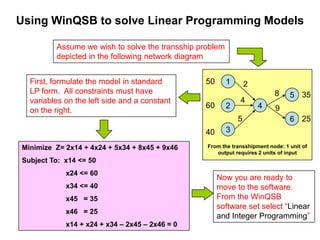
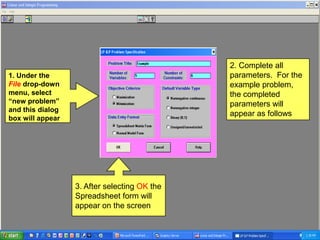
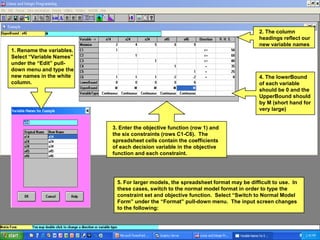
The document provides instructions for using WinQSB software to solve a linear programming transshipment problem. It describes how to:
1) Formulate the transshipment problem as a linear program with an objective function and constraints
2) Enter the model into the WinQSB software by defining the variables, objective function, and constraints either using a spreadsheet format or normal model format
3) Solve the linear program using the software and save/print the optimal solution.