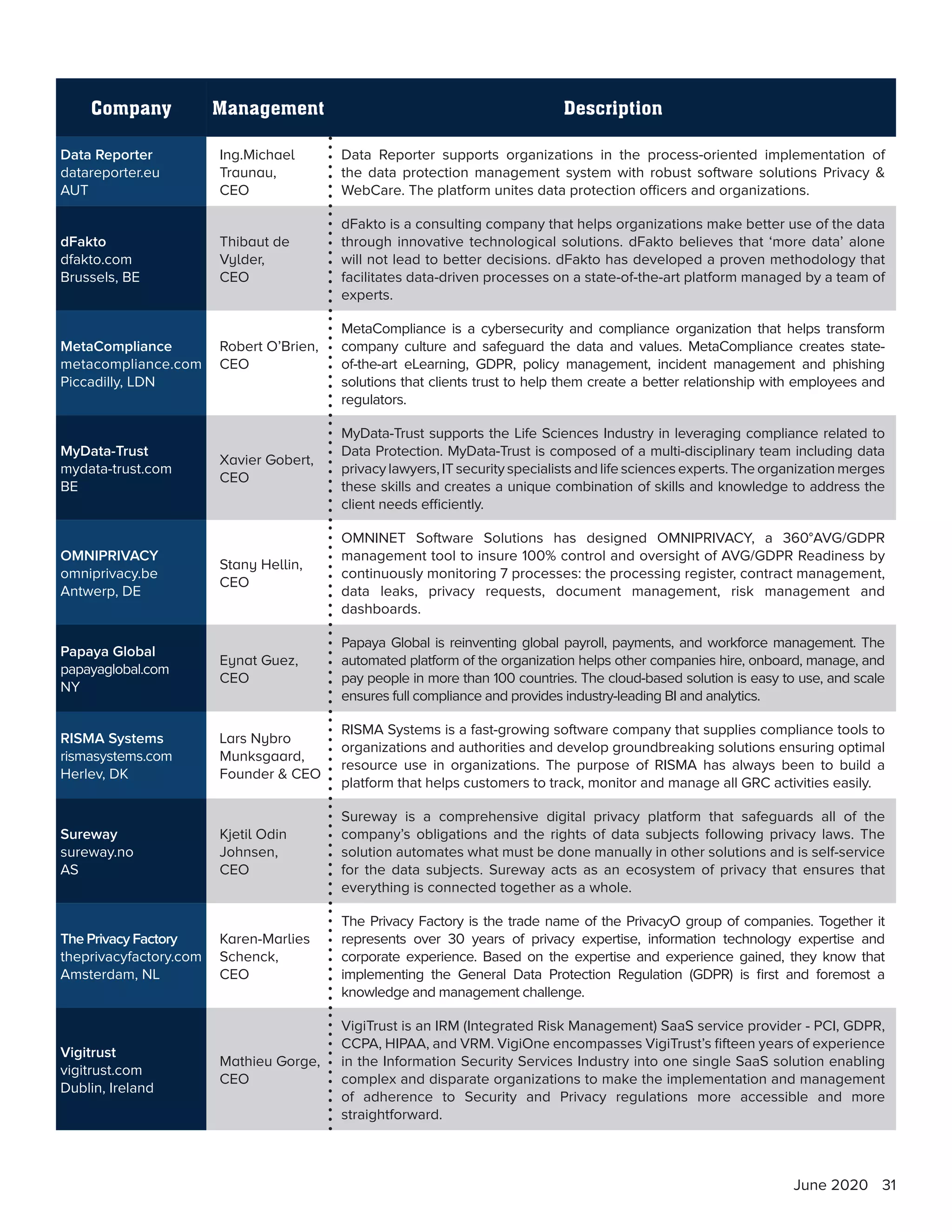
The document discusses the significance of GDPR in establishing strong data protection standards and its evolving role in a digital landscape post-implementation. It highlights the necessity for organizations to adopt comprehensive governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) practices, using technology to enhance data security and maintain compliance. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of continuous vigilance and the use of managed detection and response (MDR) solutions for effective cybersecurity and GDPR adherence.