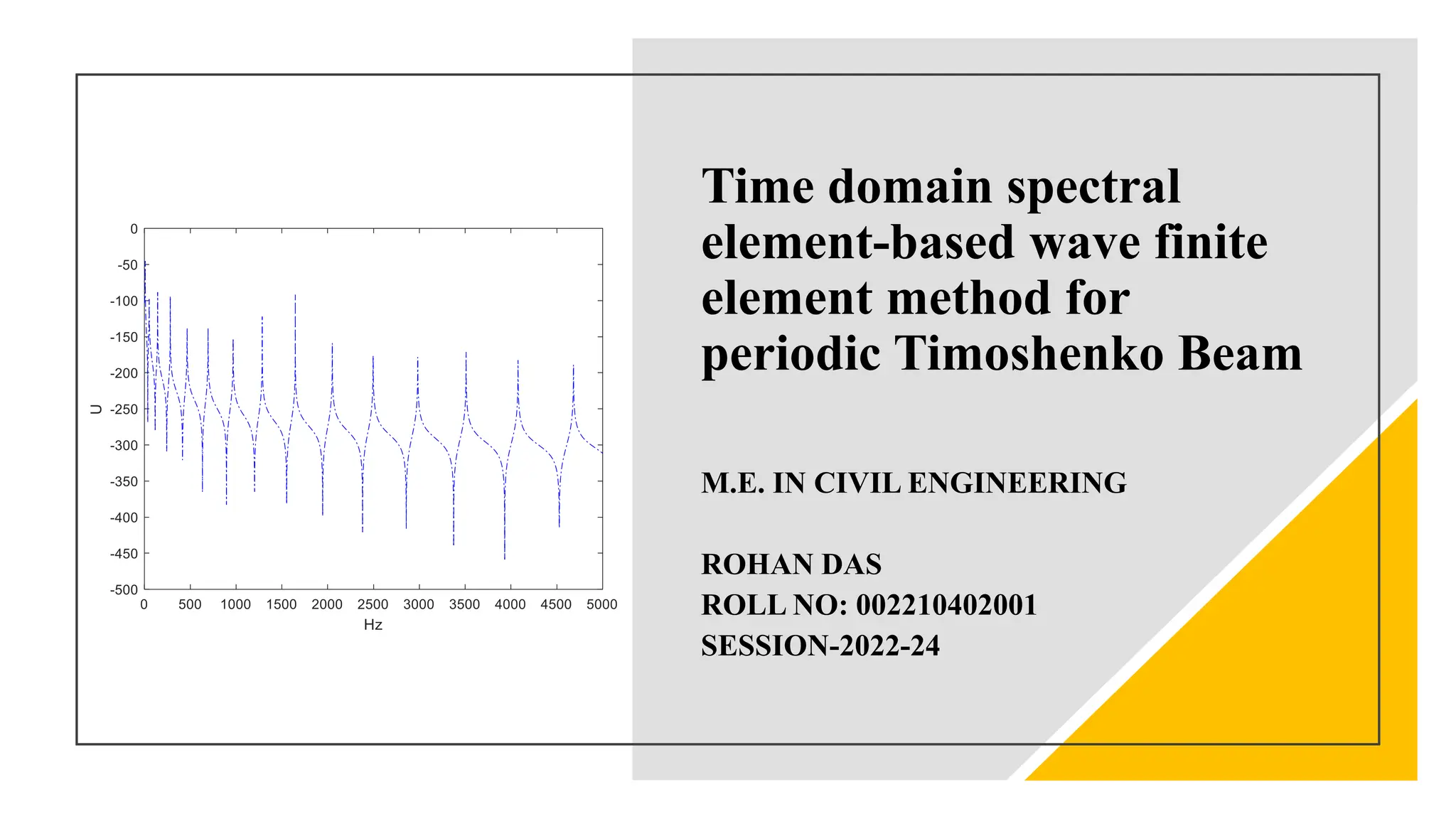
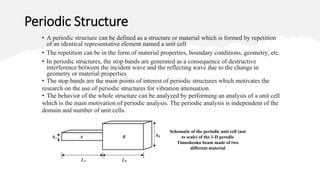
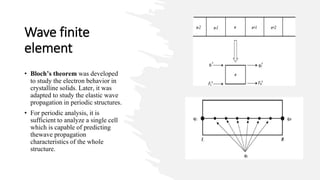
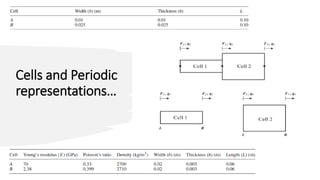
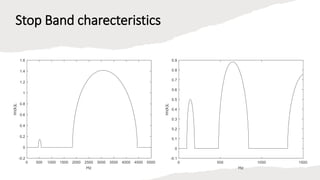
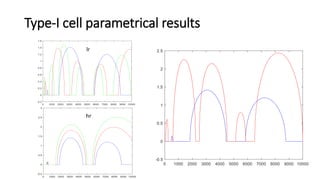
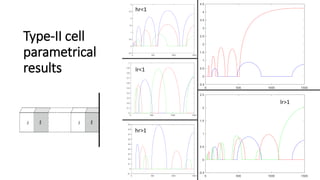
This document discusses the time domain spectral element-based wave finite element method for analyzing periodic Timoshenko beams, which are defined by repetitive unit cells. It highlights the significance of stop bands in periodic structures that result from destructive interference, motivating research into vibration attenuation. Various analysis methods, especially the transfer matrix method and spectral element method, are compared, noting the computational efficiency of the latter over conventional finite element methods.