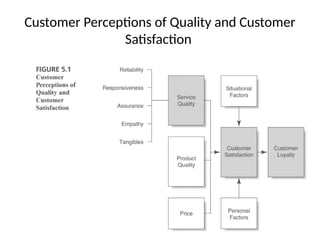
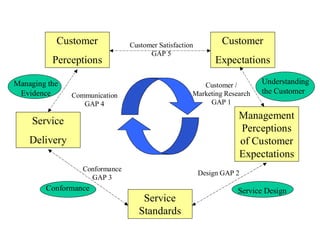
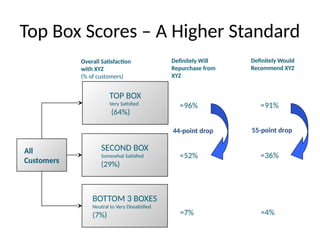
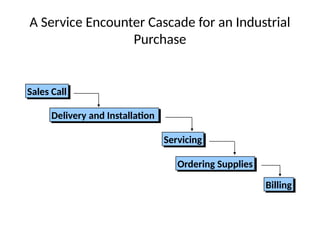
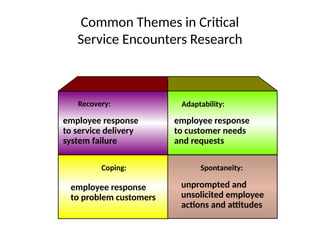
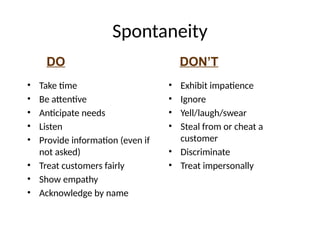
The document examines the principles of Total Quality Management (TQM), focusing on customer-centric approaches, employee involvement, and continual improvement to enhance customer satisfaction. It discusses the five dimensions of service quality: reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, and tangibles, which influence customer perceptions and expectations. Additionally, it addresses service encounter dynamics and recovery strategies essential for maintaining positive customer relationships.