This document provides information about gathering data qualitatively and quantitatively. It begins by stating the expected learning outcomes, which are to define and differentiate qualitative and quantitative data, and classify examples by data type. It then explains that quantitative data involves measuring or counting, while qualitative data is gathered through interviews, surveys, and observations. Examples of collecting both types of data are also provided, such as using surveys to gather quantitative ratings or qualitative opinions. The document concludes with a quiz to test the understanding of differentiating qualitative and quantitative data and examples.


![Gathering Data Qualitatively and
Quantitatively
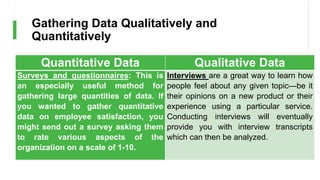
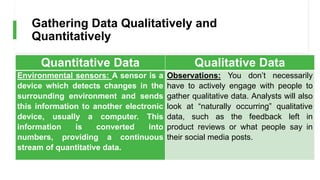
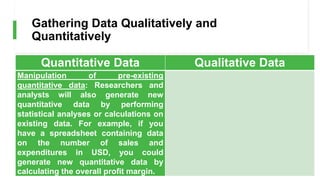
Quantitative data is generated by
measuring or counting certain entities, or by
performing calculations, while Qualitative
data is gathered through interviews,
surveys, and observations [4].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic2-gatheringdataqualitativelyandquantitatively-230826070801-2b64bbf2/85/Topic2-Gathering-Data-Qualitatively-and-Quantitatively-pptx-3-320.jpg)


![Differentiating Qualitative and Quantitative
Data
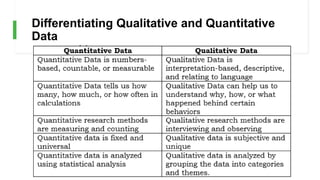
What is the difference between Qualitative and
Quantitative Data? [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic2-gatheringdataqualitativelyandquantitatively-230826070801-2b64bbf2/85/Topic2-Gathering-Data-Qualitatively-and-Quantitatively-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![What are the examples of Qualitative and
Quantitative Data? [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic2-gatheringdataqualitativelyandquantitatively-230826070801-2b64bbf2/85/Topic2-Gathering-Data-Qualitatively-and-Quantitatively-pptx-11-320.jpg)








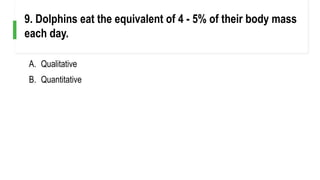
![A. Qualitative
B. Quantitative [6]
10. Dolphins have smooth skin.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic2-gatheringdataqualitativelyandquantitatively-230826070801-2b64bbf2/85/Topic2-Gathering-Data-Qualitatively-and-Quantitatively-pptx-21-320.jpg)
![References
[4] Stevens, E. (2022, November 30). Quantitative vs qualitative data: What’s the
difference? Career Foundry. https://careerfoundry.com/en/blog/data-
analytics/difference-between-quantitative-and-qualitative-data
[5] Qualitative vs. quantitative data: what's the difference? (2021, October 6).
Fullstory. https://www.fullstory.com/blog/qualitative-vs-quantitative-data/
[6] https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/63f0145b8407ad001eb4610c/qualitative-vs-
quantitative](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic2-gatheringdataqualitativelyandquantitatively-230826070801-2b64bbf2/85/Topic2-Gathering-Data-Qualitatively-and-Quantitatively-pptx-23-320.jpg)