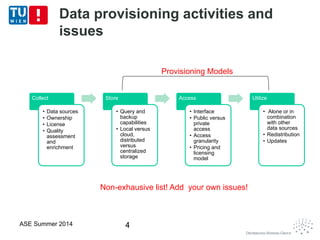
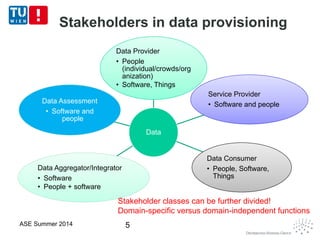
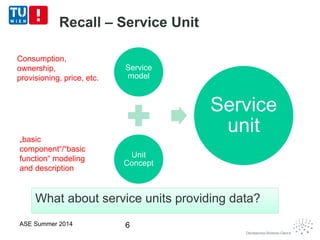
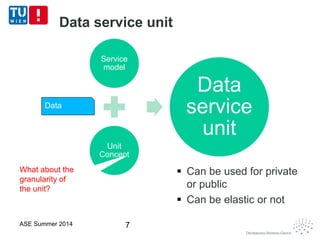
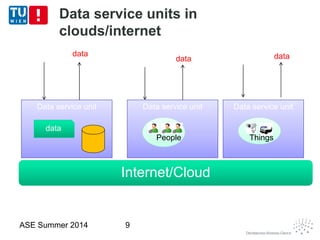
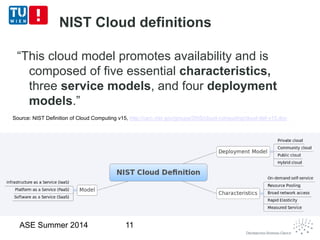
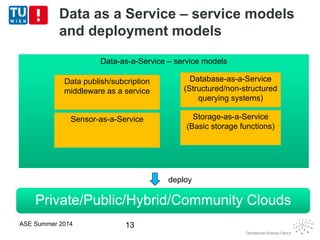
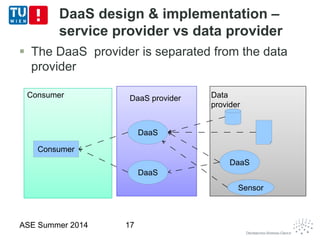
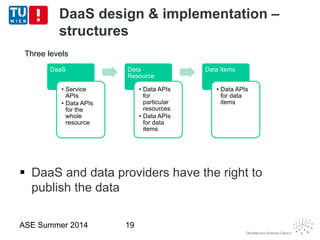
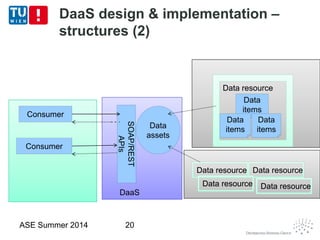
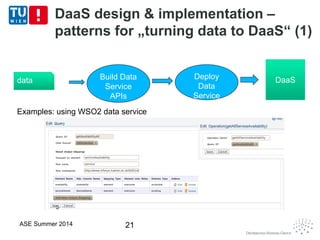
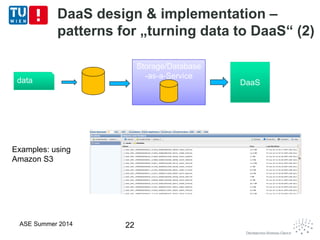
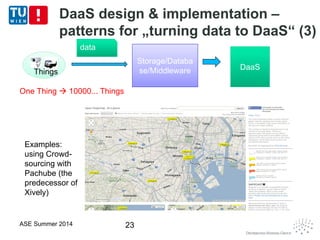
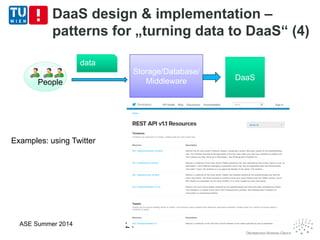
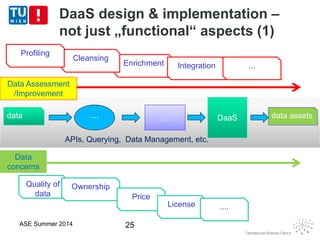
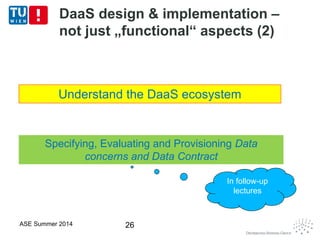
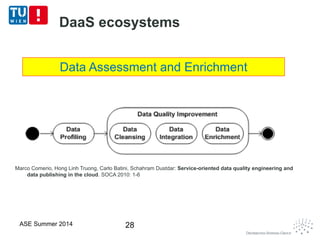
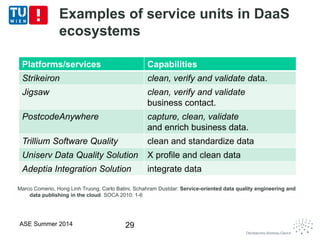
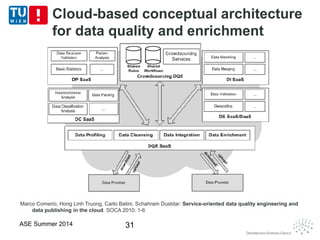
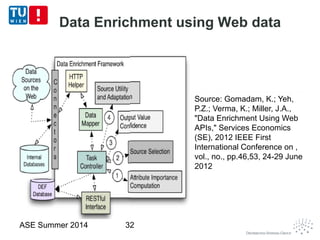
This document discusses concepts related to data as a service (DaaS), including data service units, DaaS design and implementation, and DaaS ecosystems. It defines data service units and how they can provide data capabilities in clouds and on the internet. It outlines characteristics of DaaS based on NIST cloud definitions and describes common DaaS service models and deployment models. The document also discusses patterns for designing and implementing DaaS, considering both functional and non-functional aspects, and provides examples of service units and architectures in DaaS ecosystems.