1) The presentation discusses the four main types of tissues in the body - epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissue.
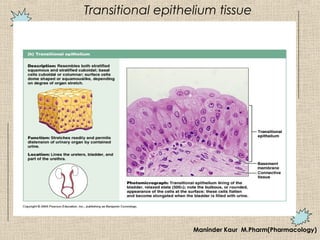
2) Epithelial tissue covers surfaces and lines body cavities. It is categorized as simple or stratified and includes squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and transitional cell types.
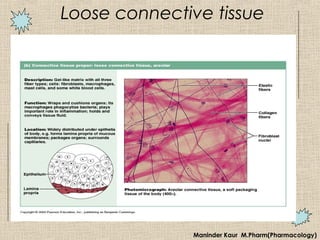
3) Connective tissue functions to support and bind other tissues. Its classes include loose, dense, adipose, cartilage and bone tissues.
4) Muscular tissue contains specialized contractile cells and includes skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle types.
5) Nervous tissue is composed of neurons specialized for conduction of electrical signals.