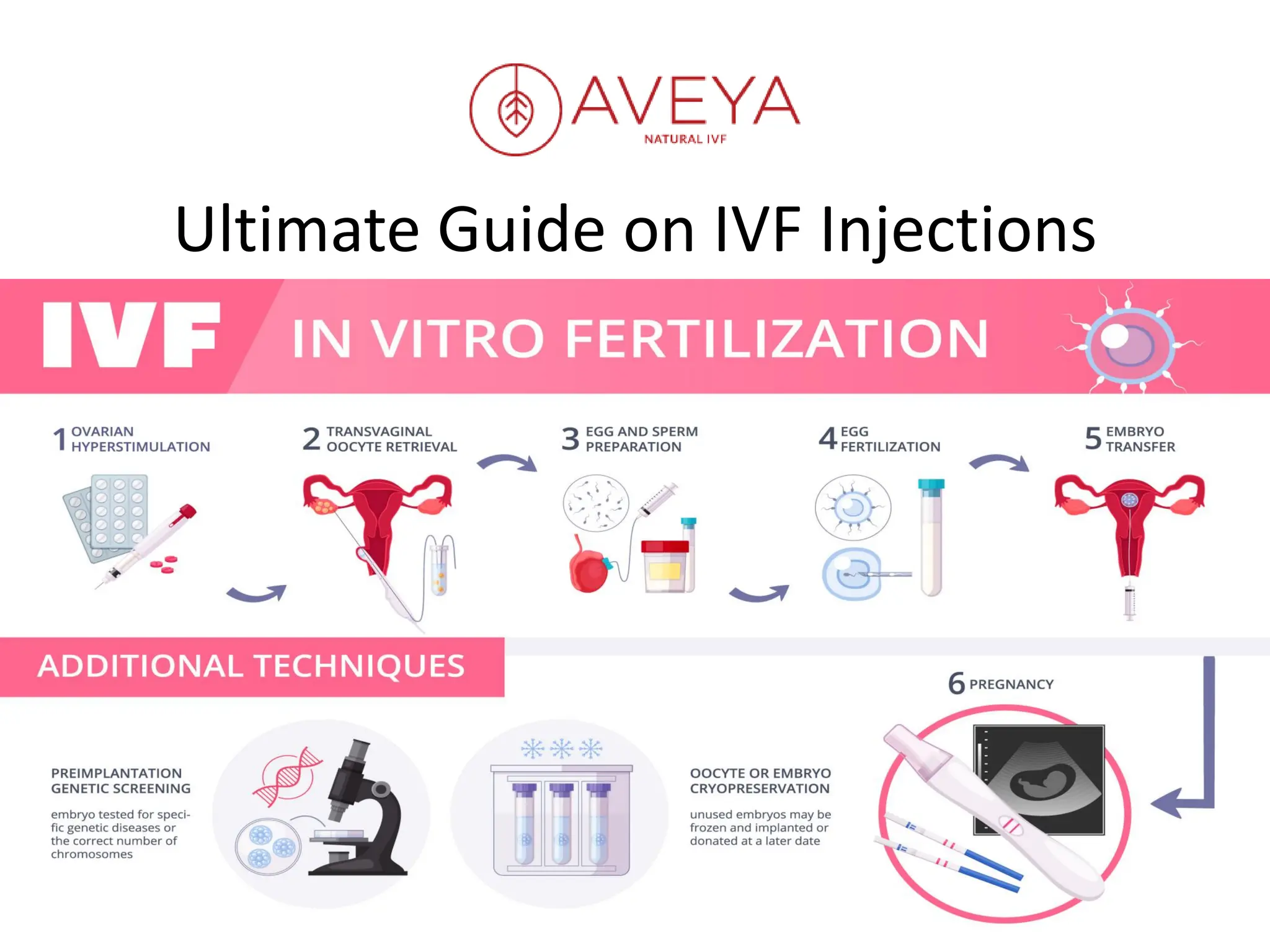
IVF injections are essential to the success of the IVF process, designed to maximize egg production, control ovulation timing, and support early pregnancy. While the number and complexity of injections can seem daunting, understanding their purpose and schedule can help reduce anxiety and improve compliance. Read more: https://aveya.in/ultimate-guide-on-ivf-injections/