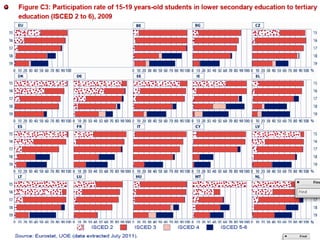
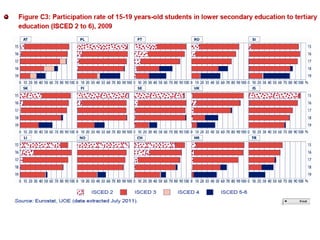
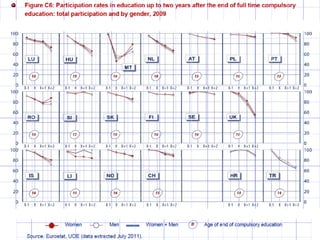
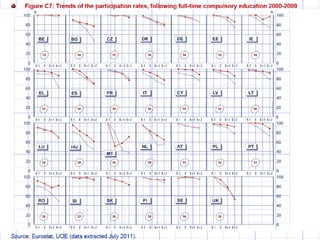
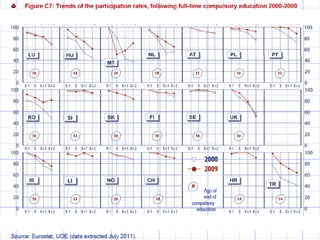
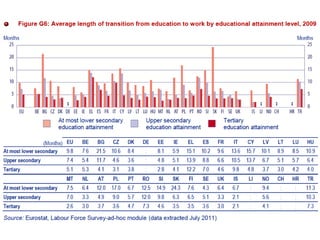
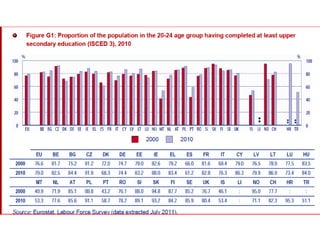
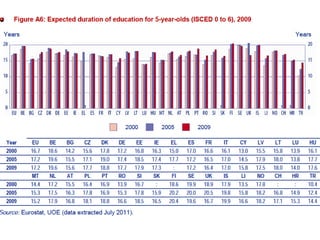
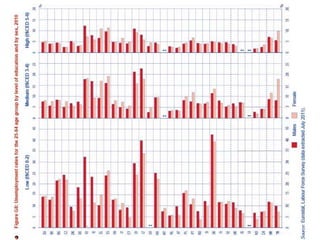
Mariano Fernández Enguita presented at a conference on early school leaving. He discussed how universal primary education was once a success but secondary education is facing failures in academic achievement and early leaving. The rise of information and learning societies has led to knowledge becoming more valuable and unequal. Schooling models are challenged by diffuse learning from other sources. Changes are needed to address disengagement from education, including reconsidering teaching quality, curriculum, support for vulnerable groups, and the very logic of schooling.