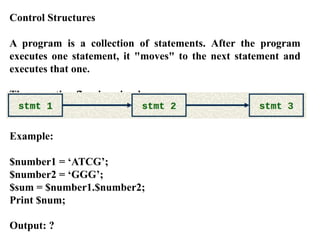
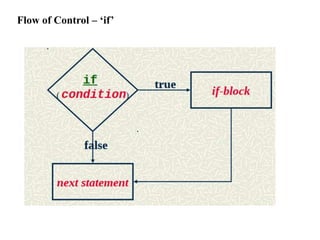
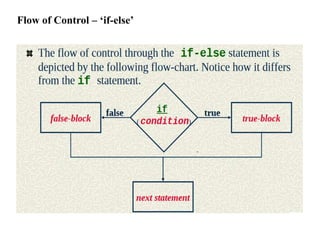
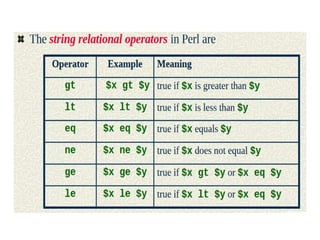
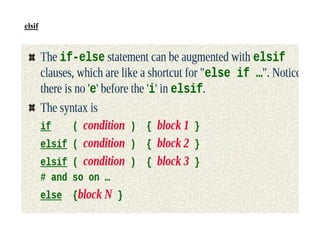
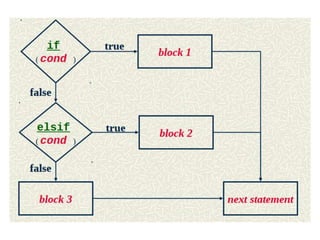
The document provides an overview of control structures in programming, detailing how statements execute sequentially and introducing conditional statements like 'if', 'else', 'elsif', and loops. It includes examples of sample programs demonstrating these control structures in action, using relational operators for comparisons. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of controlling the flow of a program based on conditions.