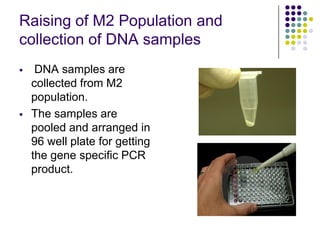
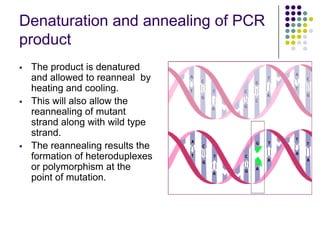
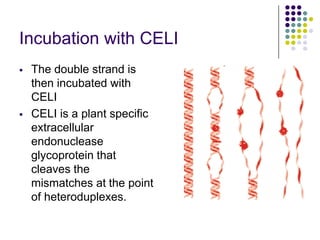
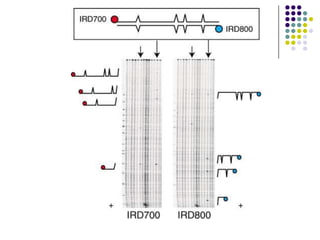
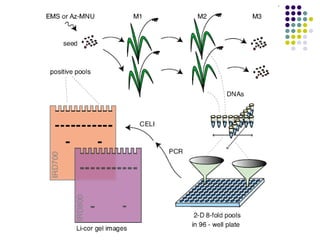
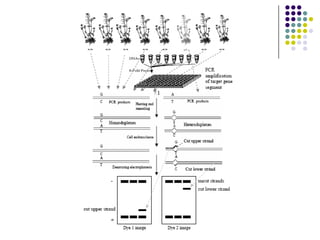
Tilling is a non-transgenic method to identify mutations in a specific gene. It involves chemically inducing mutations in seeds using EMS, growing the M1 and M2 populations, collecting DNA samples, performing PCR to amplify the gene of interest, and treating the PCR products with an endonuclease called CELI. CELI cleaves mismatches between mutant and wild type strands, forming heteroduplexes. These cleaved products are then detected on a gel, identifying individuals with mutations in the gene of interest. Tilling has been used to discover mutations in many crops like wheat, maize, rice and more.