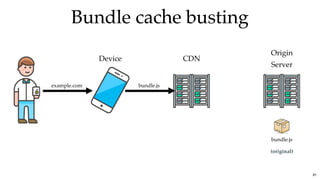
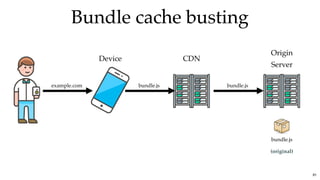
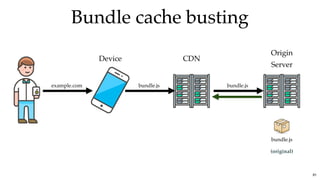
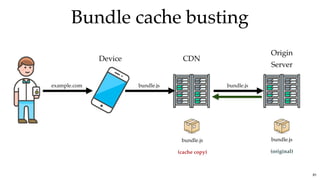
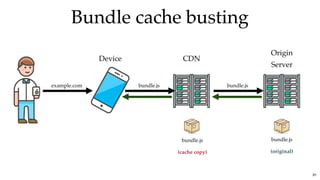
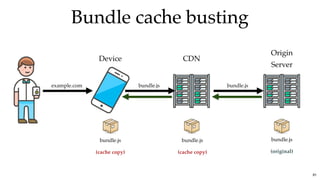
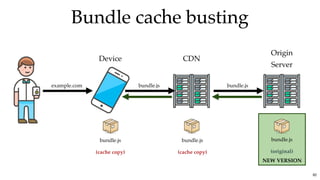










![Bundle cache bustingBundle cache busting
Webpack SolutionWebpack Solution
output: {
filename: '[name].[contenthash].js'
}
85](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-196-320.jpg)
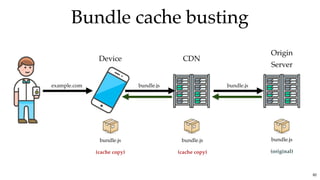
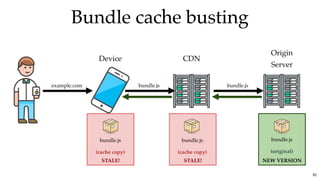
![Bundle cache bustingBundle cache busting
Webpack SolutionWebpack Solution
...
bundle.9f61f58dd1cc3bb82182.js
bundle.aacdf58ef1aa12382199.js
bundle.ed61f68defef3bb82221.js
output: {
filename: '[name].[contenthash].js'
}
85](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unbundling-the-javascript-module-bundler-oredev-2018-181125142934/85/Unbundling-the-JavaScript-module-bundler-Oredev-21-Nov-2018-197-320.jpg)