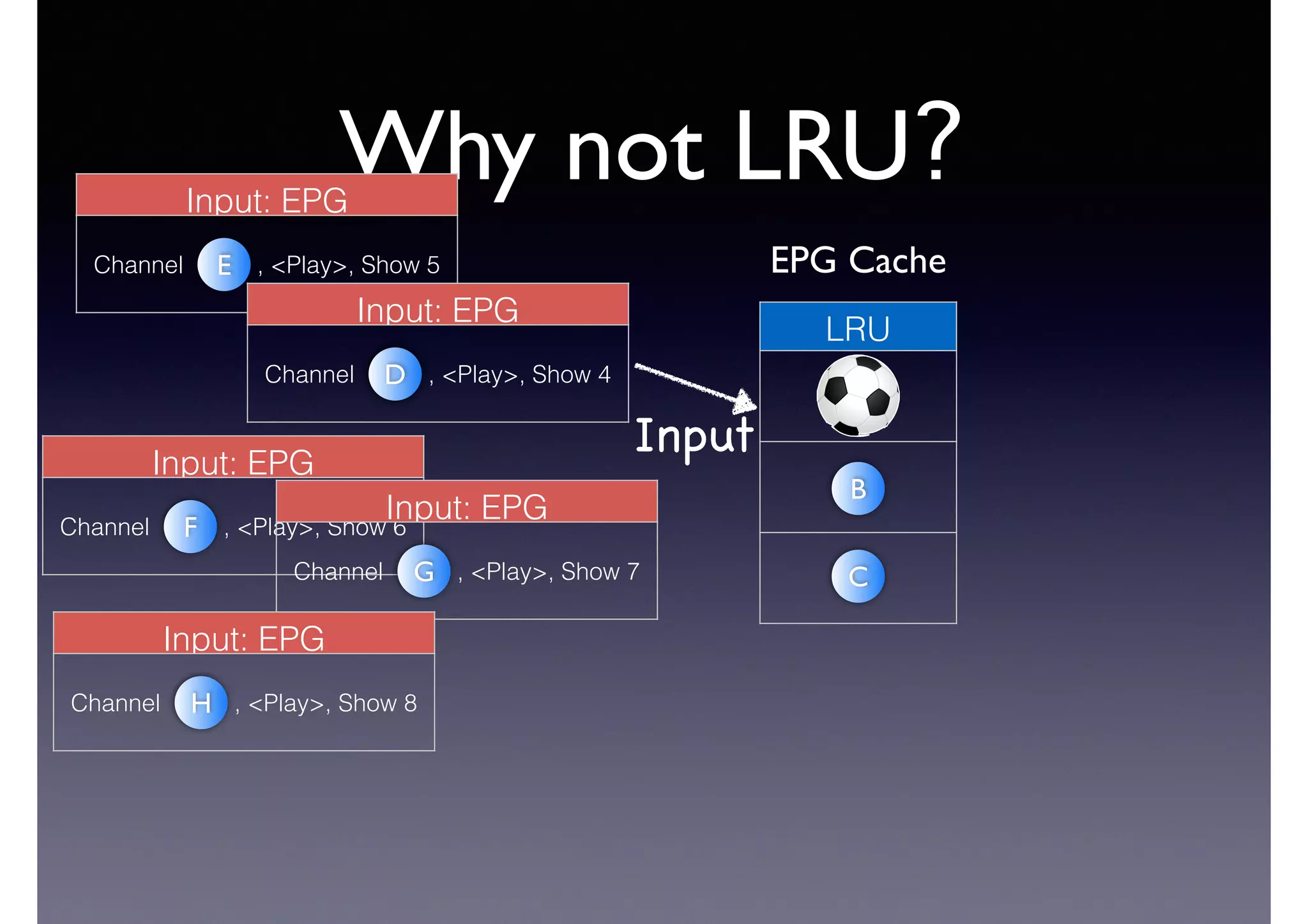
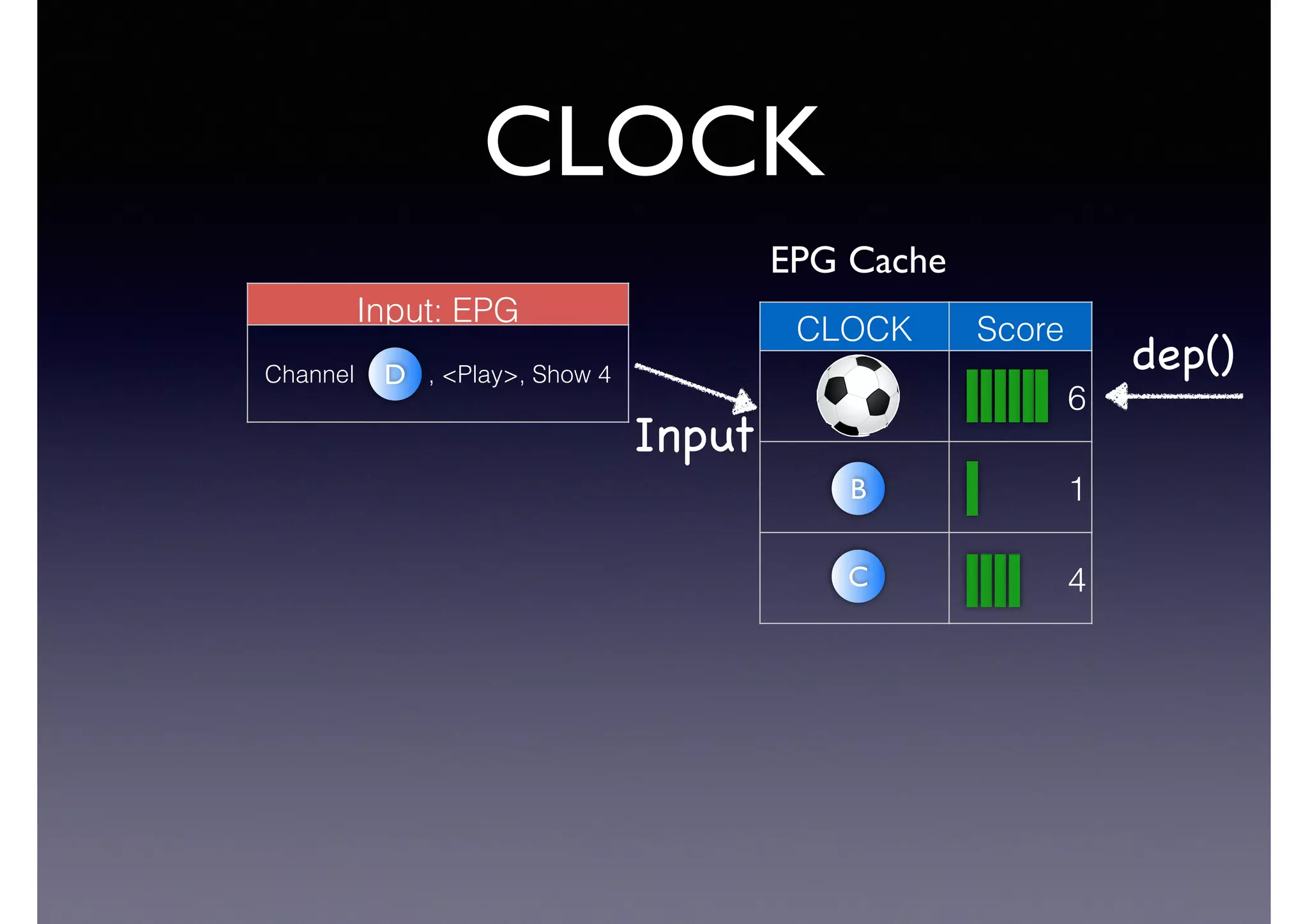
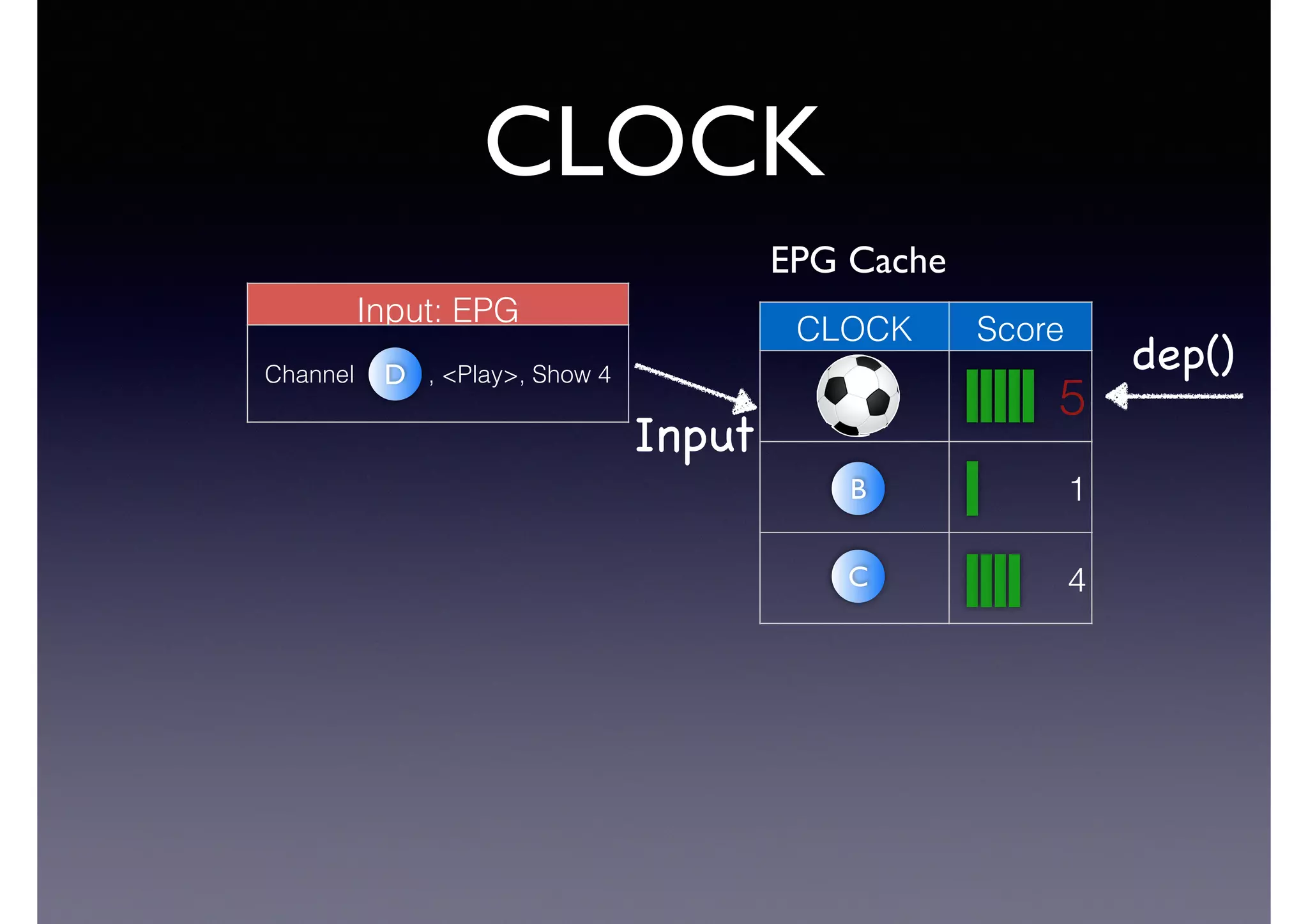
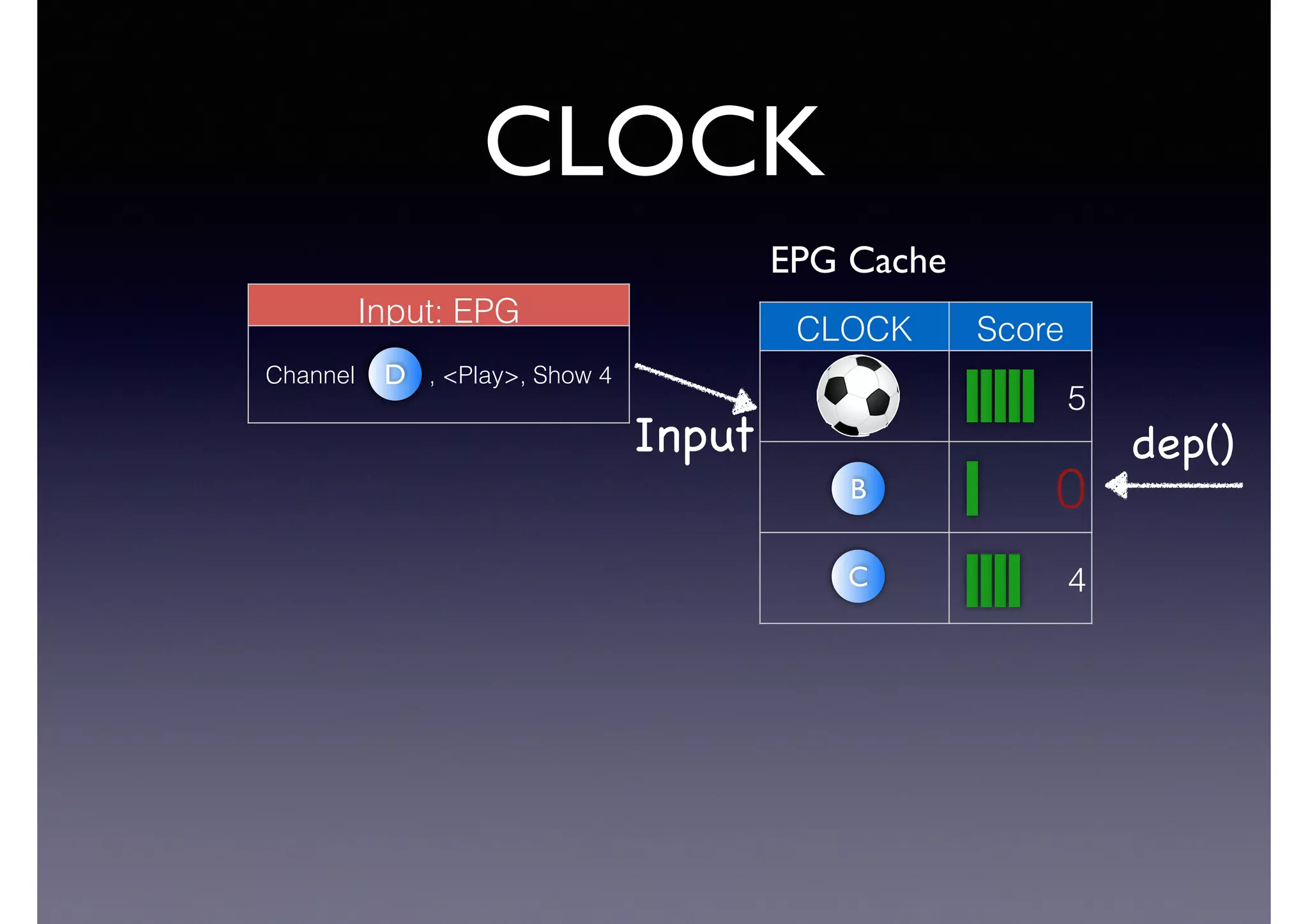
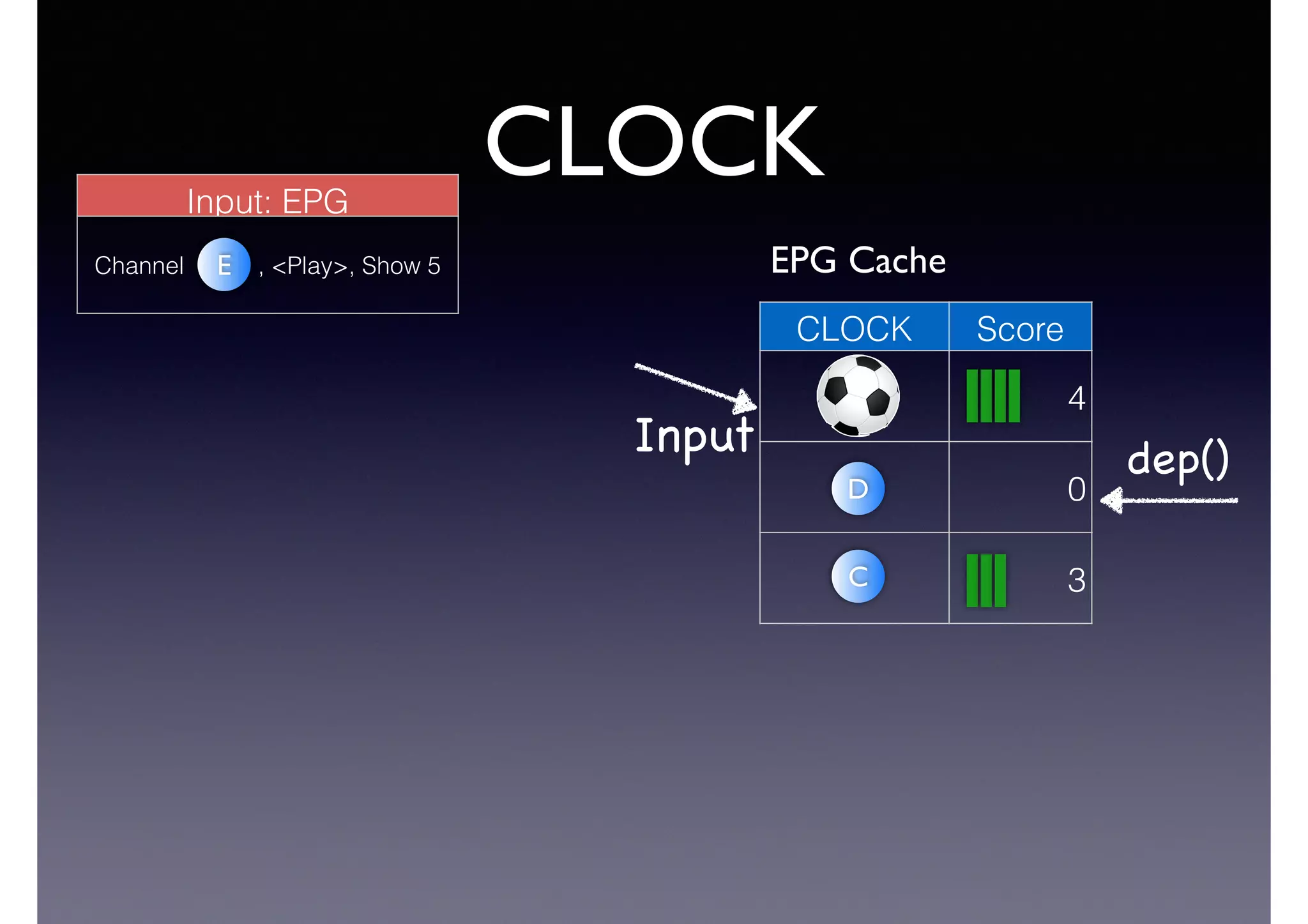
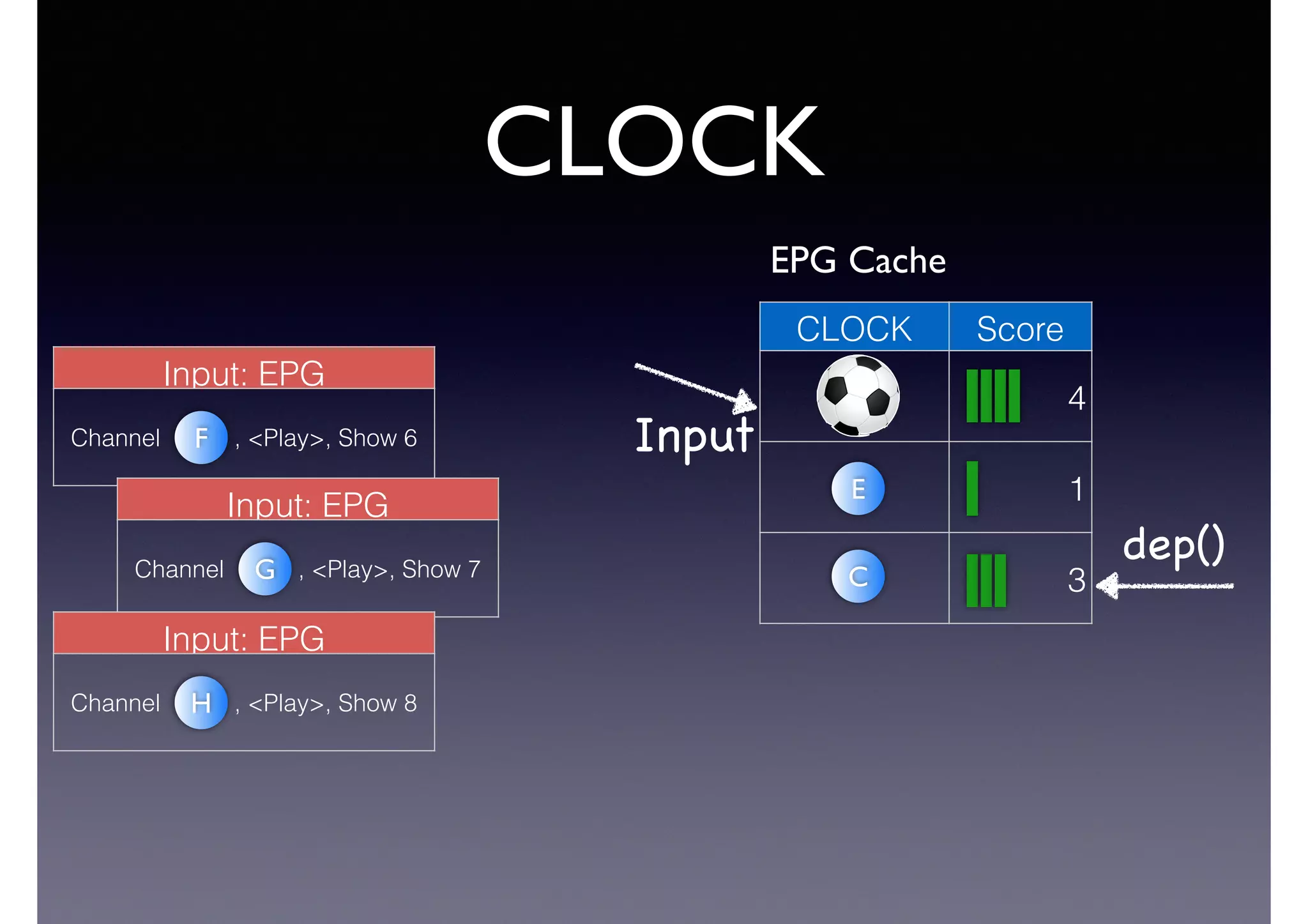
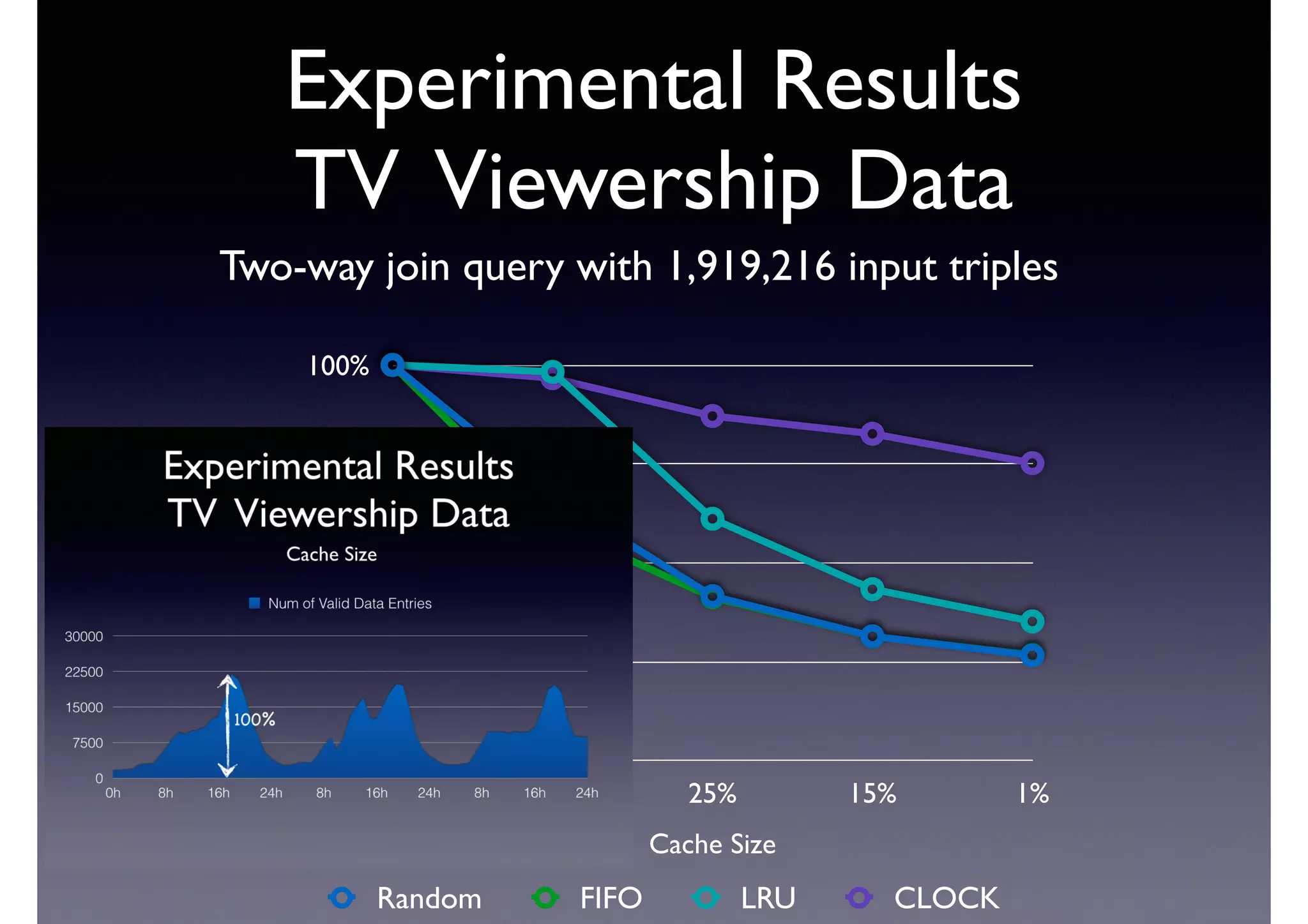
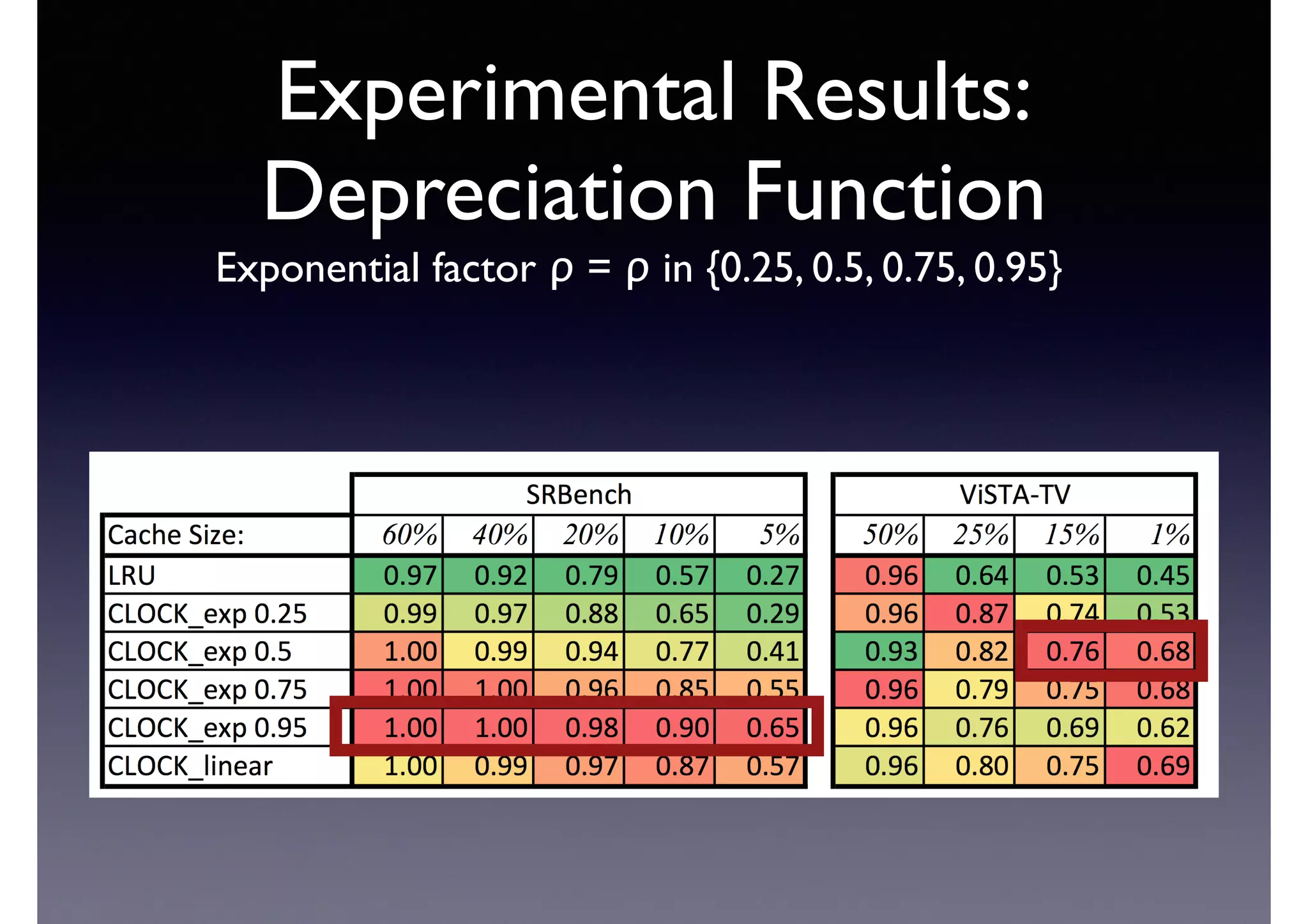
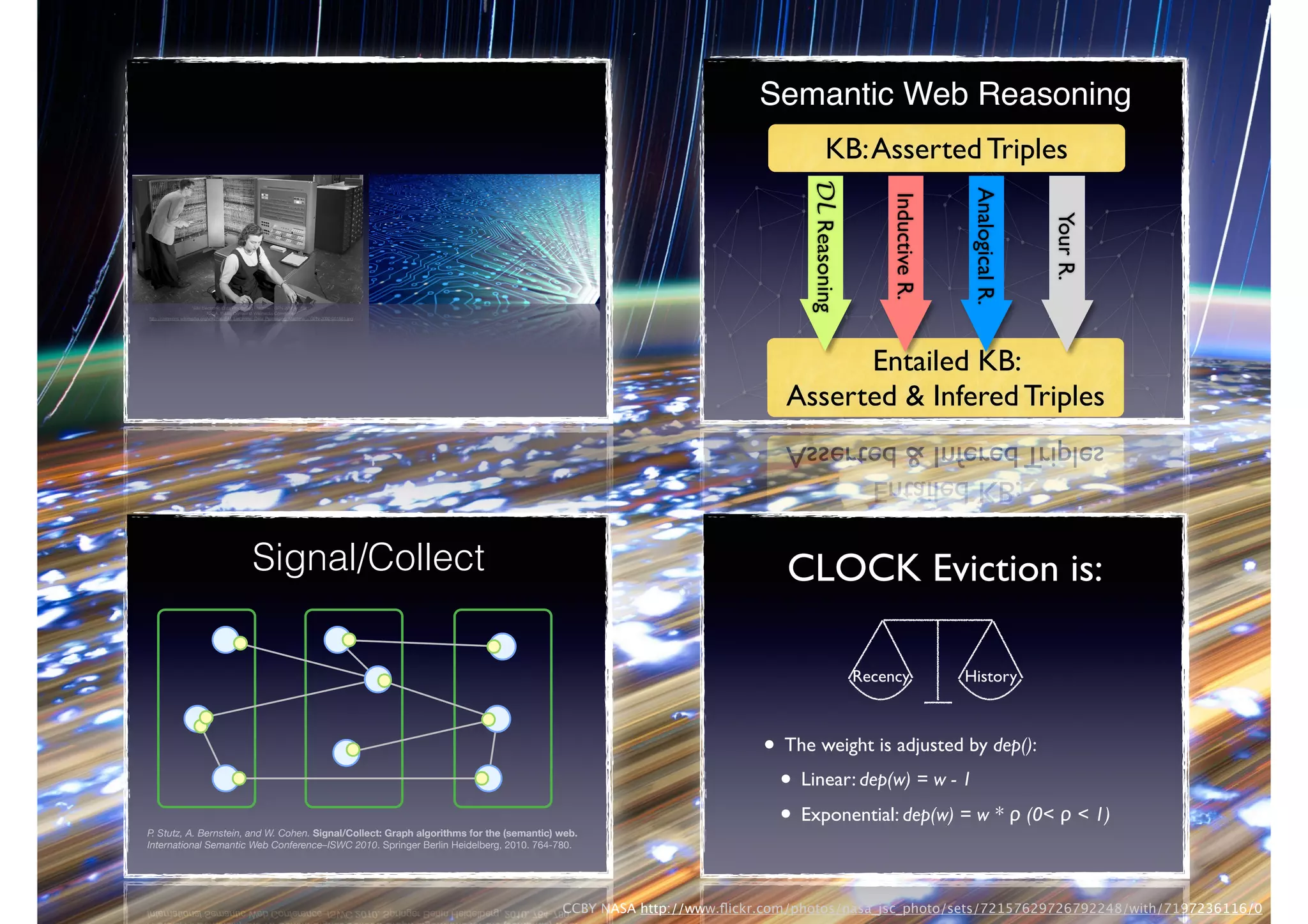
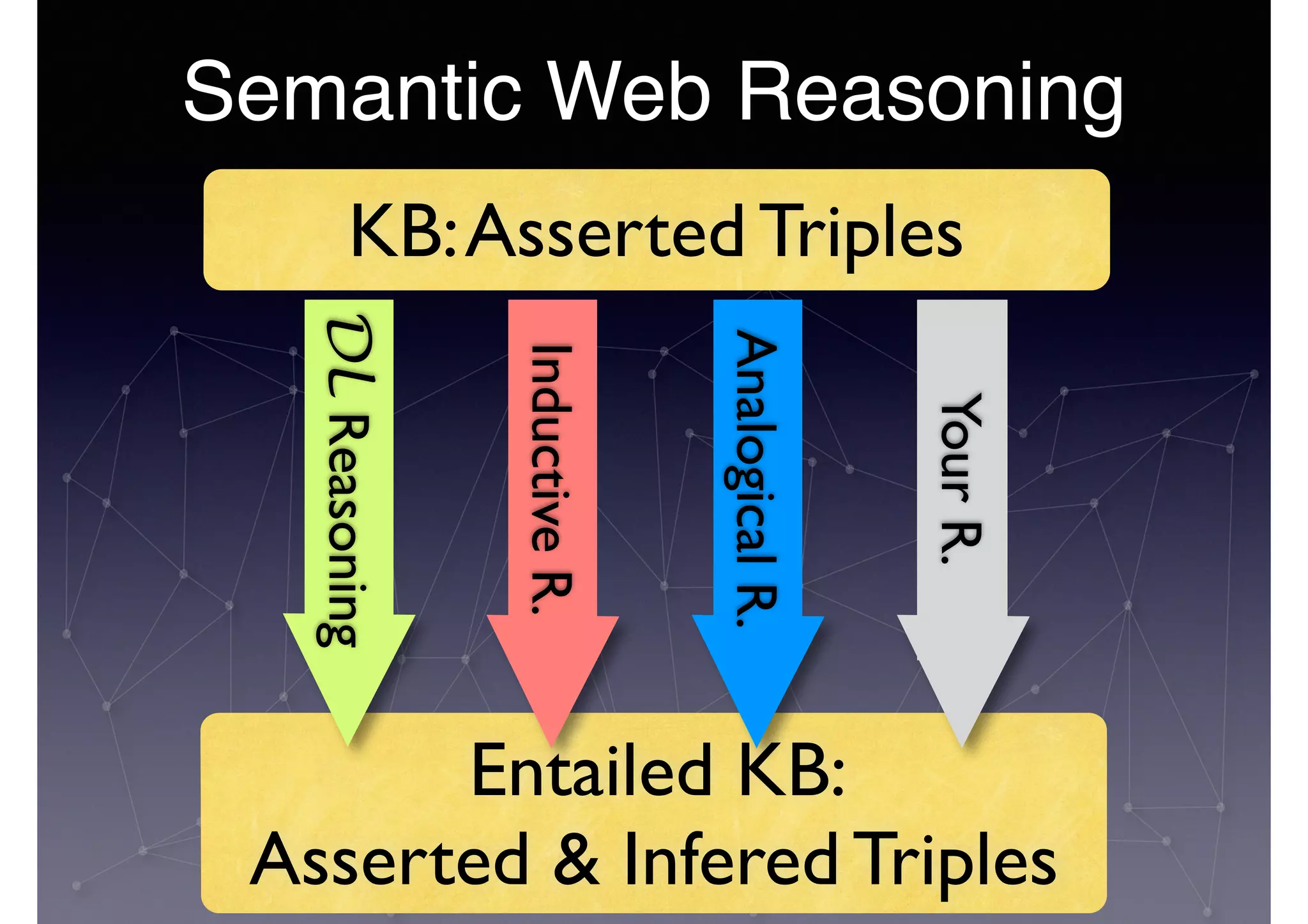
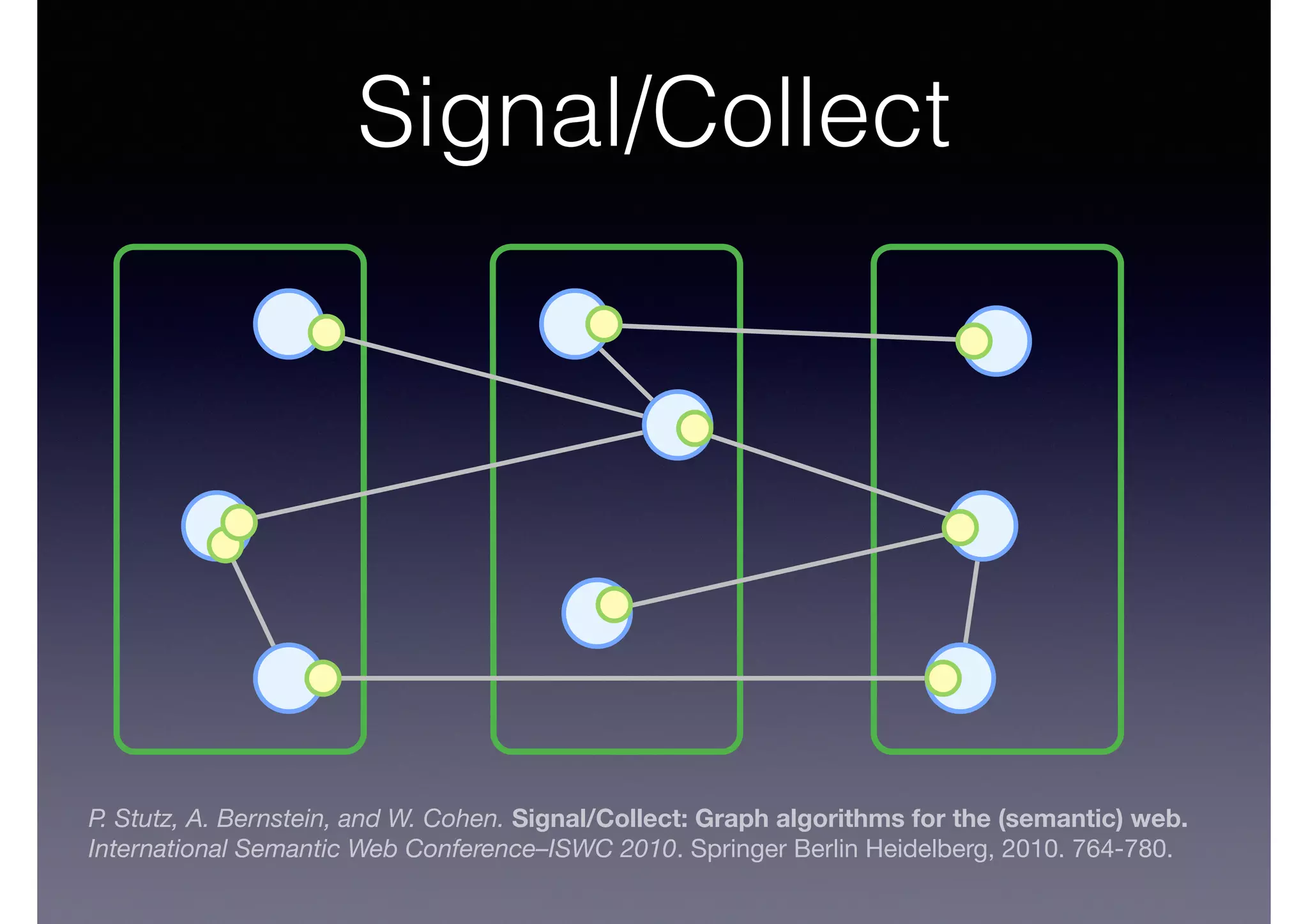
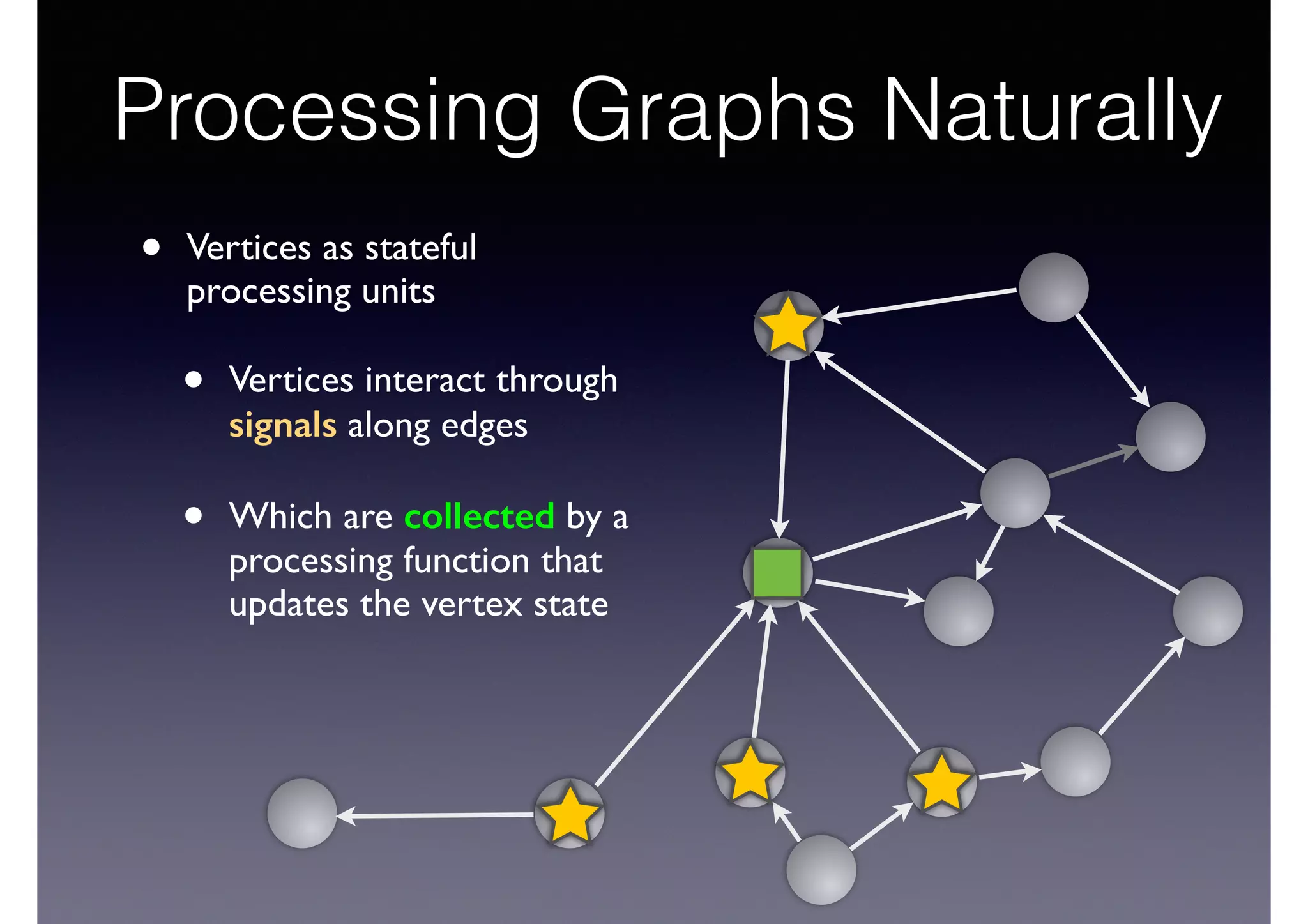
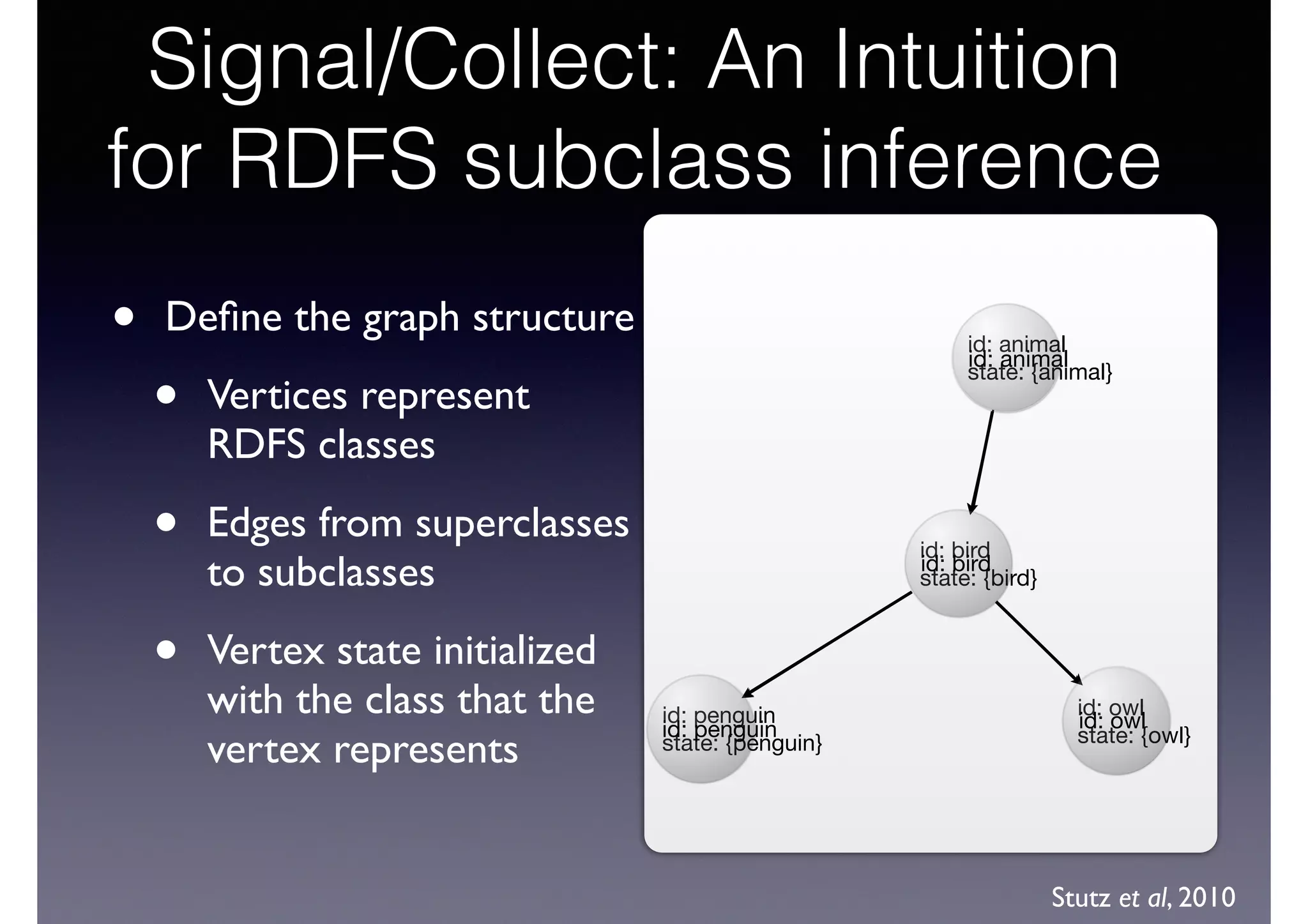
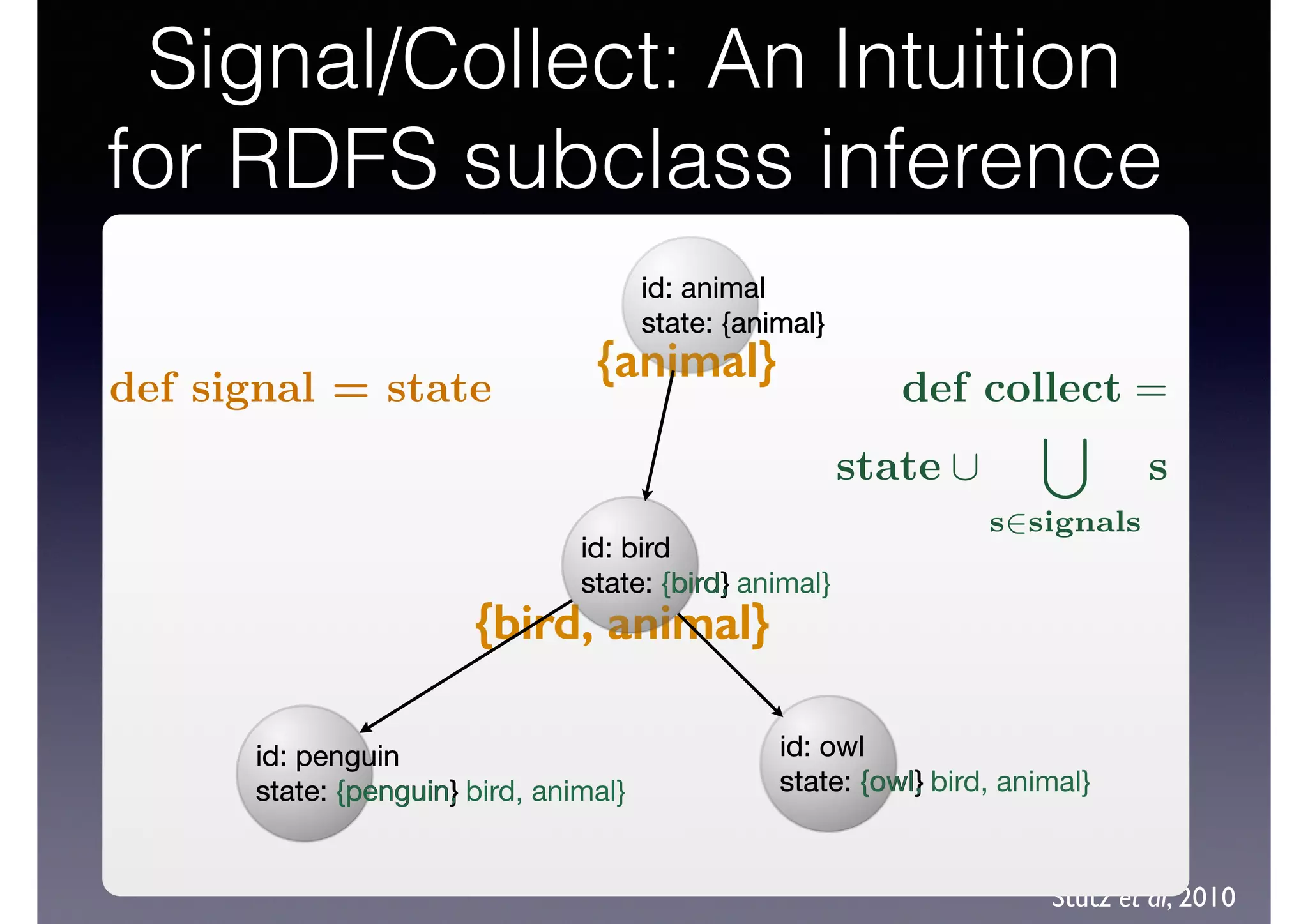
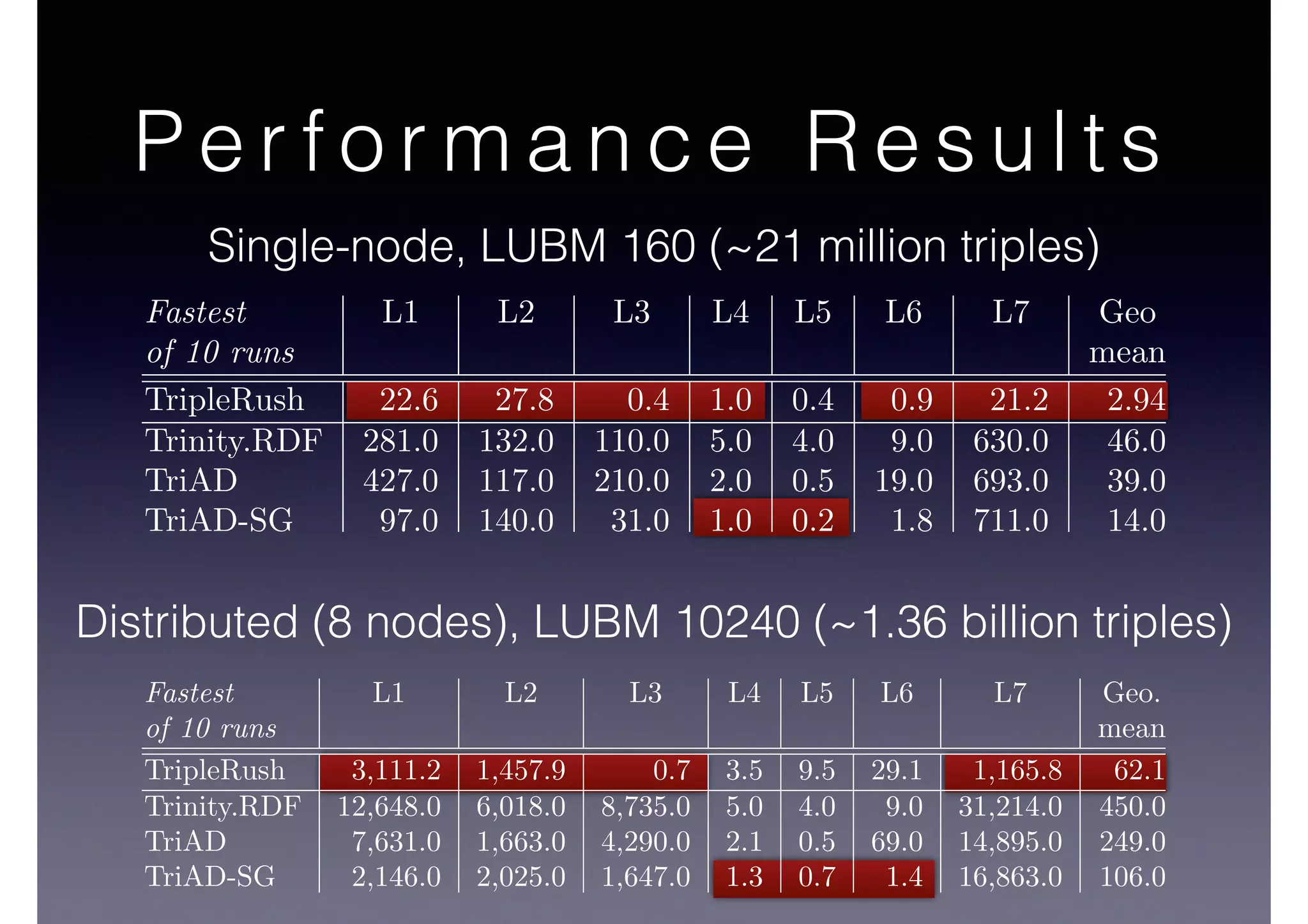
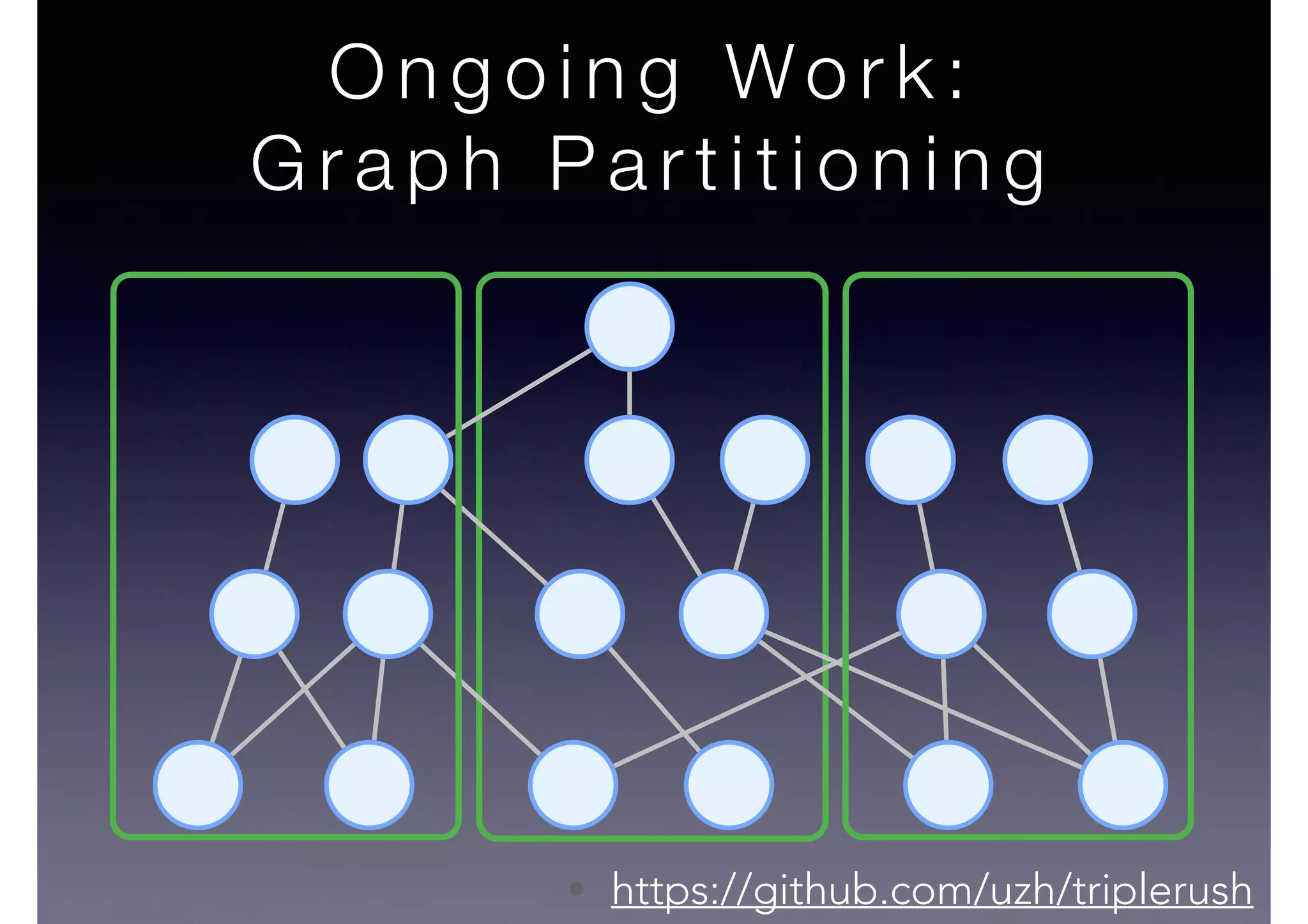
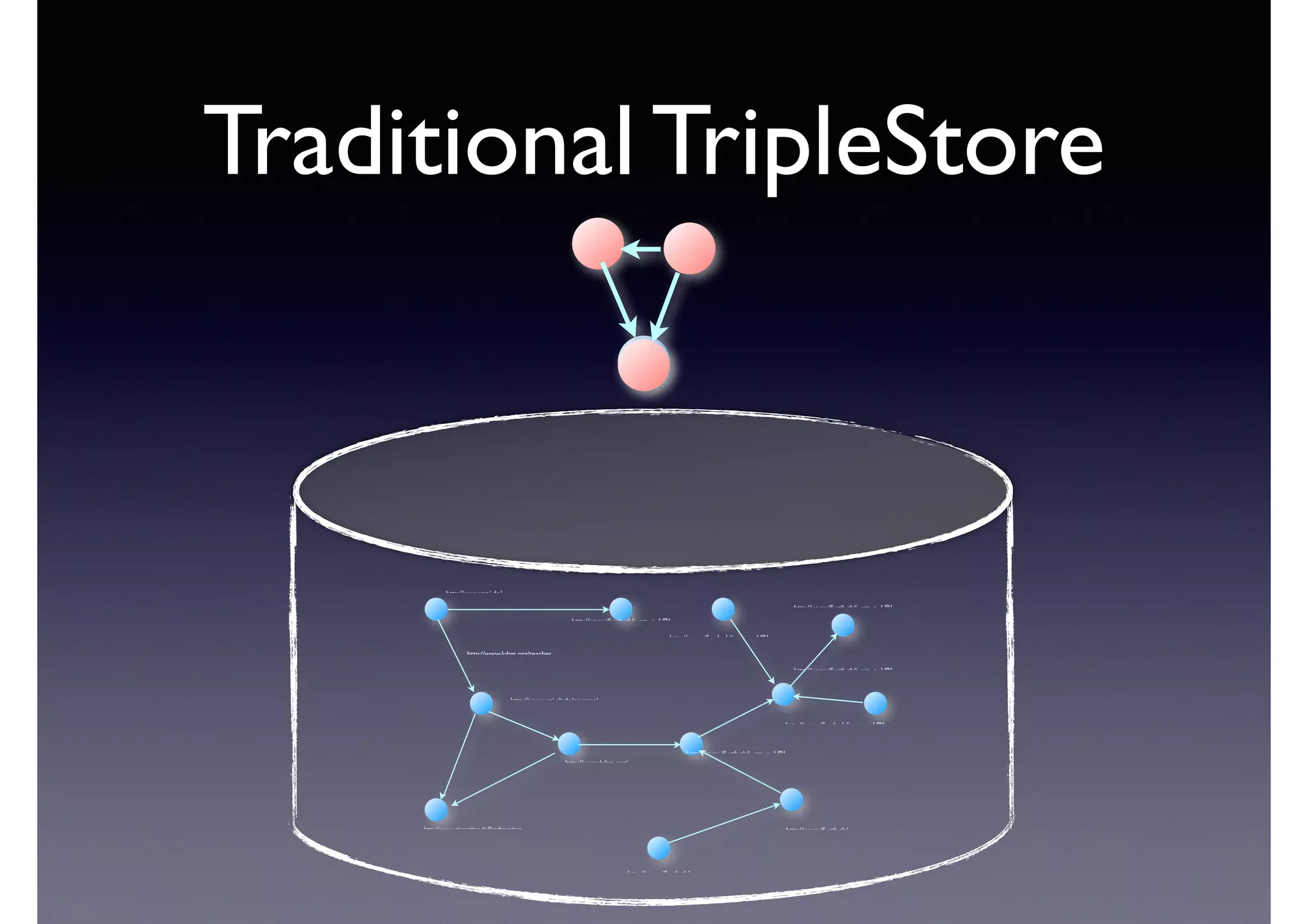
The document discusses processing linked data at high speeds using the Signal/Collect graph algorithm framework. It provides examples of how Signal/Collect can be used to perform tasks like RDFS subclass inference and PageRank calculation on semantic graphs. It also summarizes performance results showing that TripleRush, an implementation of Signal/Collect, outperforms other graph processing systems on benchmark datasets. Finally, it discusses ongoing work on graph partitioning with TripleRush.







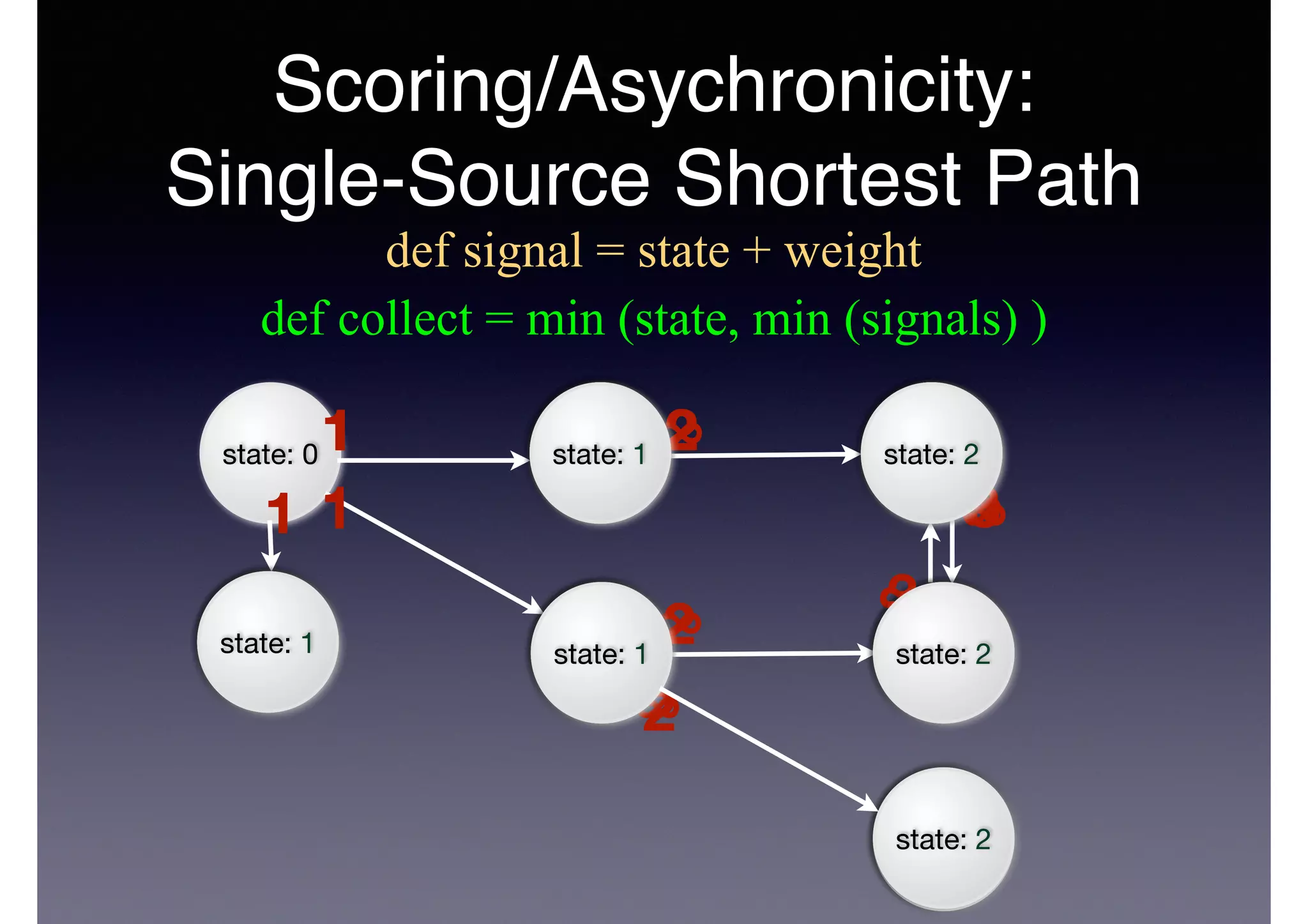
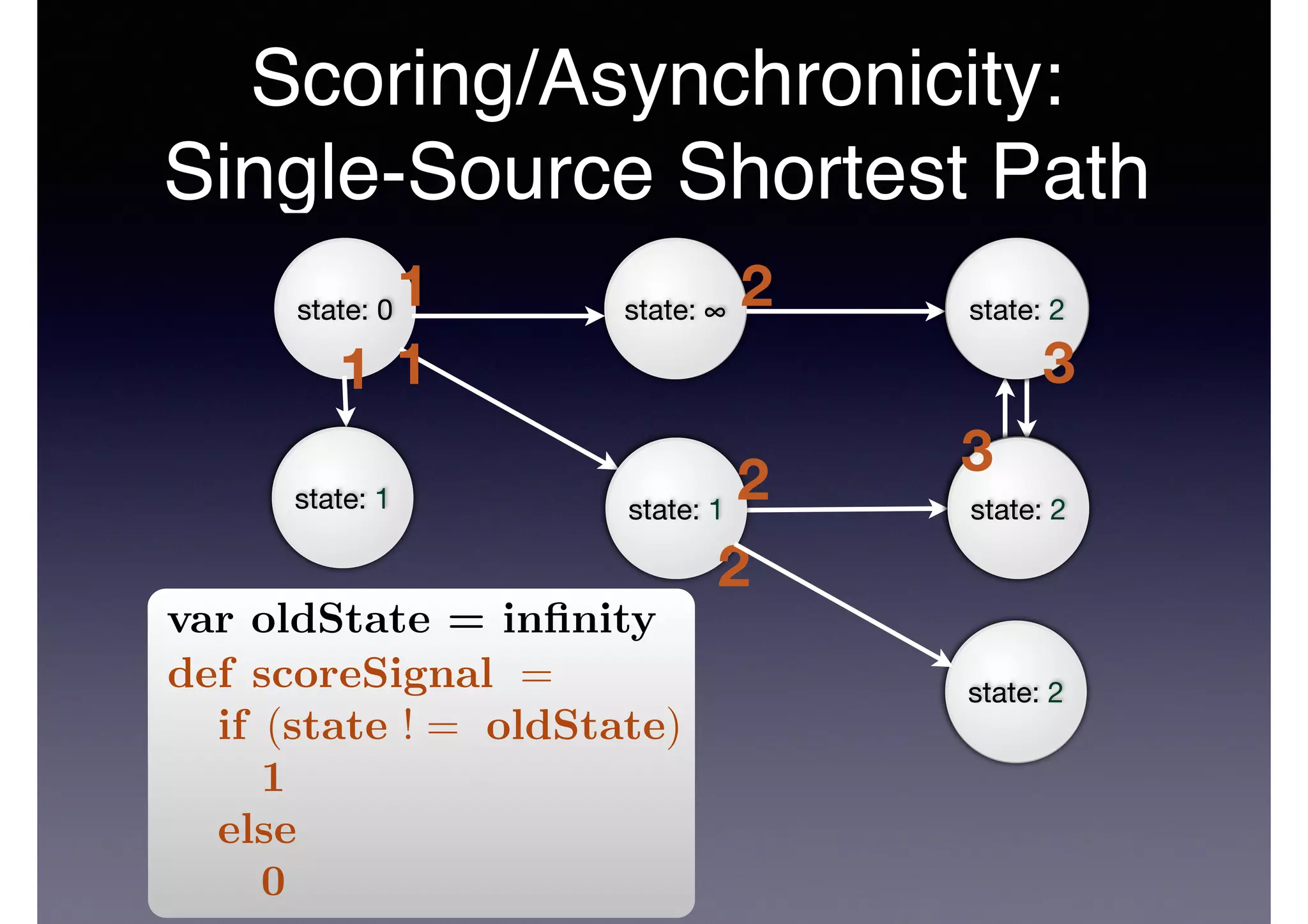
![PageRank in Code
class Document(id: Any) extends Vertex(id, 0.15) {
def collect = 0.15 + 0.85 * signals[Double].foldLeft(0.0)(_ + _)
}
Algorithm
class Citation(citer: Any, cited: Any) extends Edge(citer, cited) {
def signal = source.state.asInstanceOf[Double] * weight / source.sumOfOutWeights
}
ExecutionInitialization
object Algorithm {
def executeCitationRank(db: SparqlAccessor) {
val computeGraph = new AsynchronousComputeGraph()
val citations = new SparqlTuples(db, "select ?source ?target where {"
+ "?source <http://lsdis.cs.uga.edu/projects/semdis/opus#cites> ?target}")
citations foreach {
case (citer, cited) =>
computeGraph.addVertex[Document](citer)
computeGraph.addVertex[Document](cited)
computeGraph.addEdge[Citation](citer, cited)
}
computeGraph.execute()
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cb2cldtks965tkq2mi6s-signature-6cd190755288fa05d0dfe2819a707a5601a50bbbd01f8bebf764d20d0a16204c-poli-140907024852-phpapp01/75/Thu-bernstein-key_warp_speed-17-2048.jpg)

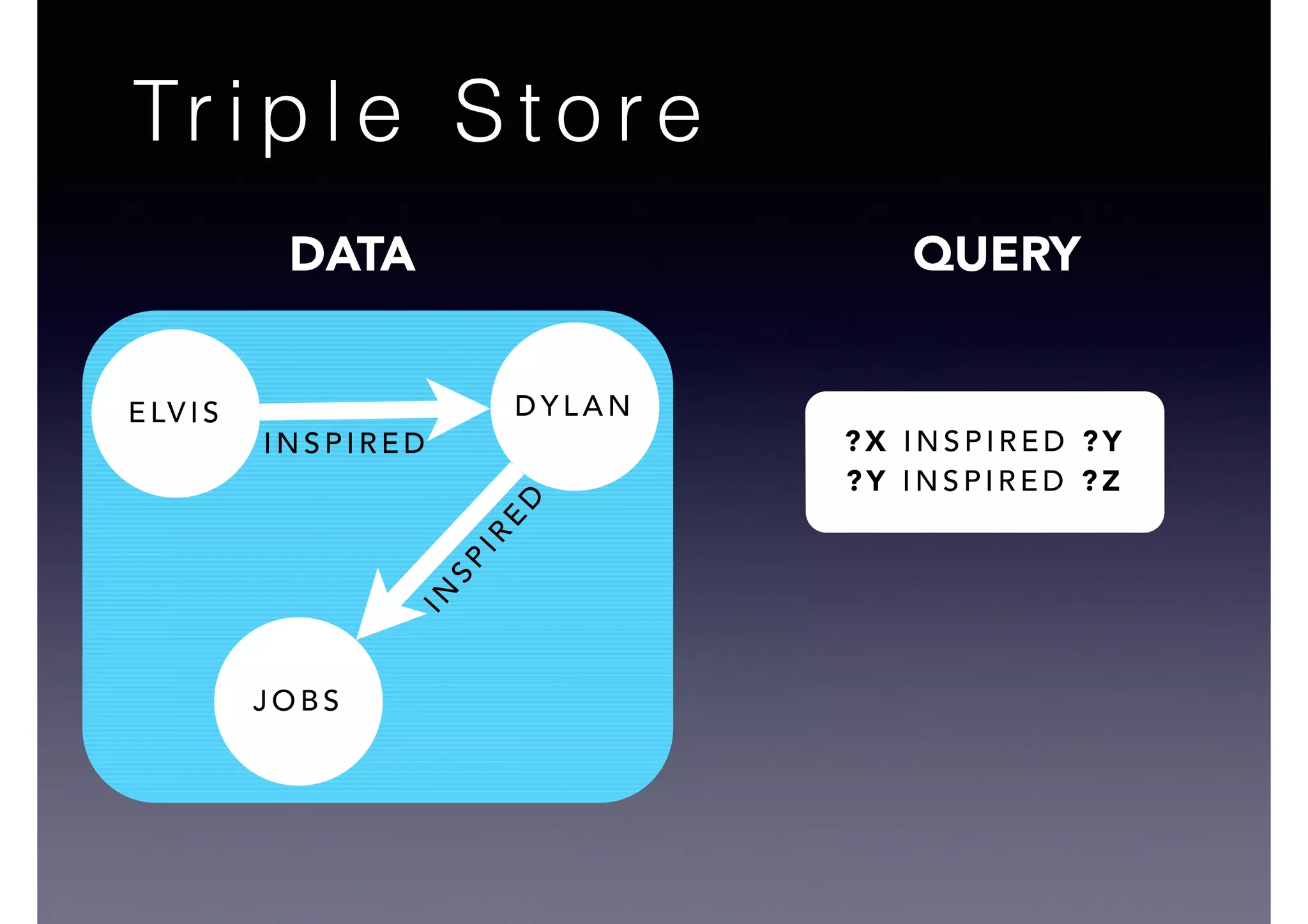
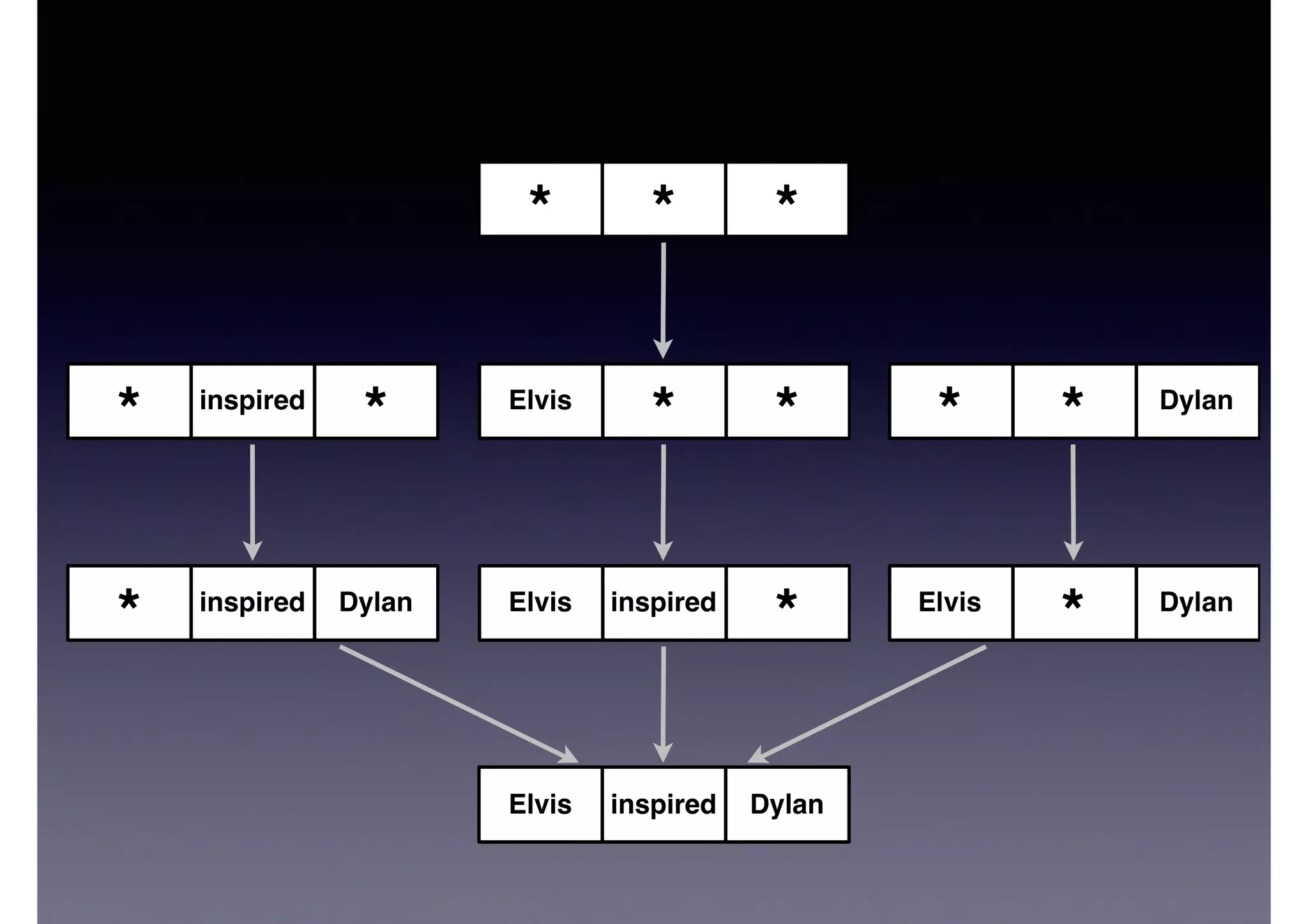
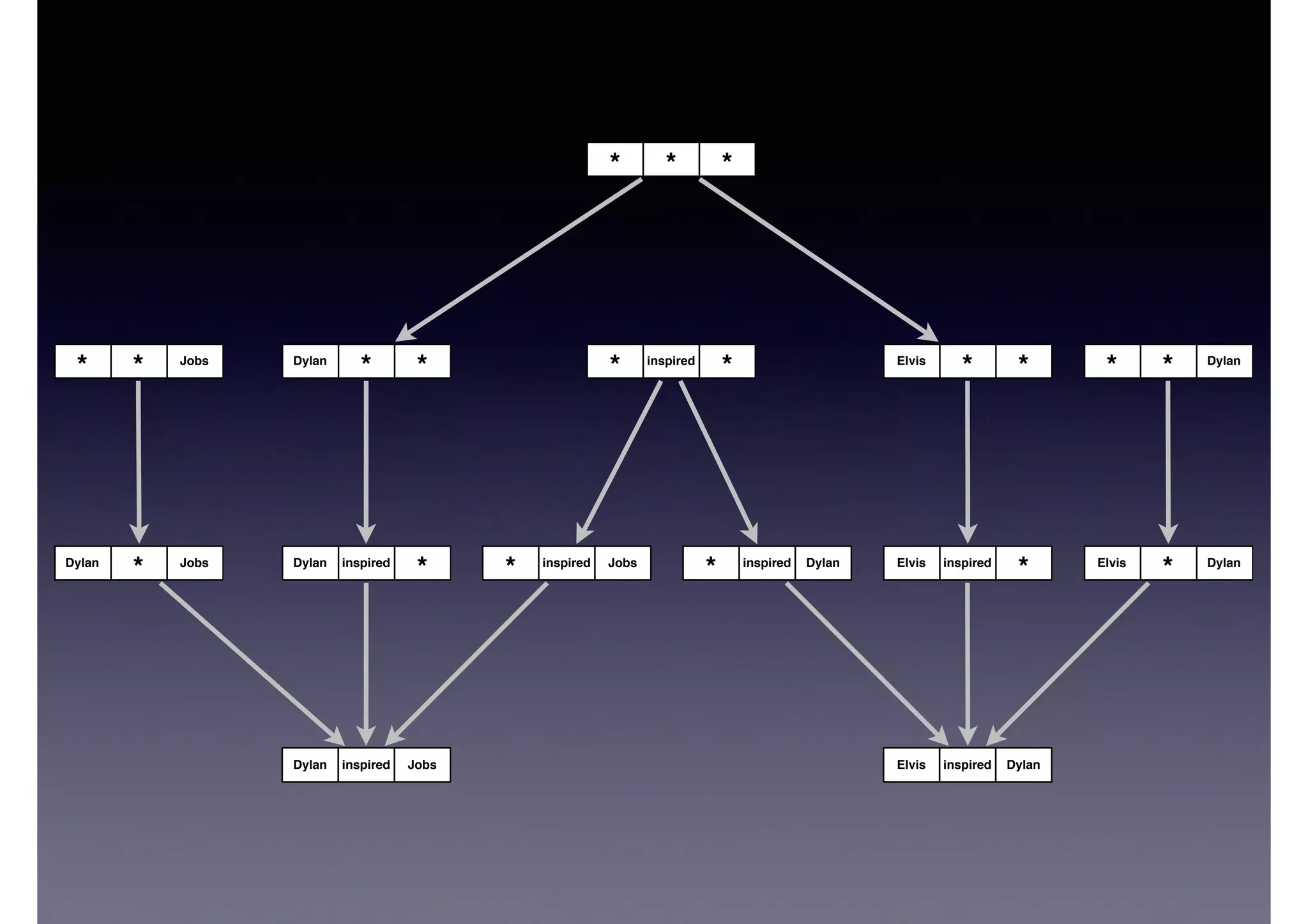
![DylanElvis inspired
Dylan
* inspired
** inspired
*Dylan inspired Jobs
* inspired
JobsDylan inspired
Query Vertex
?X inspired ?Y!
?Y inspired ?Z
?X inspired ?Y!
?Y inspired ?Z
Elvis inspired Dylan!
Dylan inspired ?Z
Dylan inspired Jobs!
Jobs inspired ?Z
No vertex with ID!
[ Jobs inspired * ]
Query Vertex
{ ?X = Elvis, ?Y = Dylan, ?Z = Jobs }
✗
Elvis inspired Dylan!
Dylan inspired Jobs
✓
?X inspired ?Y!
?Y inspired ?Z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cb2cldtks965tkq2mi6s-signature-6cd190755288fa05d0dfe2819a707a5601a50bbbd01f8bebf764d20d0a16204c-poli-140907024852-phpapp01/75/Thu-bernstein-key_warp_speed-22-2048.jpg)
![DylanElvis inspired
Dylan
* inspired
** inspired
*Dylan inspired Jobs
* inspired
JobsDylan inspired
Query Vertex
?X inspired ?Y!
?Y inspired ?Z
?X inspired ?Y!
?Y inspired ?Z
Elvis inspired Dylan!
Dylan inspired ?Z
Dylan inspired Jobs!
Jobs inspired ?Z
No vertex with ID!
[ Jobs inspired * ]
Query Vertex
{ ?X = Elvis, ?Y = Dylan, ?Z = Jobs }
✗
Elvis inspired Dylan!
Dylan inspired Jobs
✓
?X inspired ?Y!
?Y inspired ?Z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cb2cldtks965tkq2mi6s-signature-6cd190755288fa05d0dfe2819a707a5601a50bbbd01f8bebf764d20d0a16204c-poli-140907024852-phpapp01/75/Thu-bernstein-key_warp_speed-23-2048.jpg)

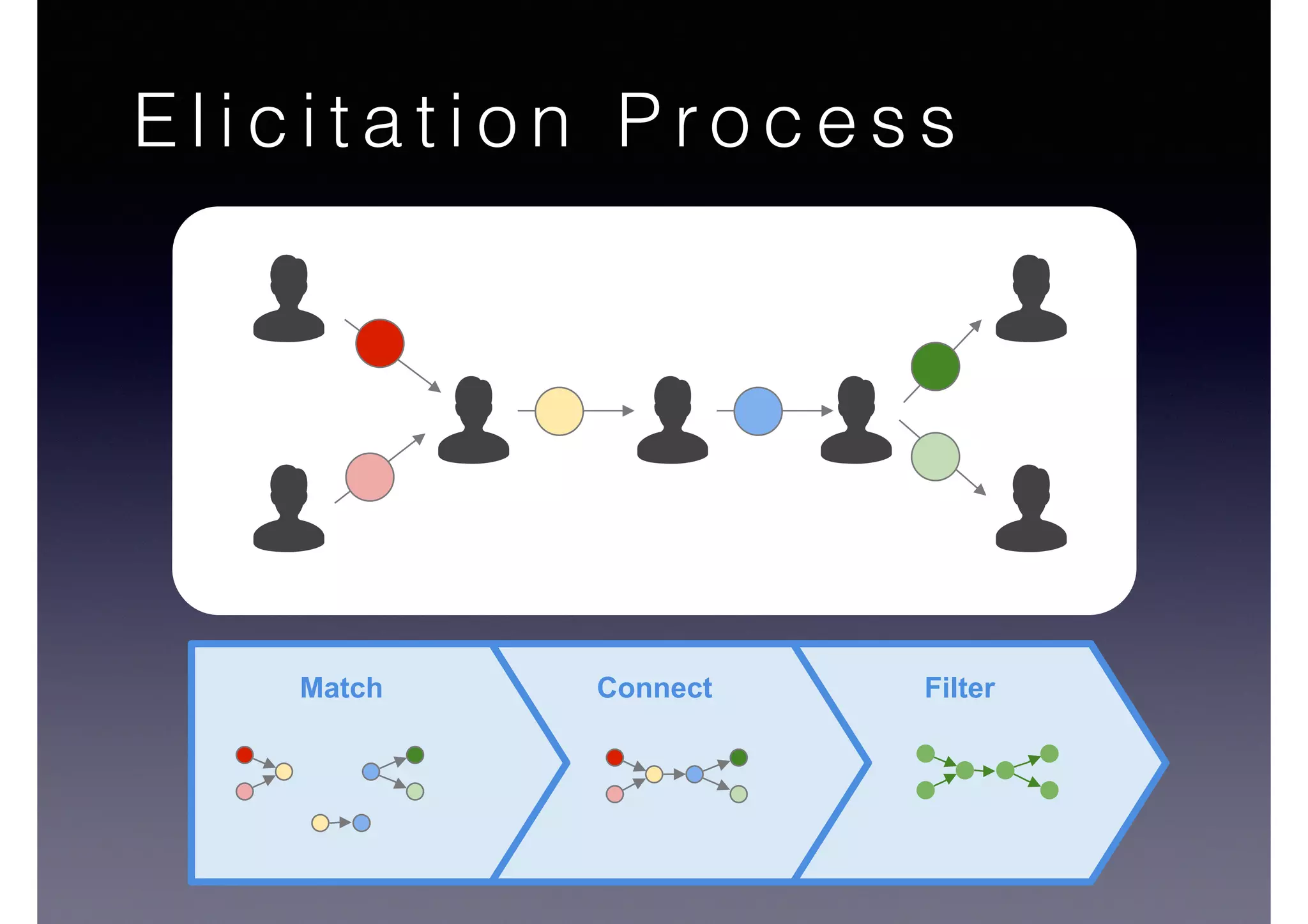
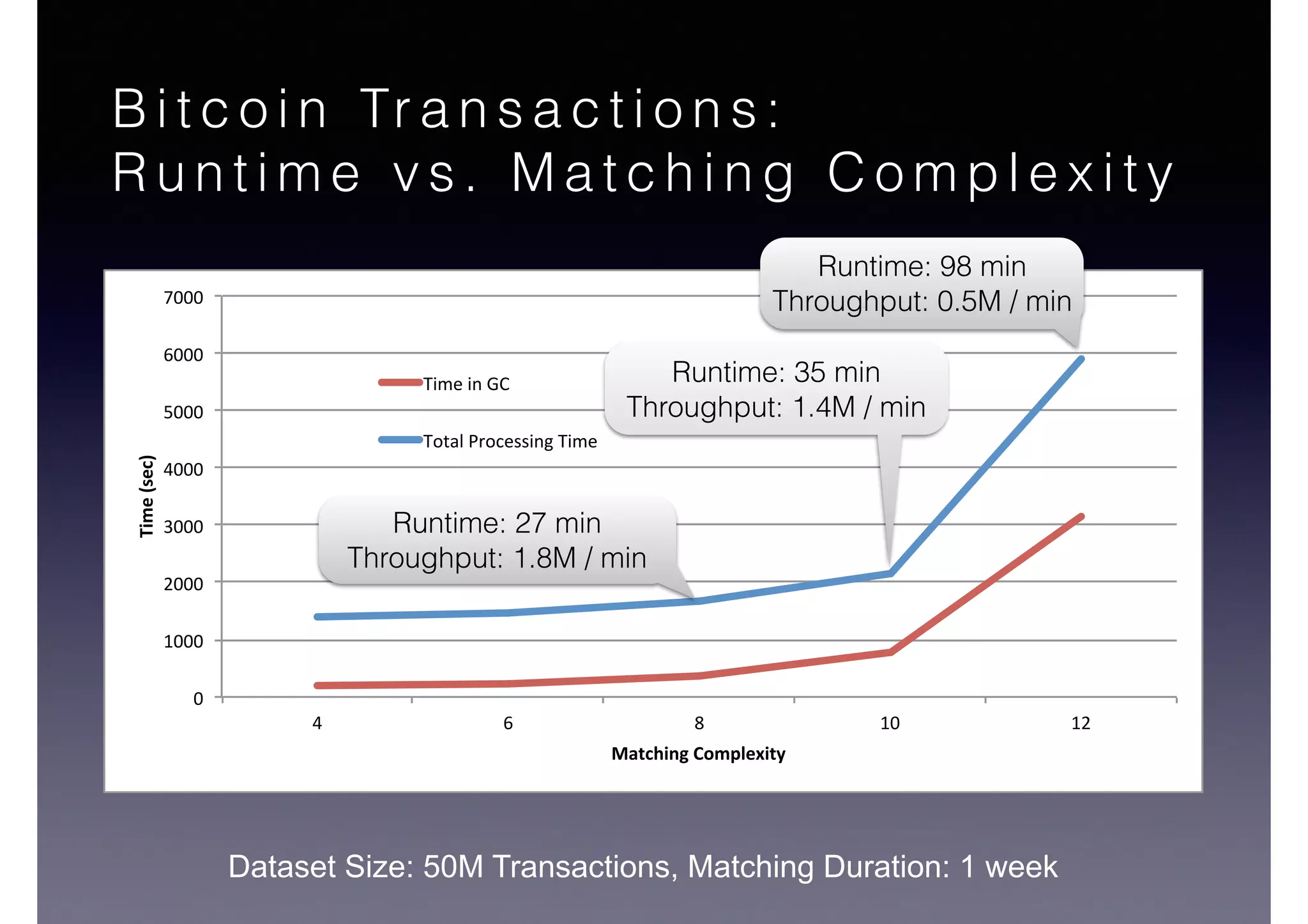

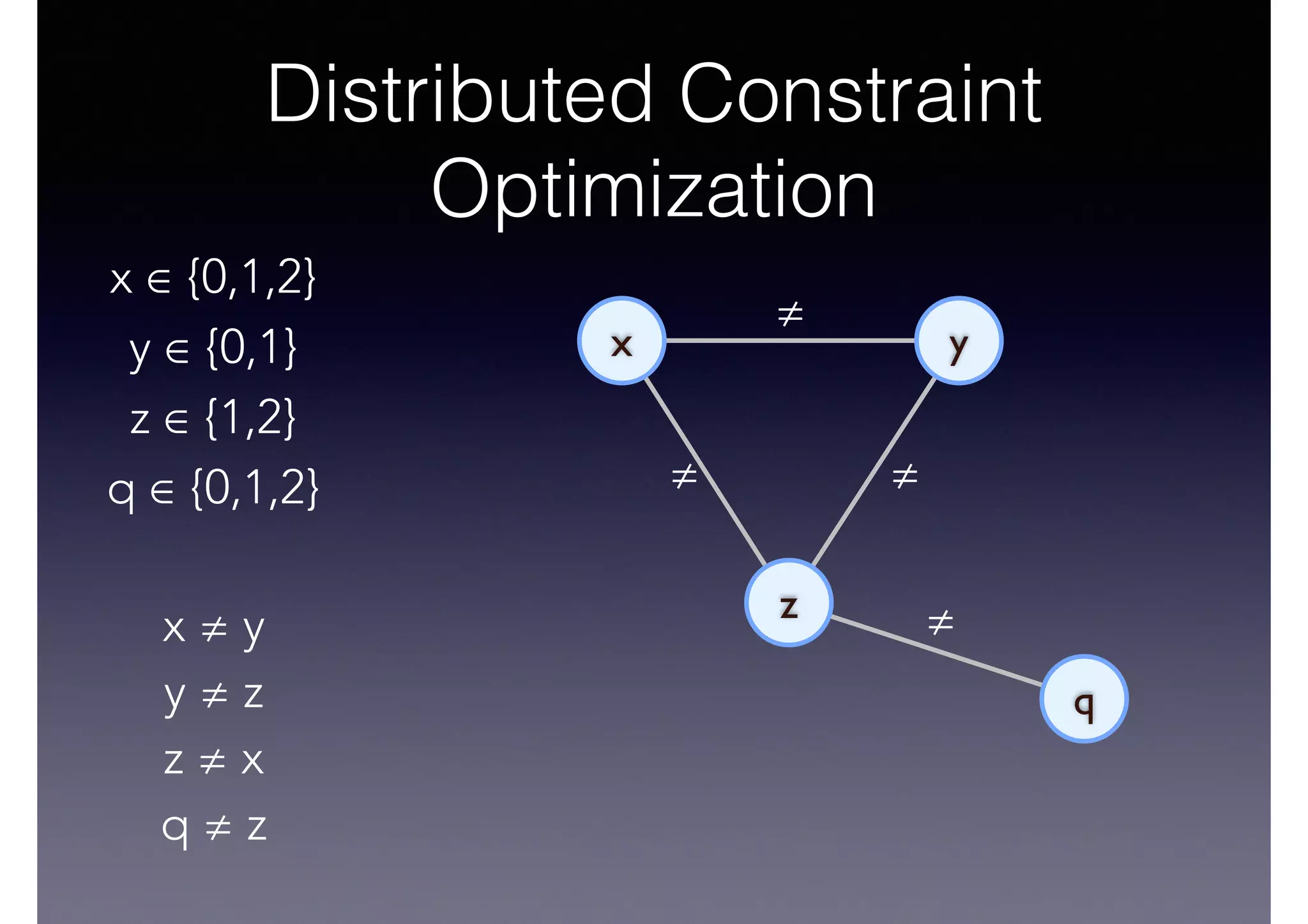







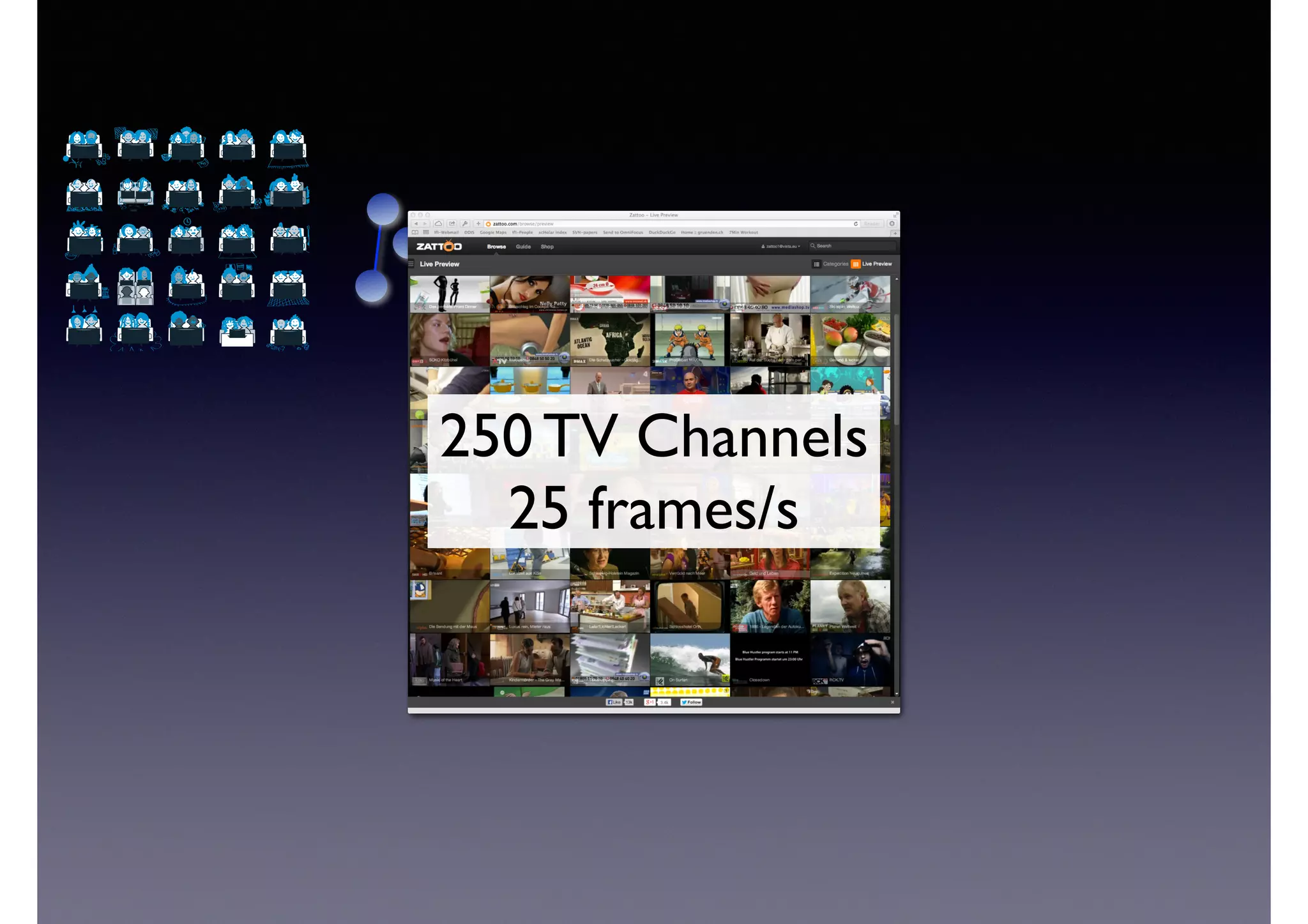
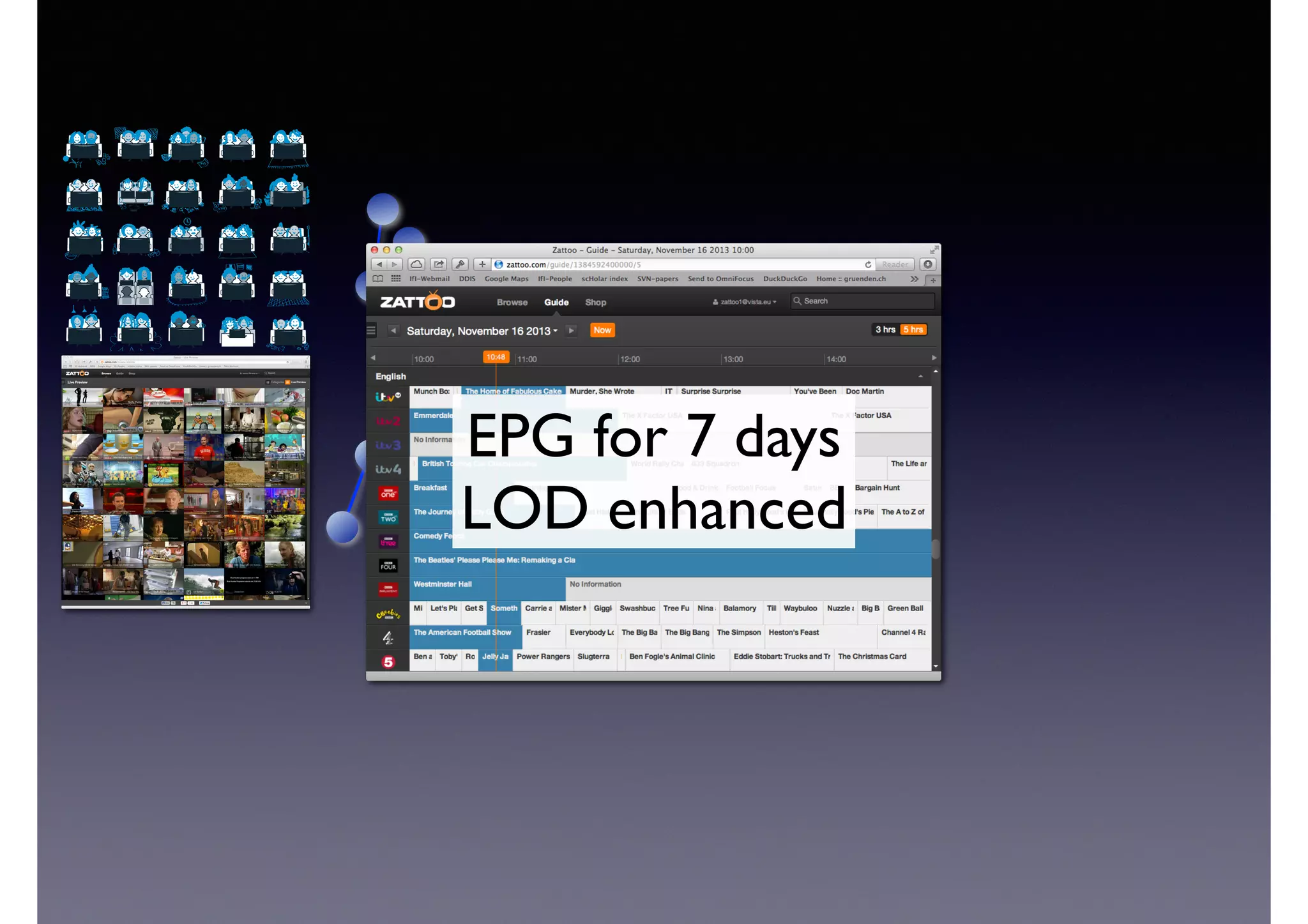
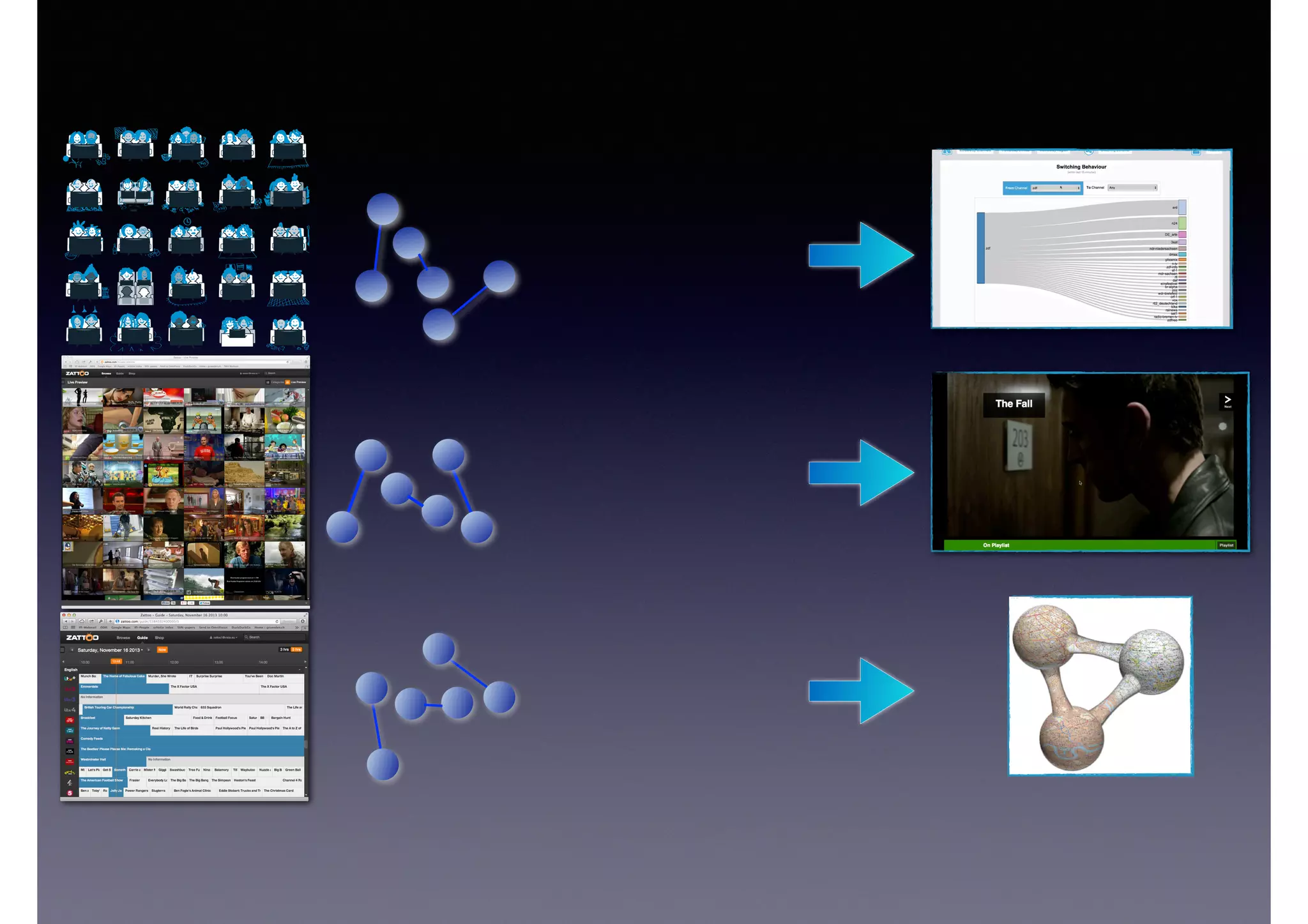
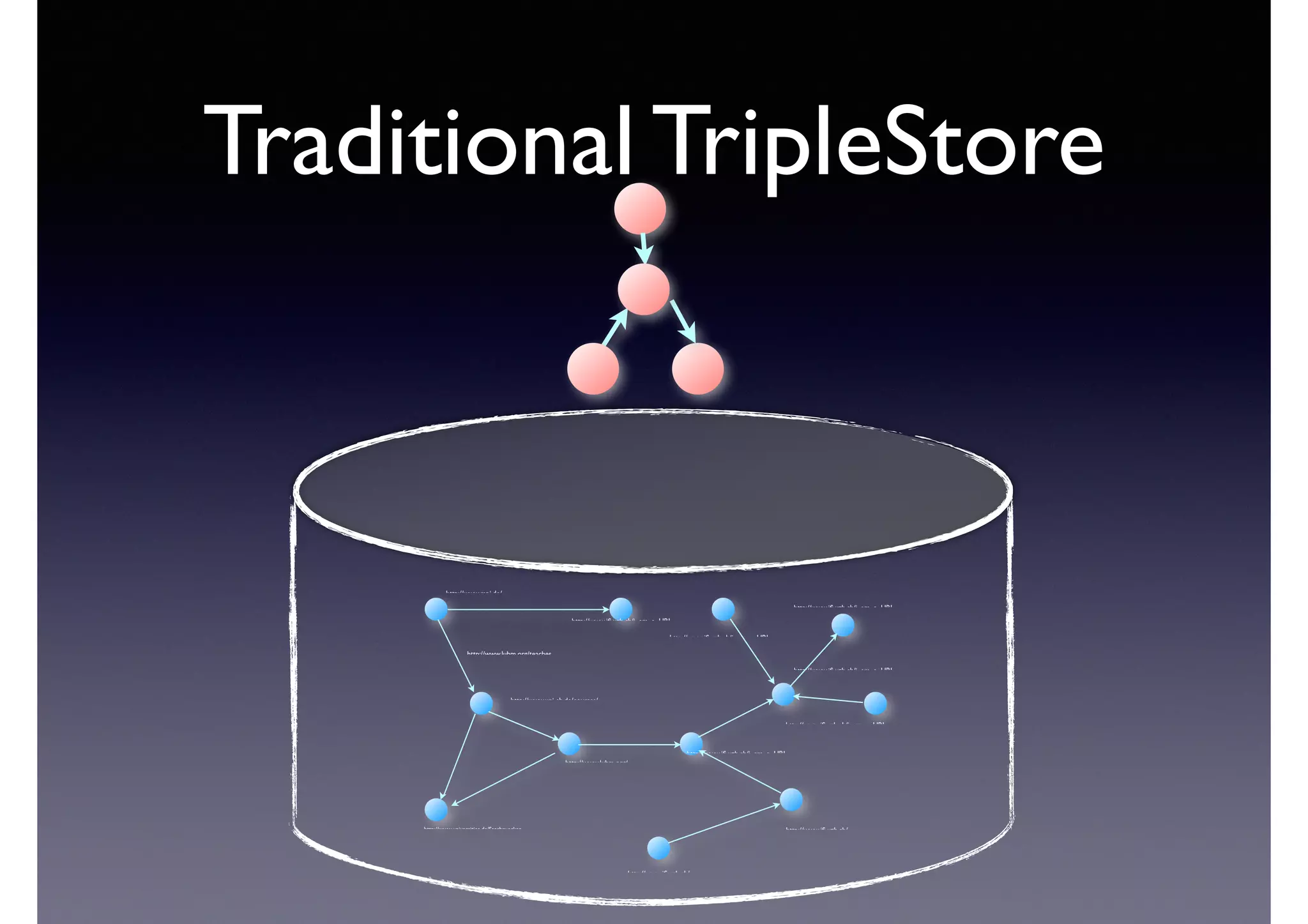
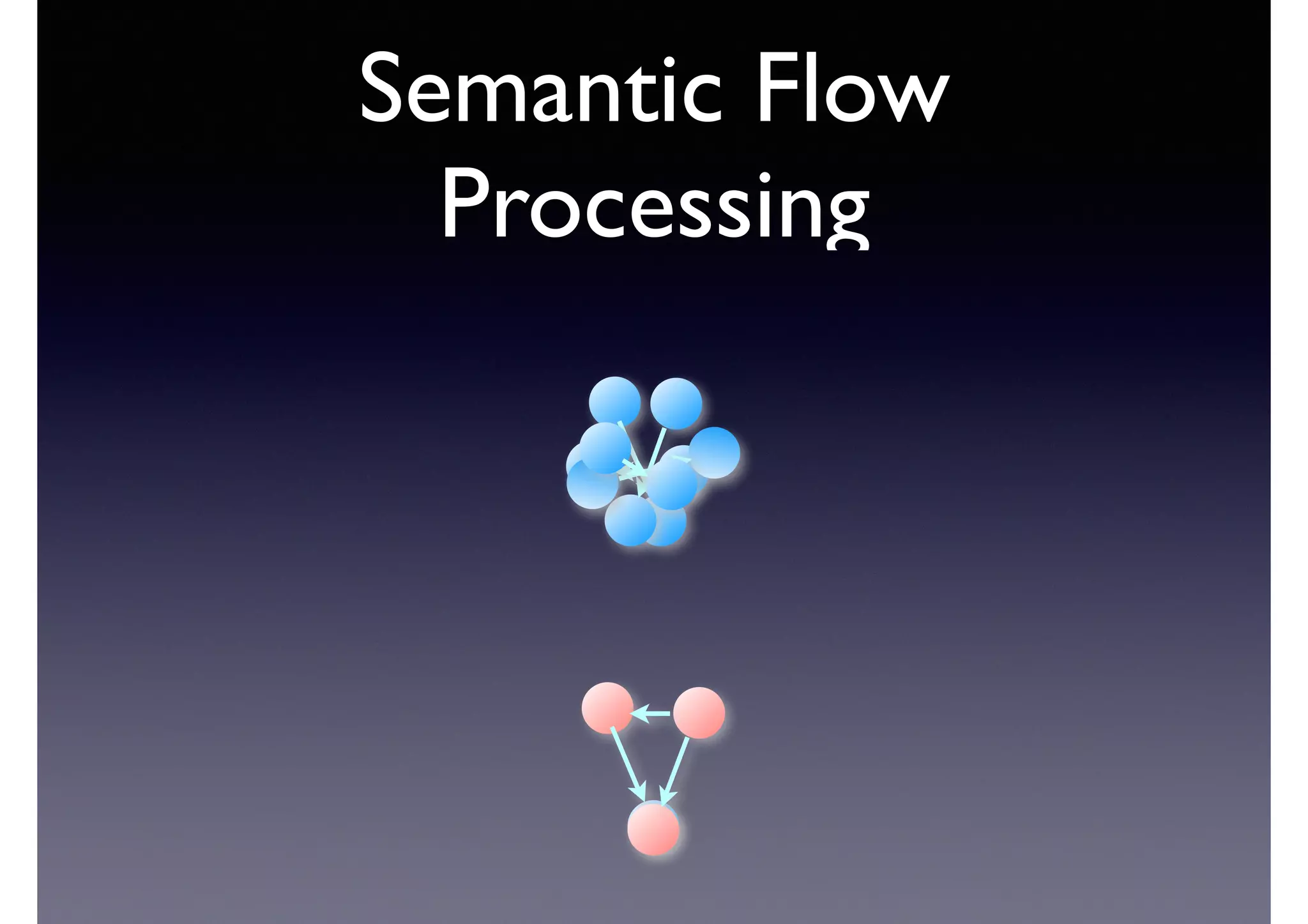
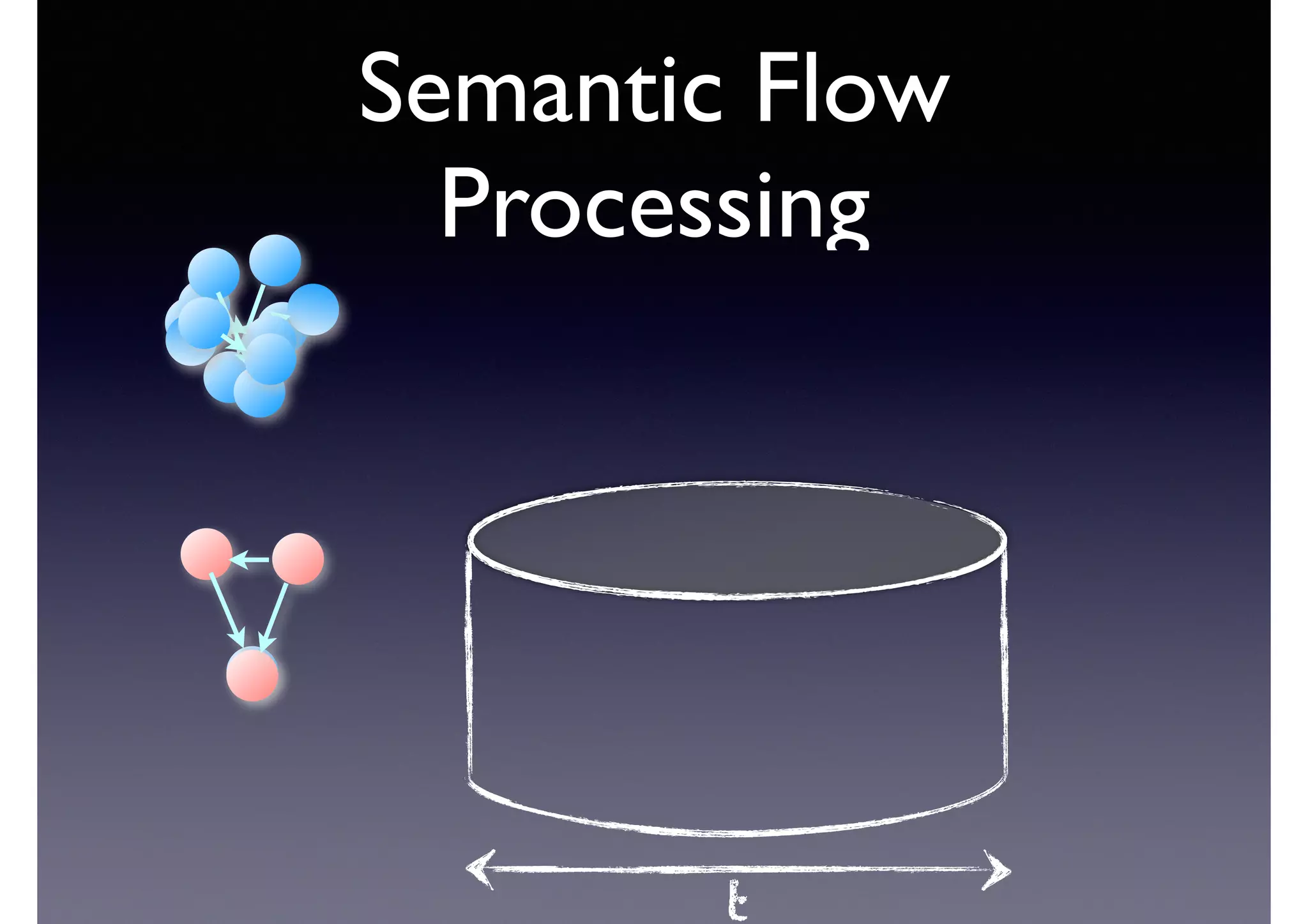
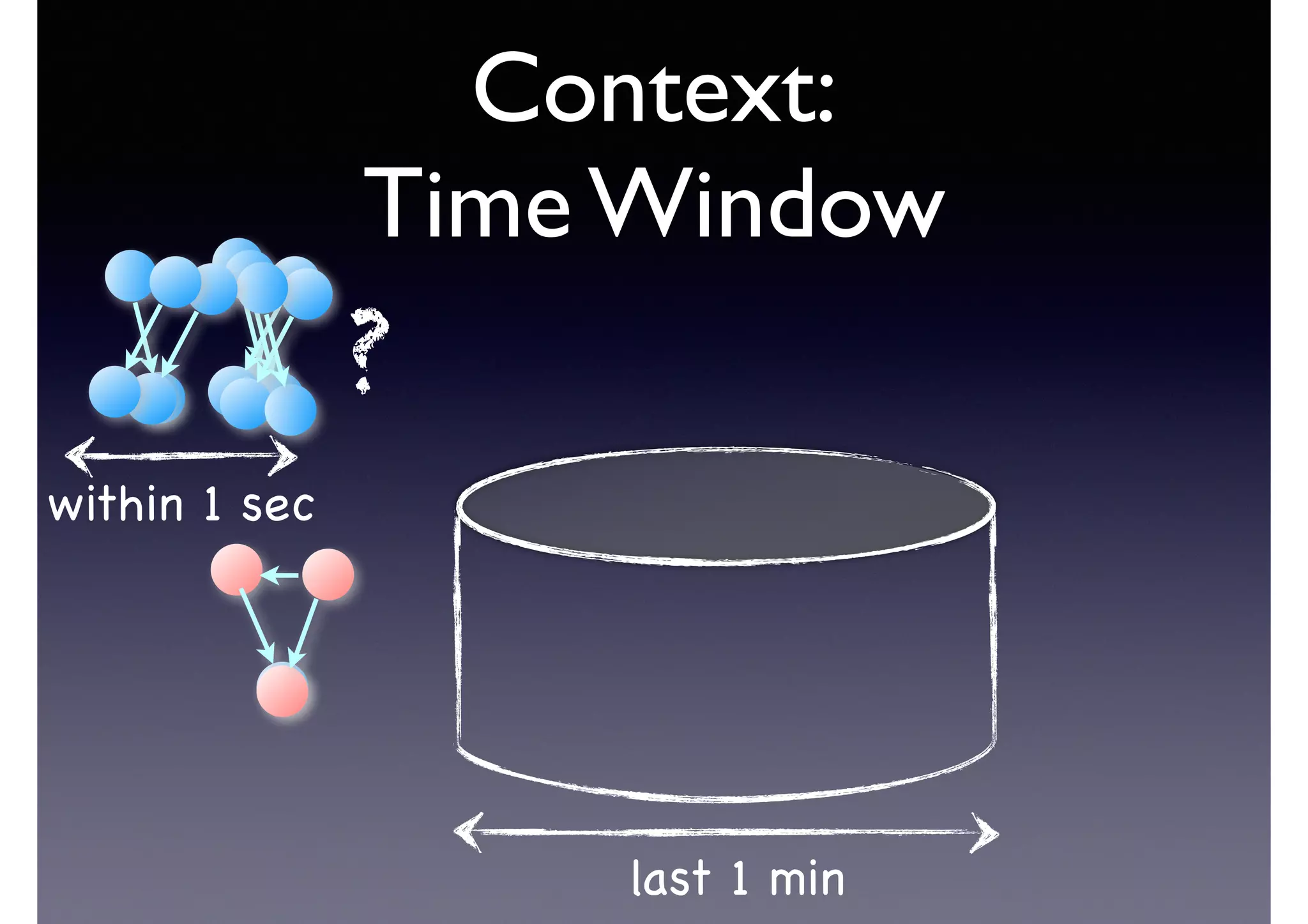
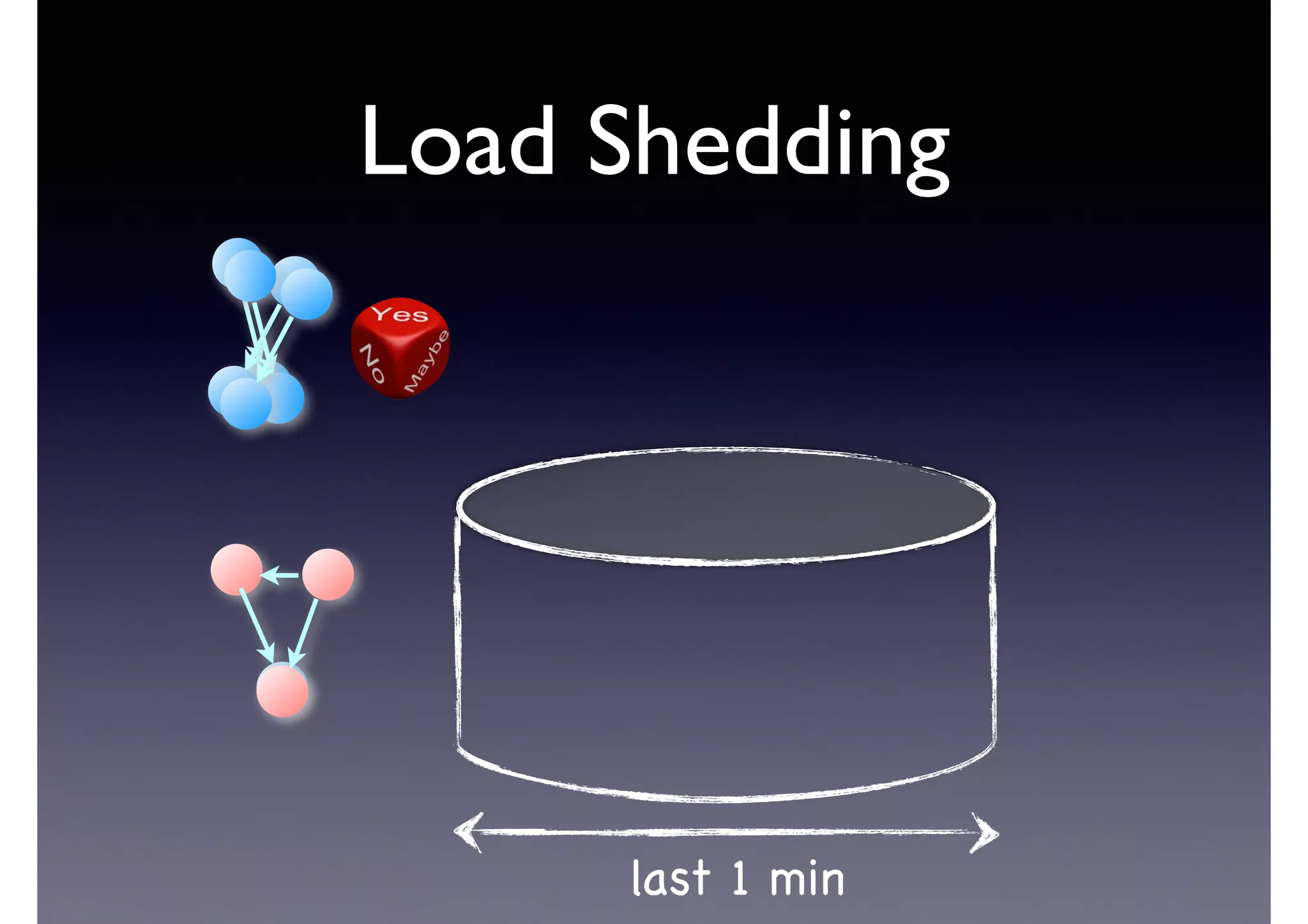
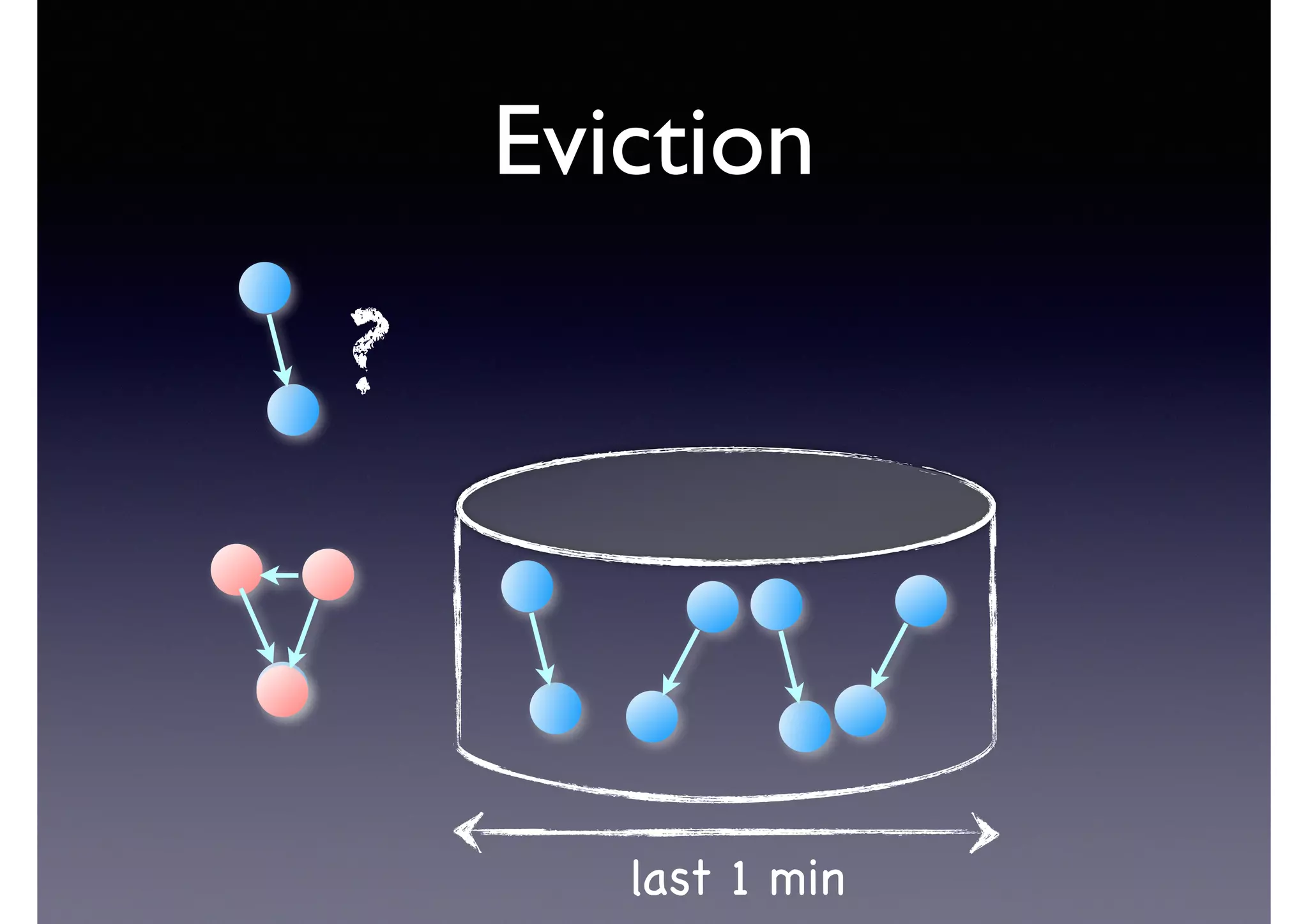
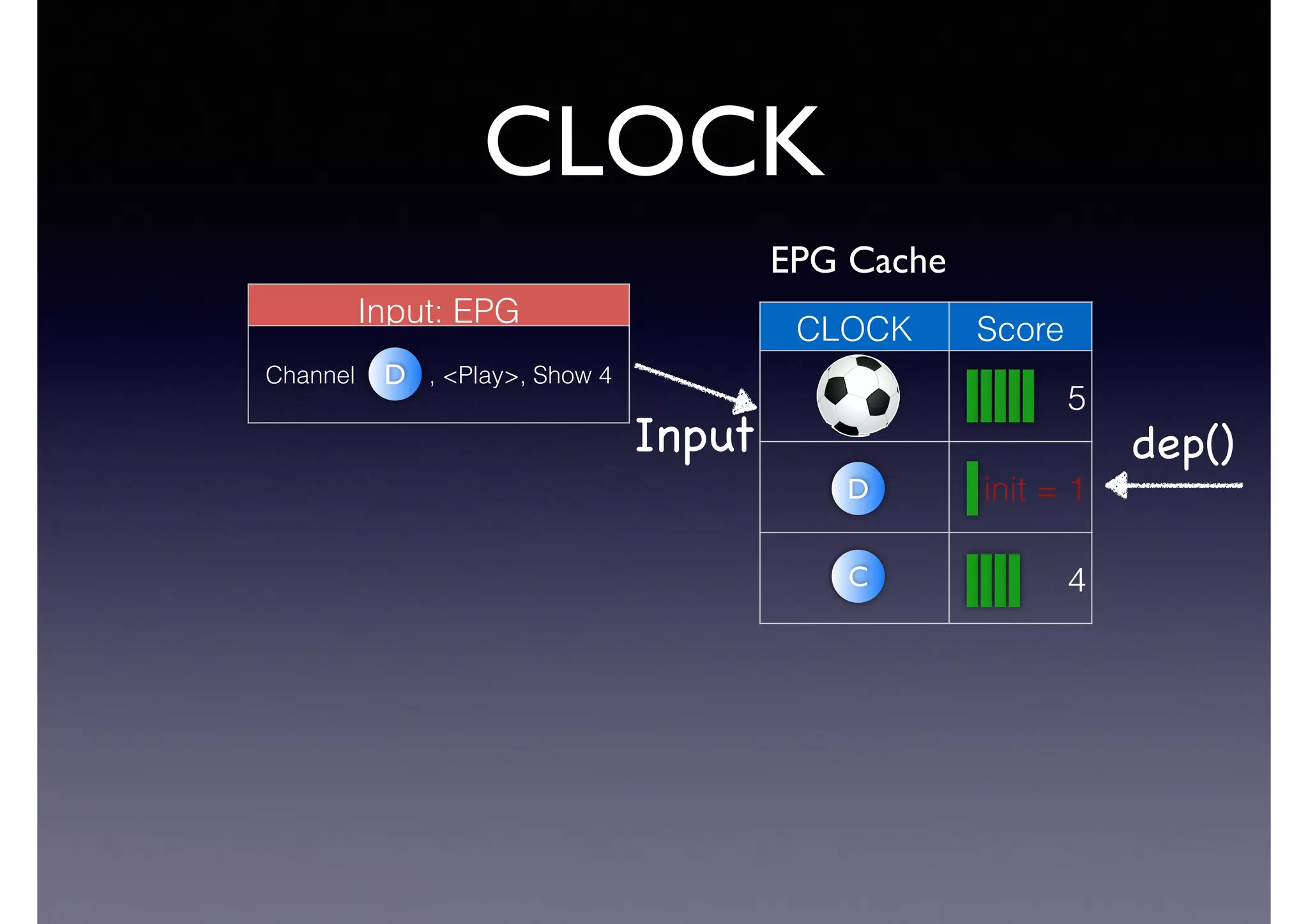
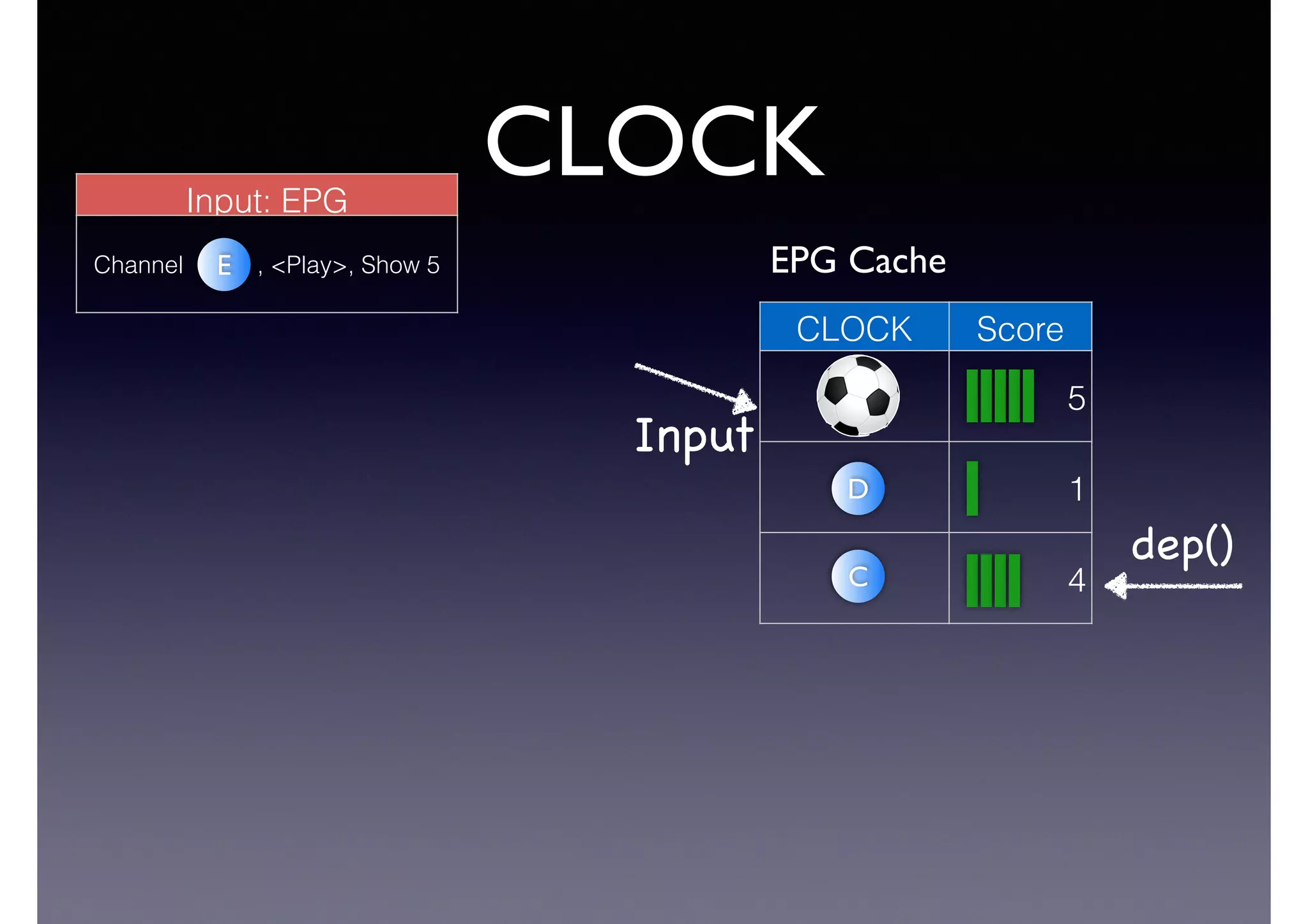
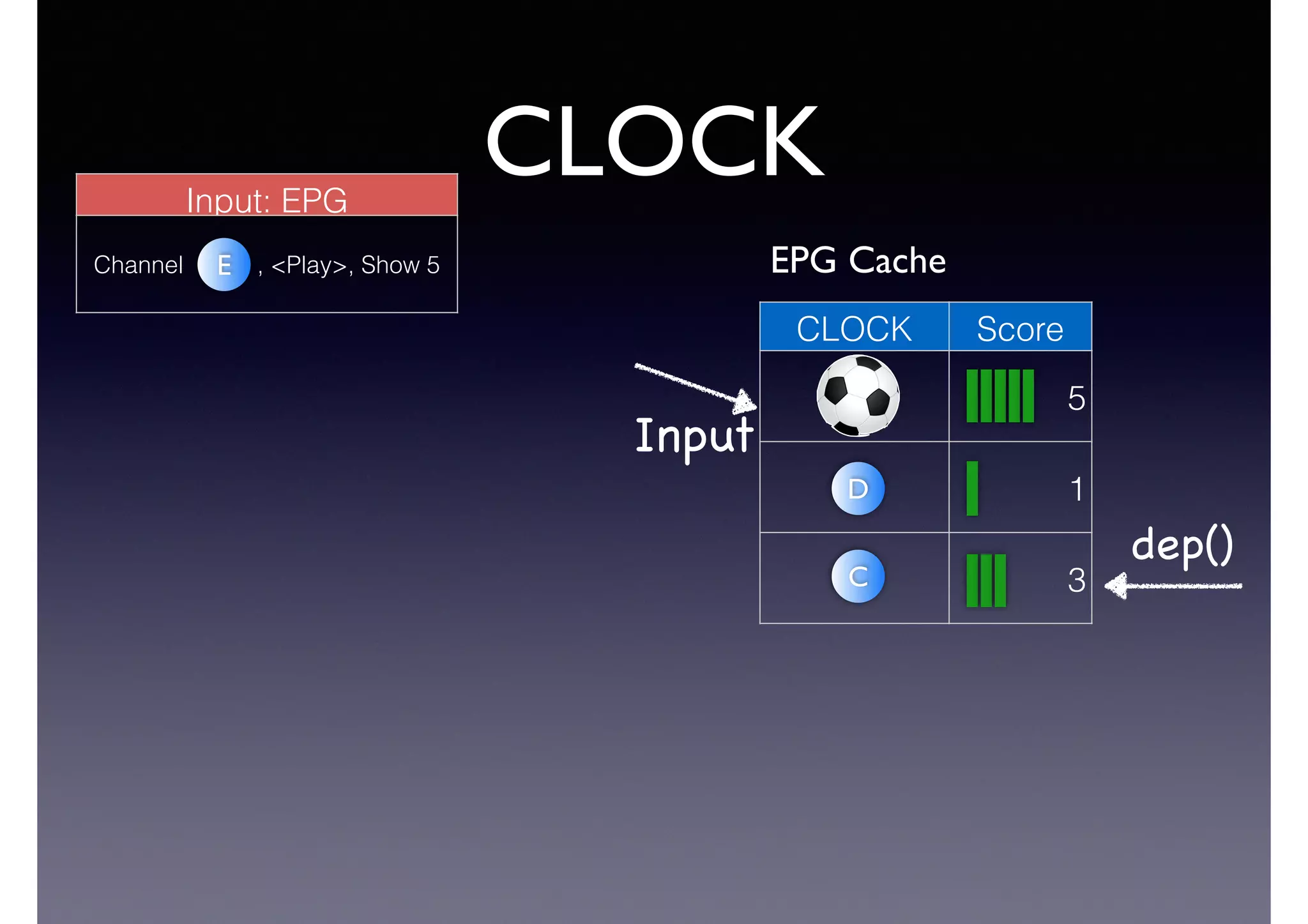
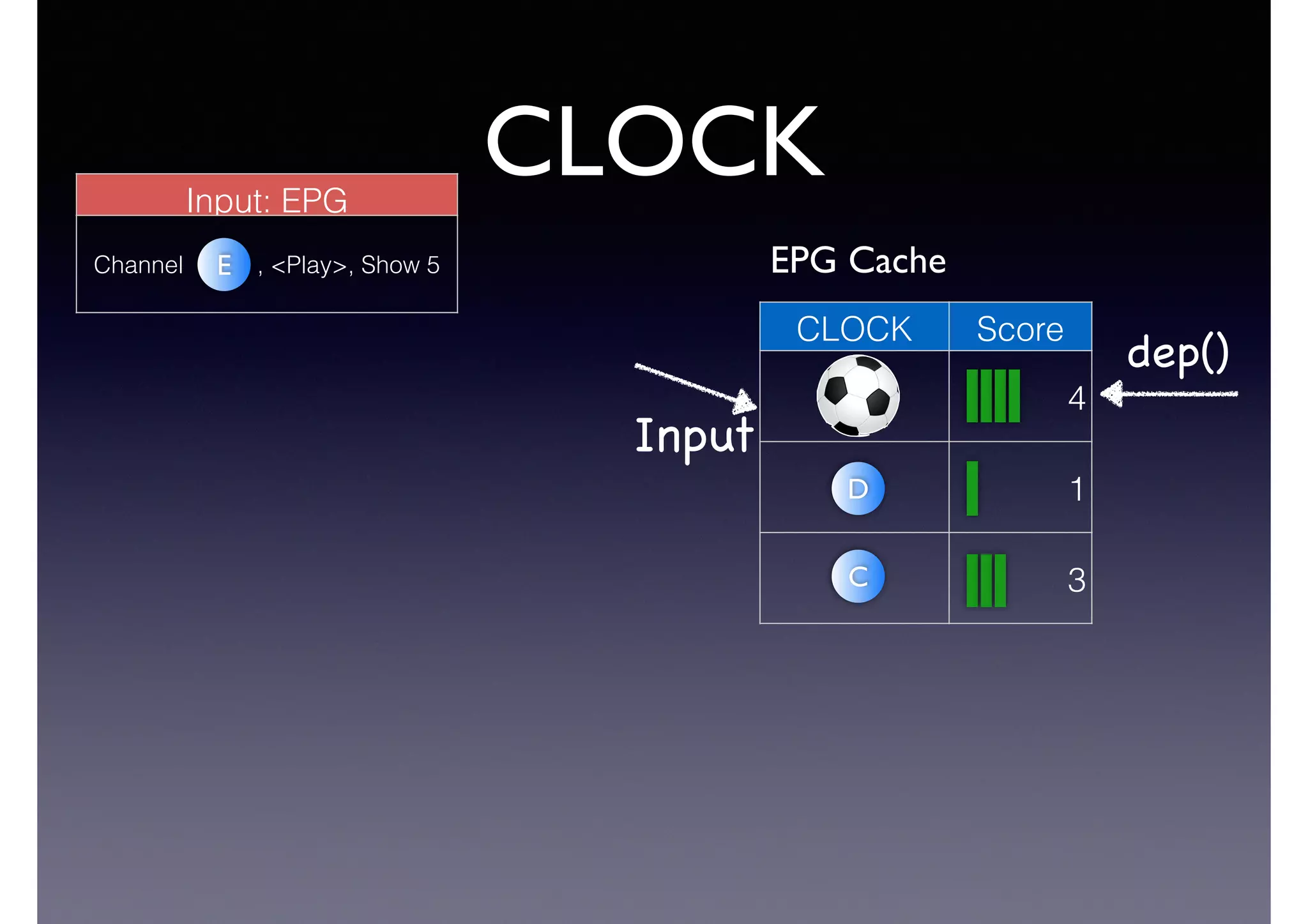
![Semantic Flow
Processing is:
• Time-stamped tripes t = <s,p,o> [time]
• Semantic flow F = [t1, t2, ... tn]
• Perform query matching on cached subset of F
• Subject to Stress—incoming data-rate
overwhelms the system’s processing
capability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cb2cldtks965tkq2mi6s-signature-6cd190755288fa05d0dfe2819a707a5601a50bbbd01f8bebf764d20d0a16204c-poli-140907024852-phpapp01/75/Thu-bernstein-key_warp_speed-48-2048.jpg)