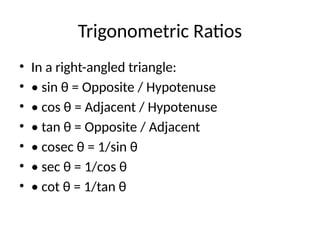
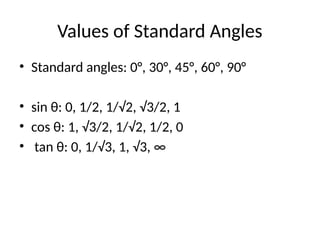
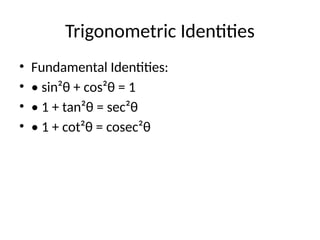
This presentation on Trigonometry introduces the fundamental concepts of the subject, including trigonometric ratios, values of standard angles, and important identities. It explains the graphical nature of trigonometric functions and highlights their real-life applications in measuring heights, distances, navigation, and engineering. With solved examples and visual explanations, the presentation aims to make trigonometry simple, practical, and engaging for learners.