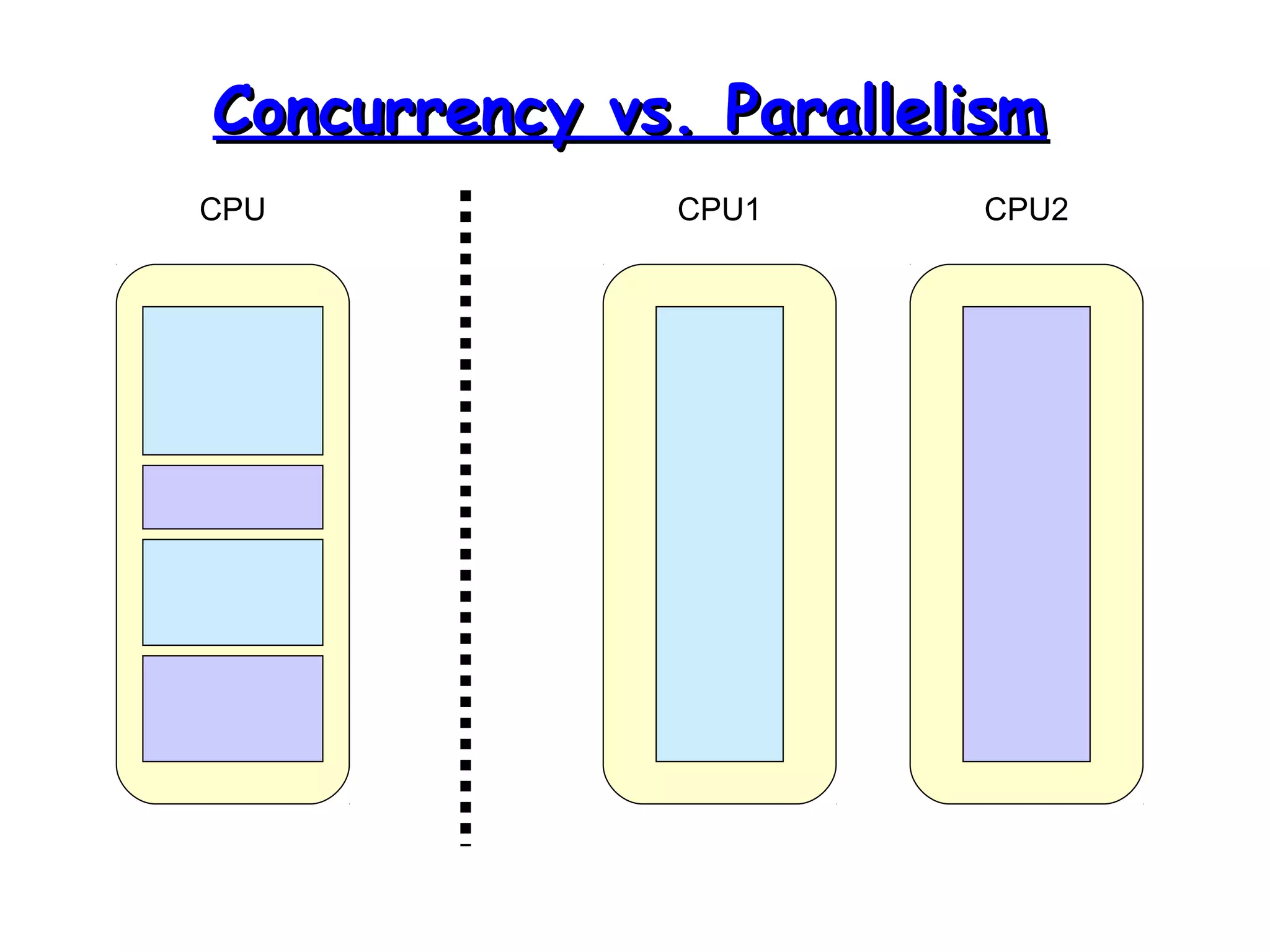
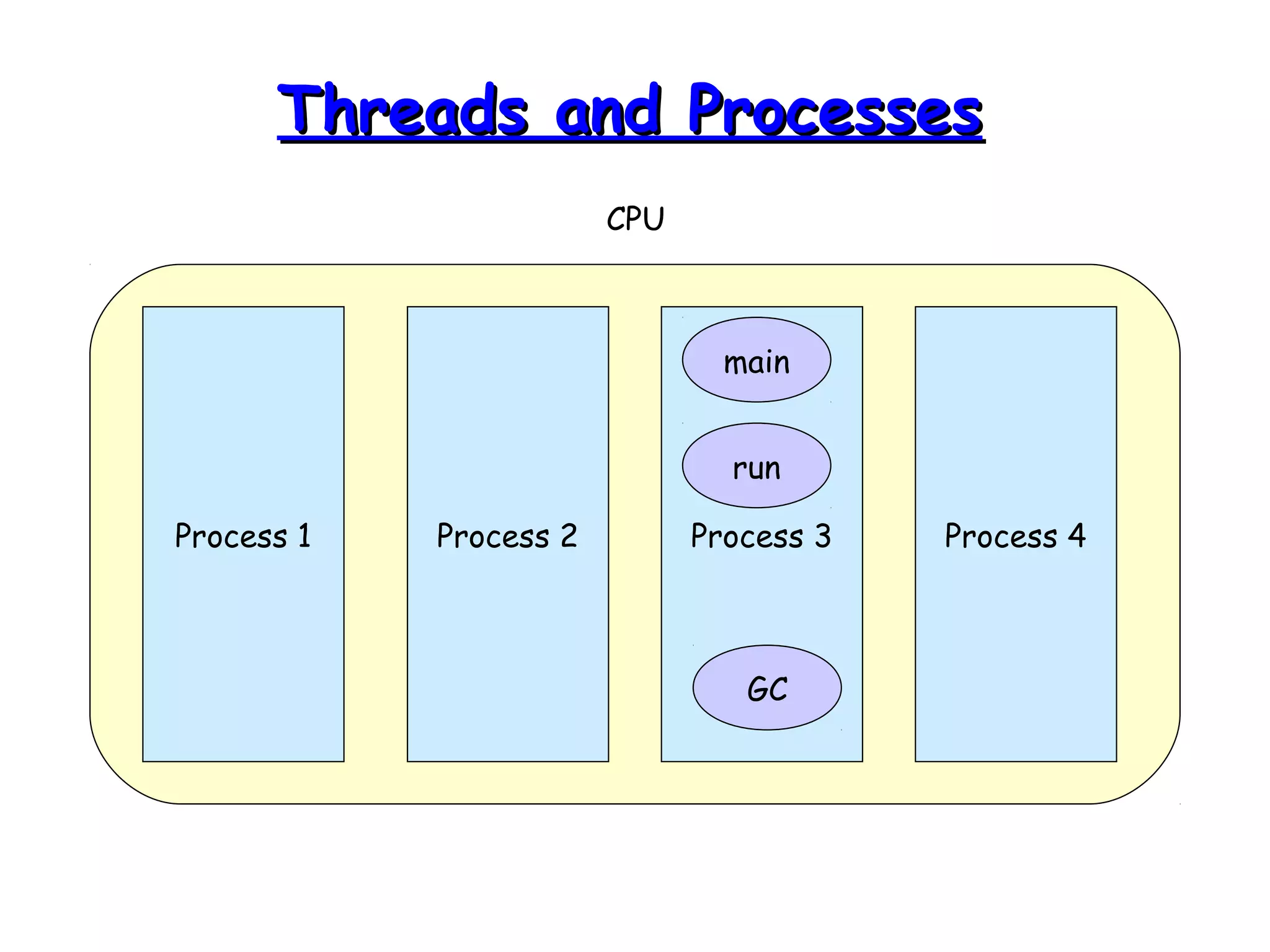
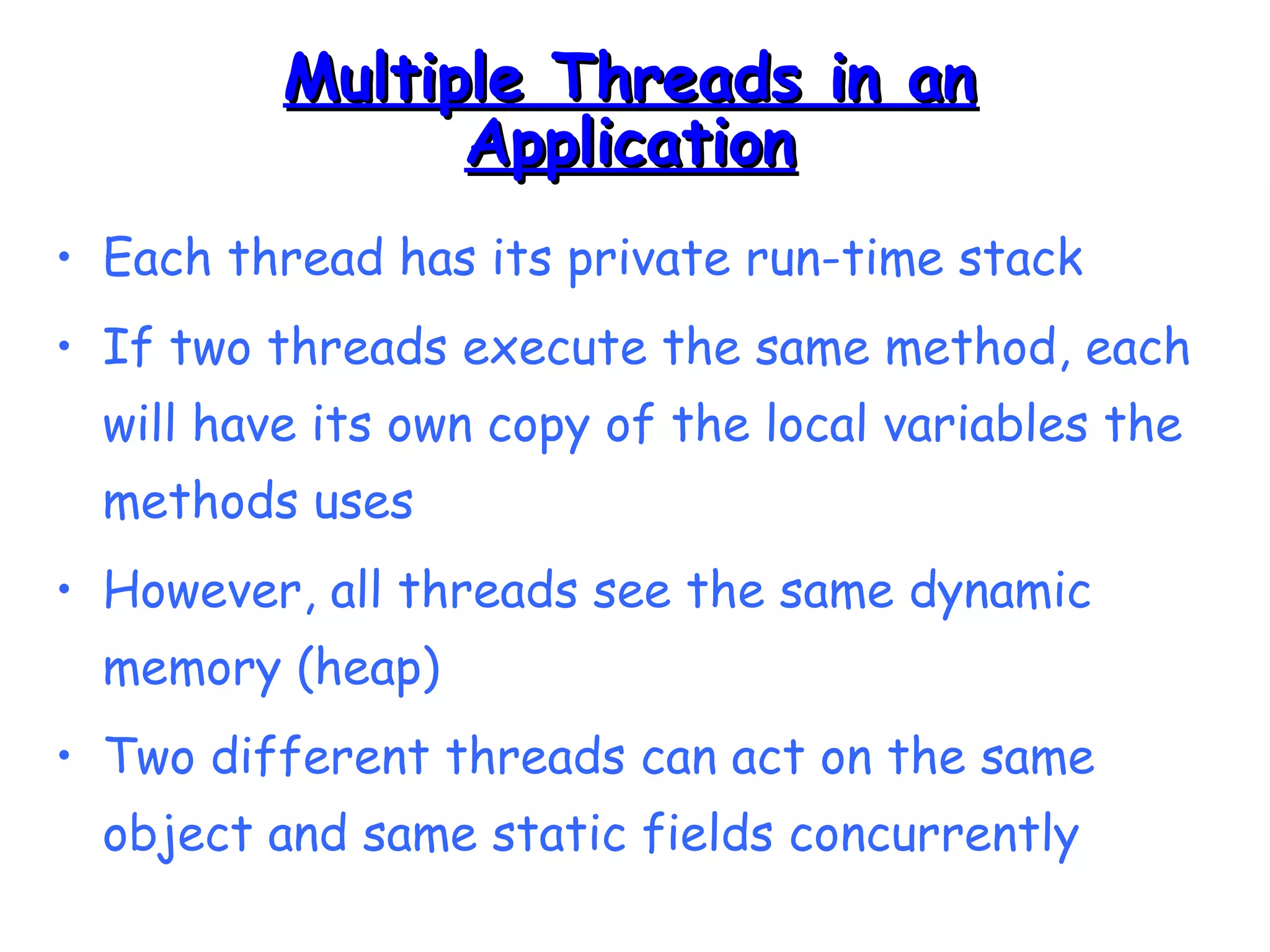
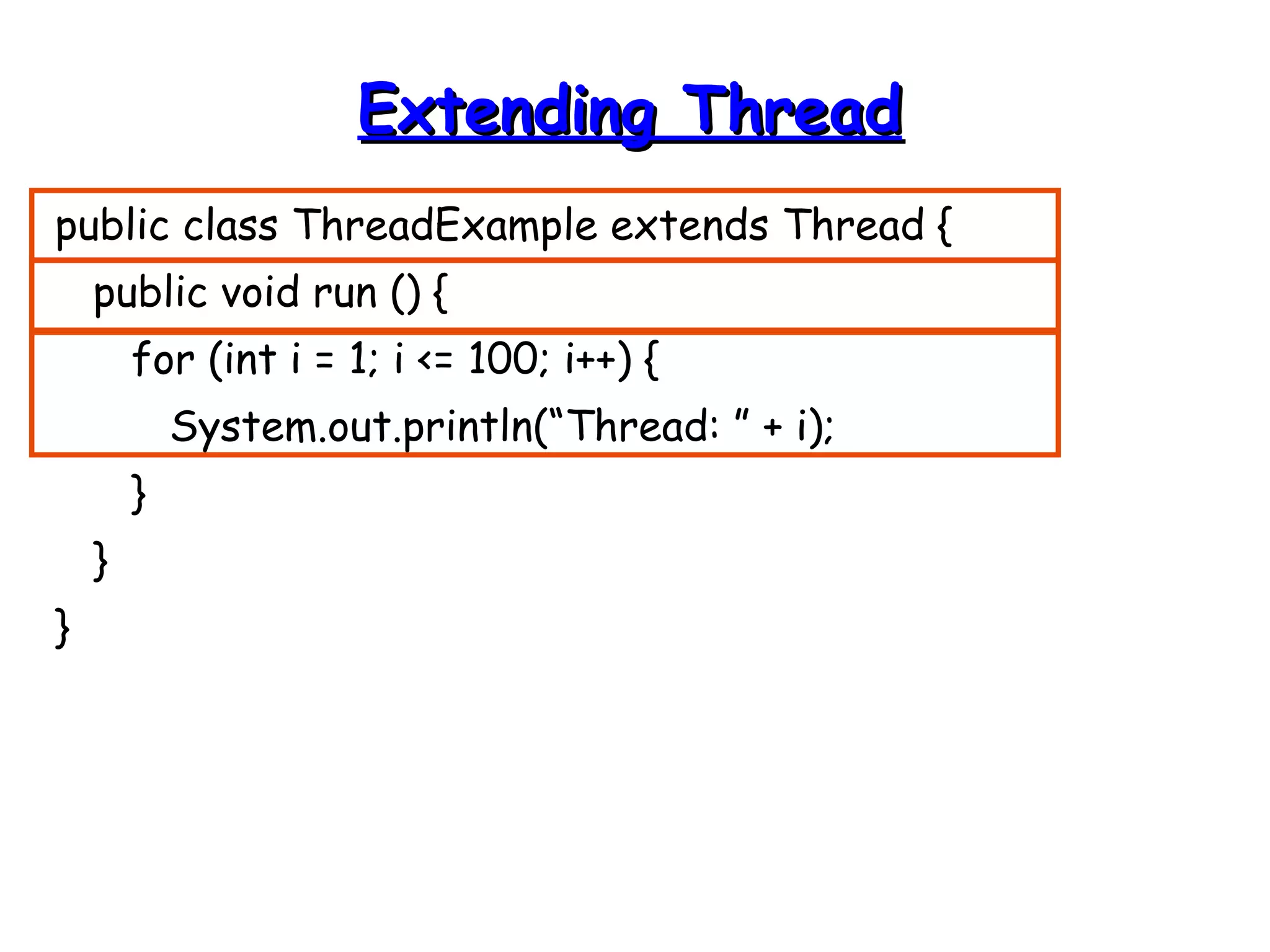
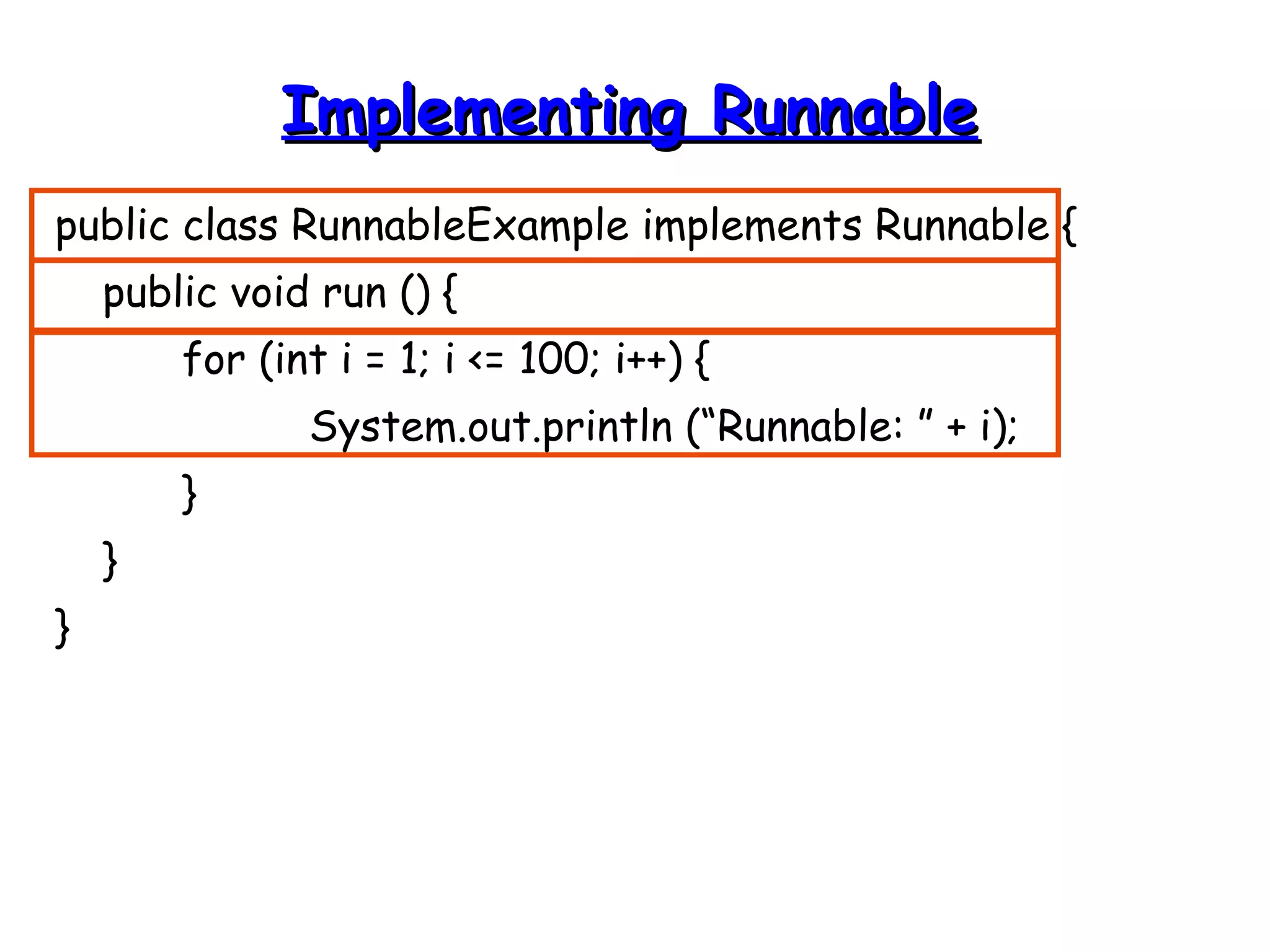
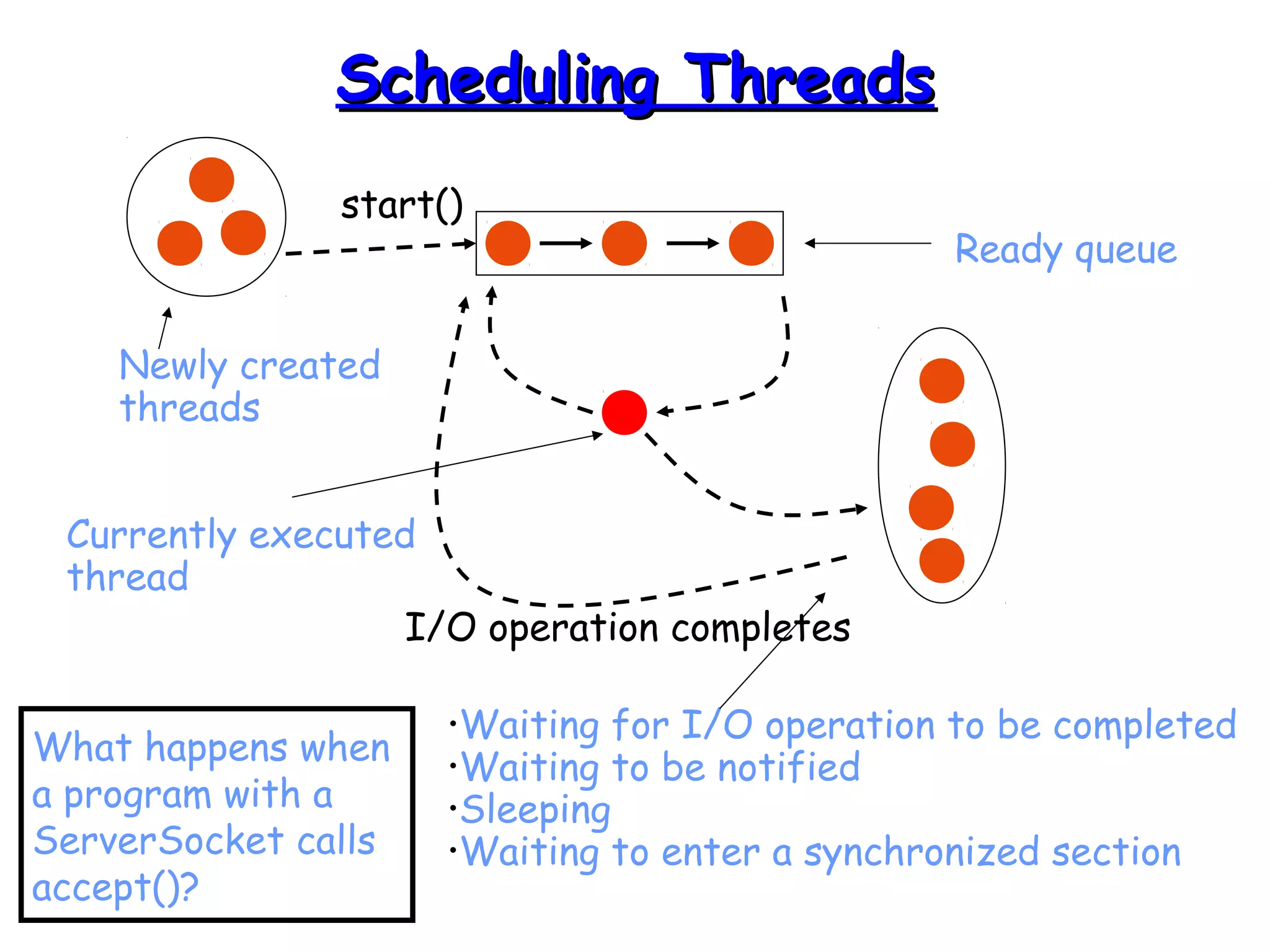
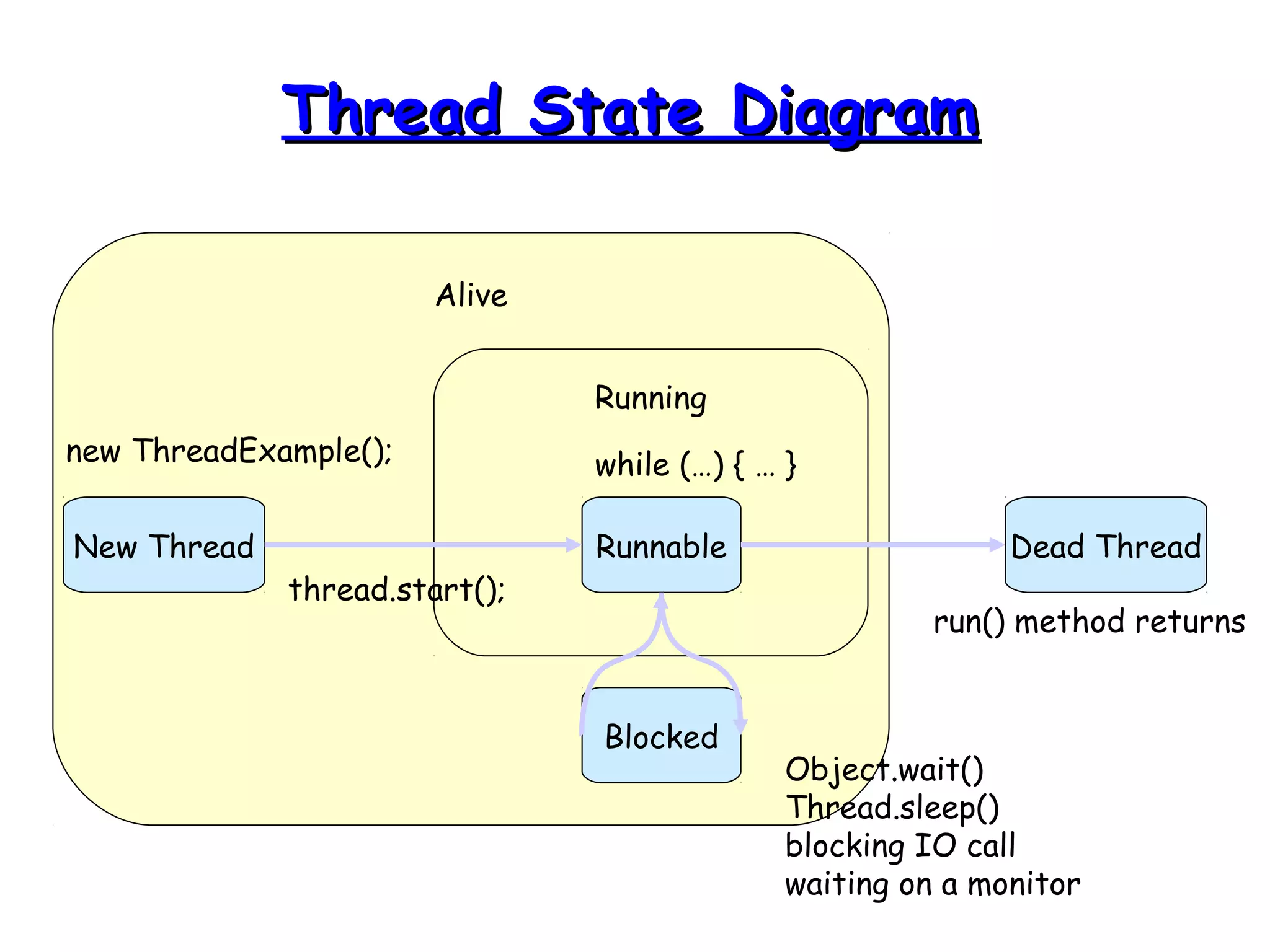
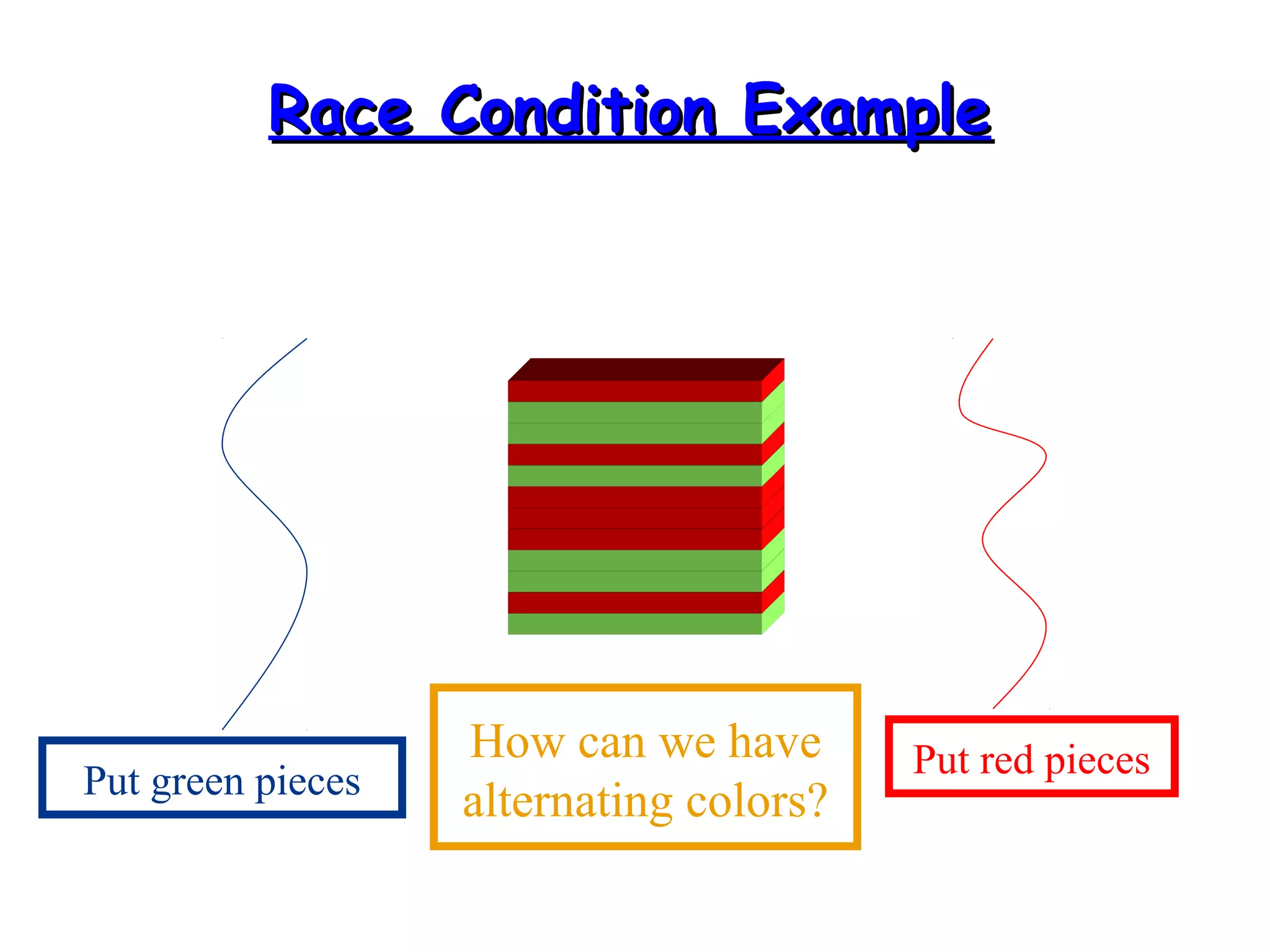
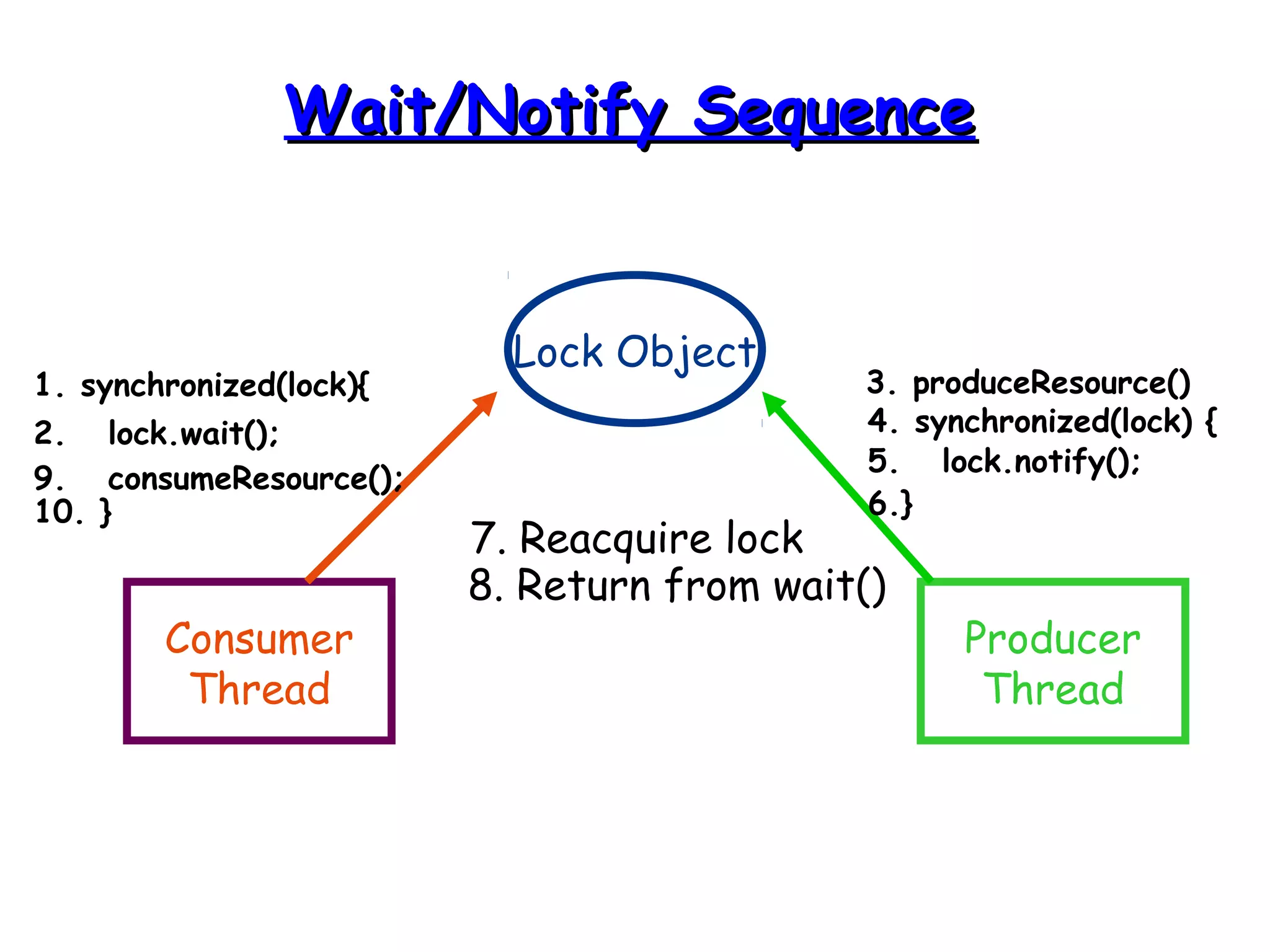
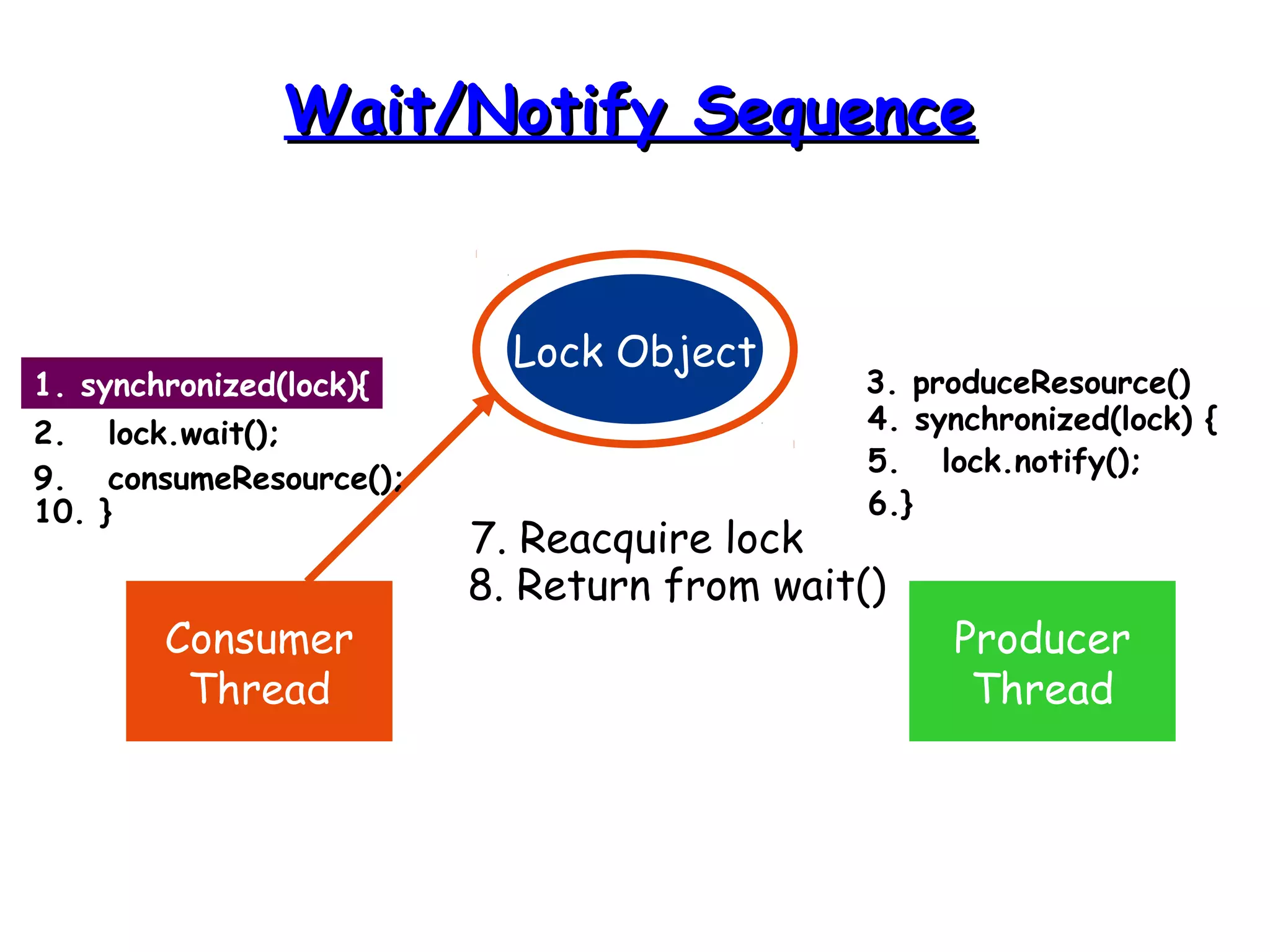
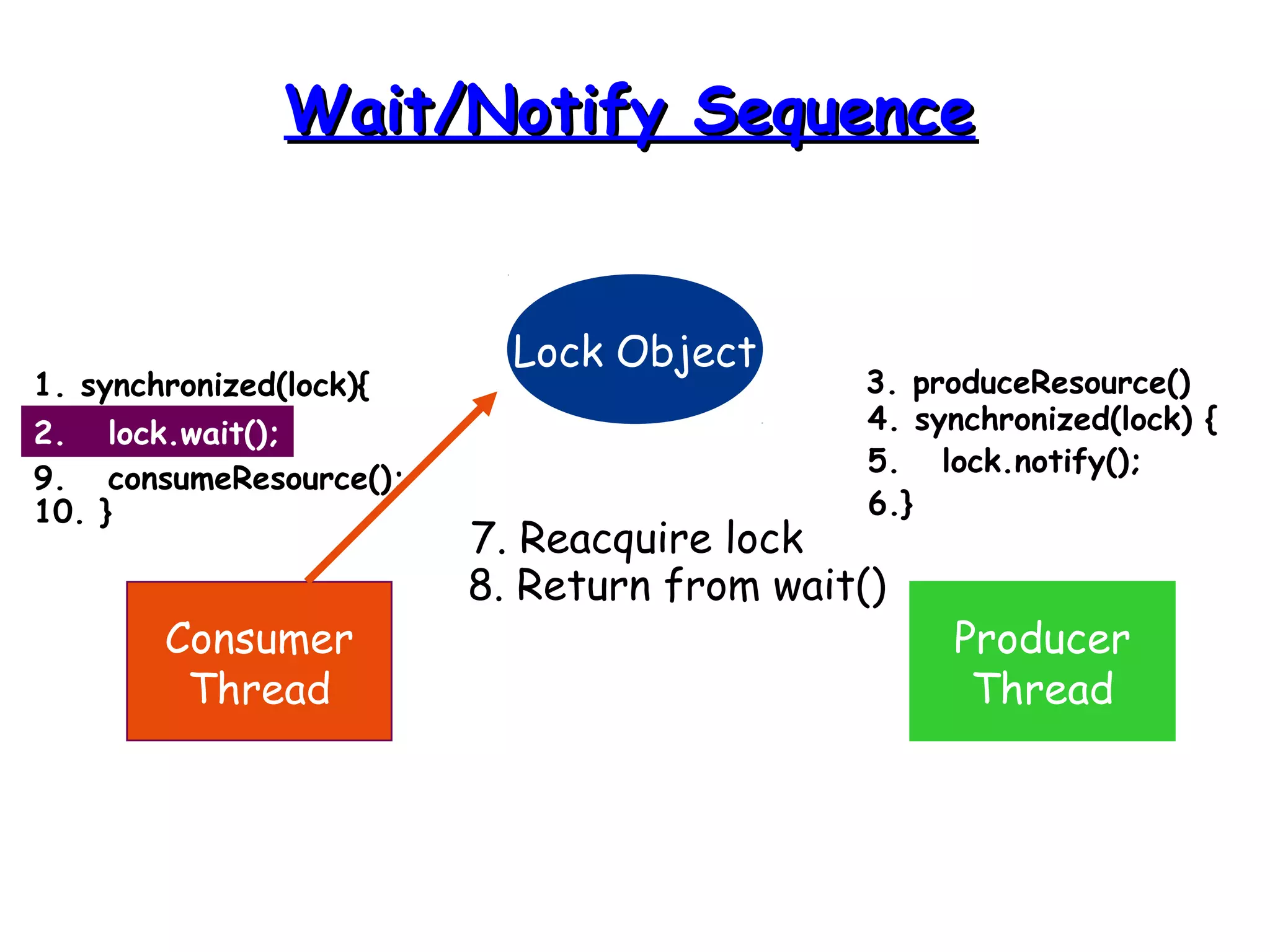
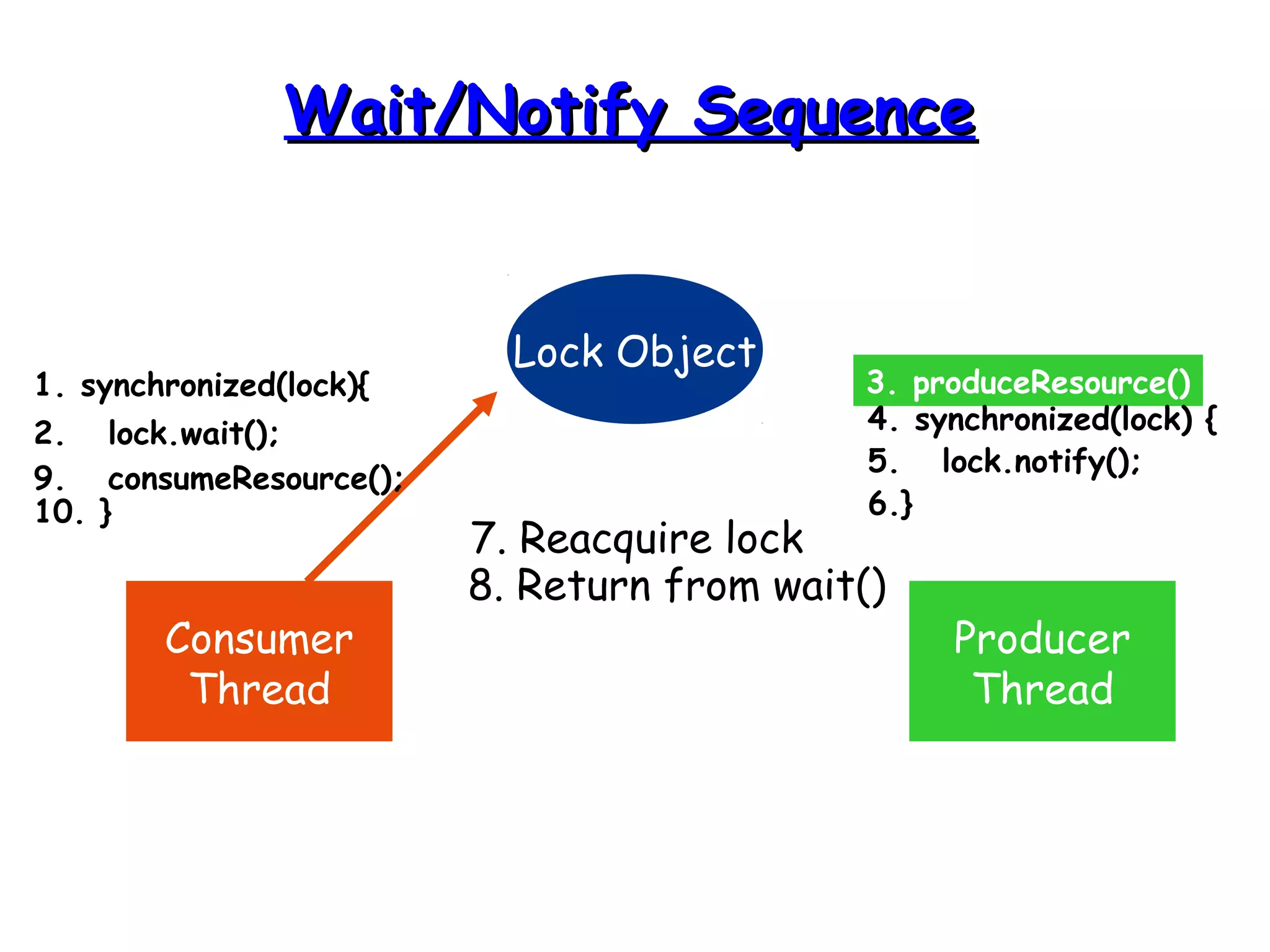
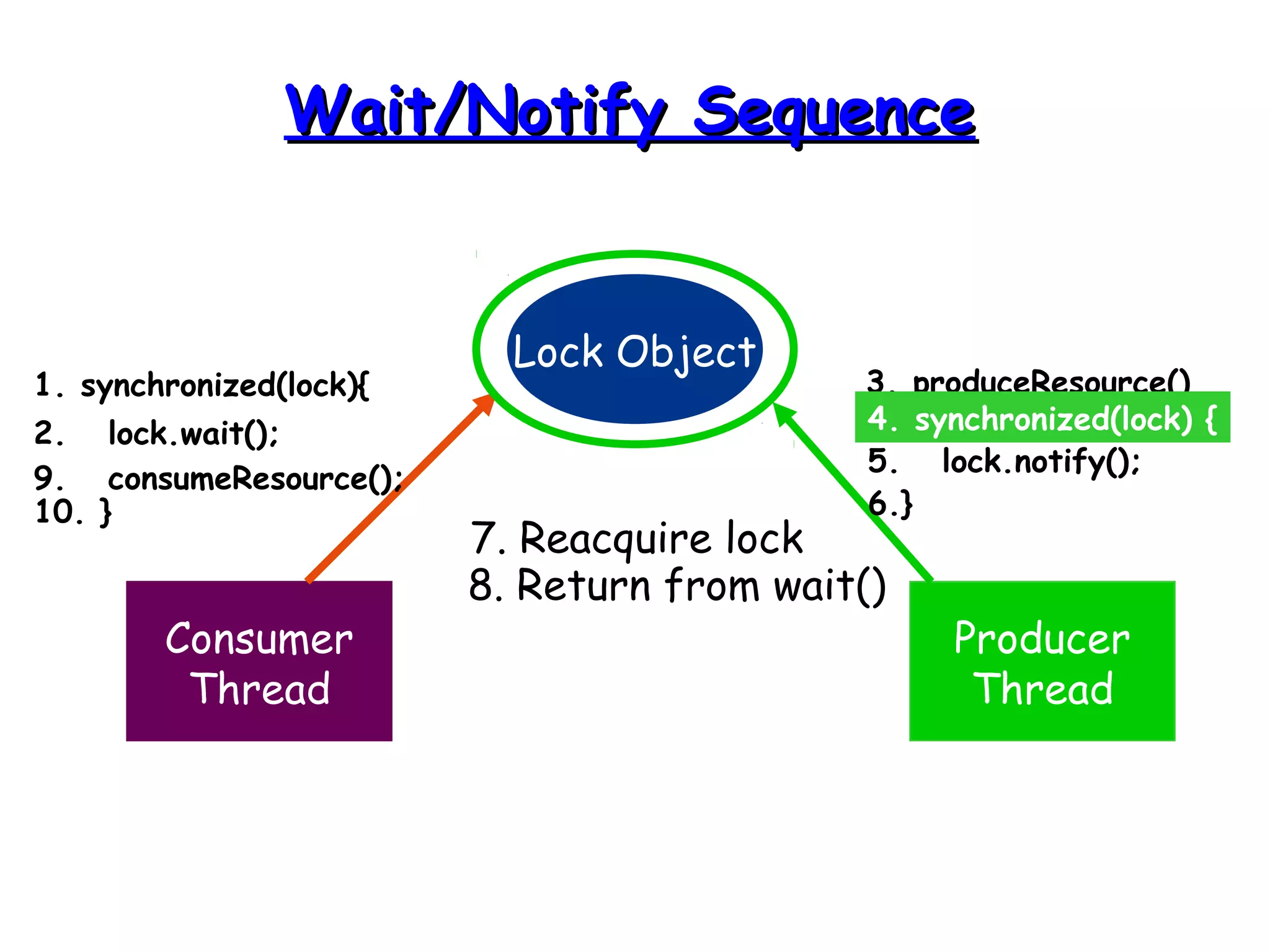
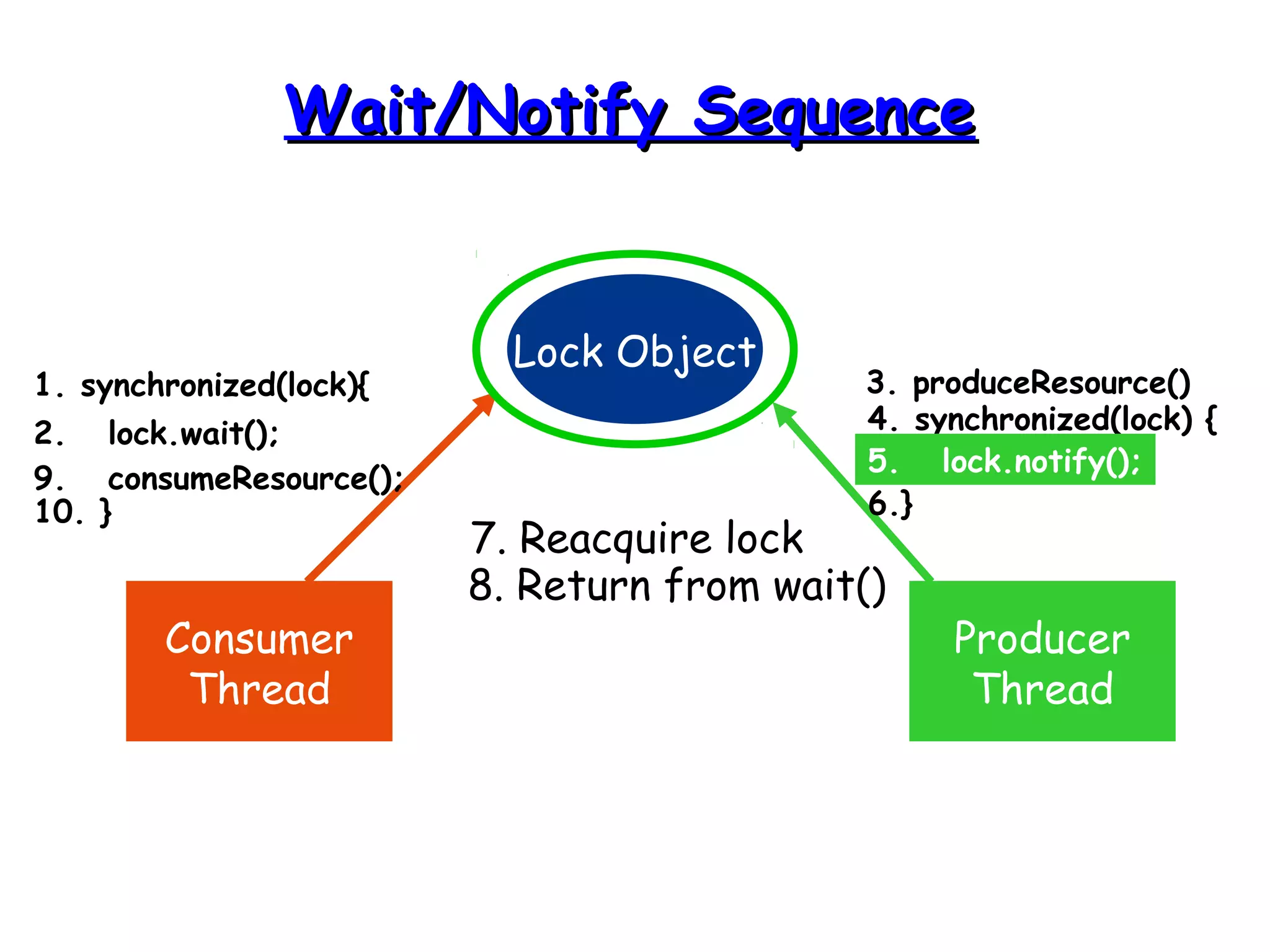
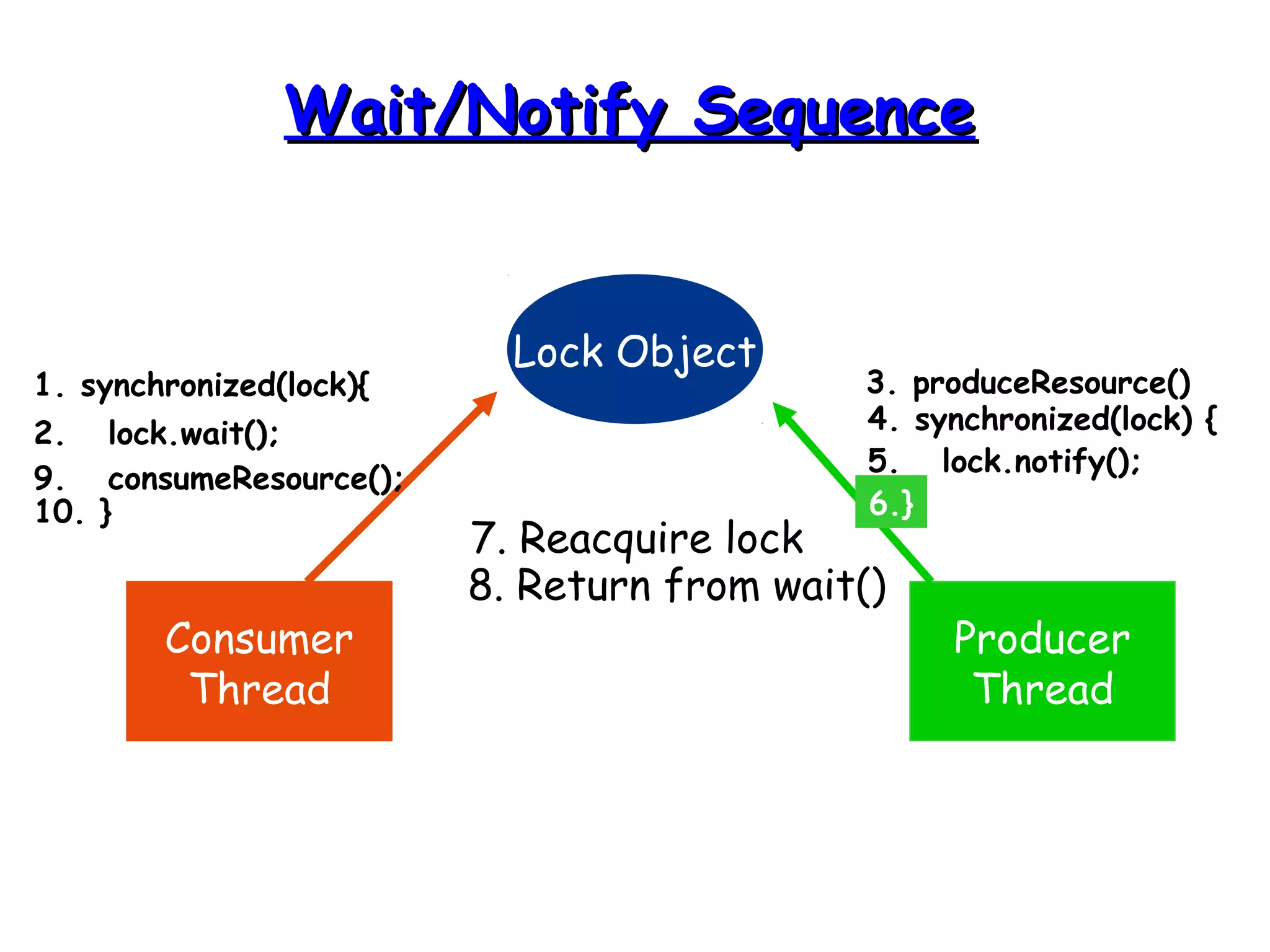
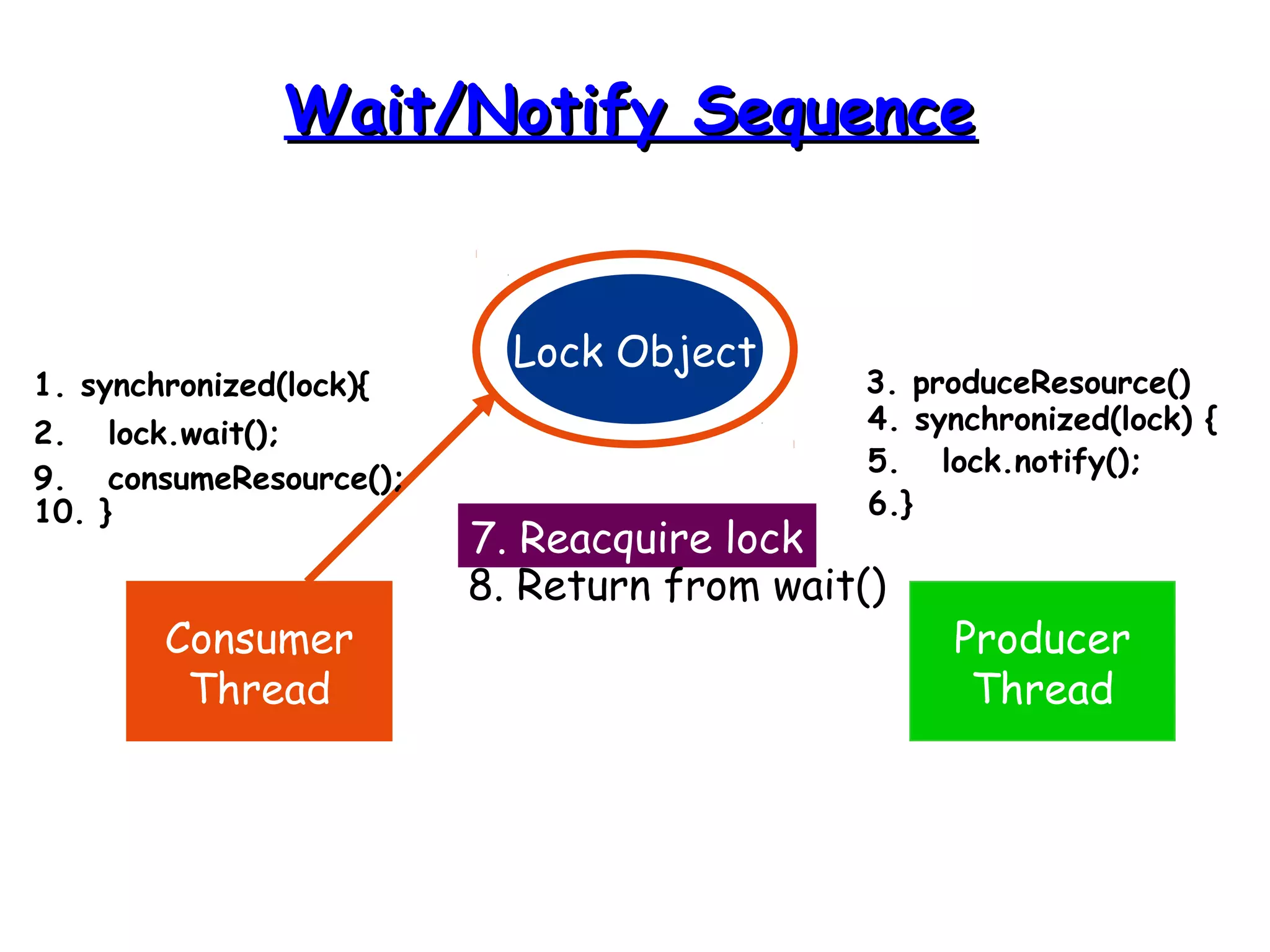
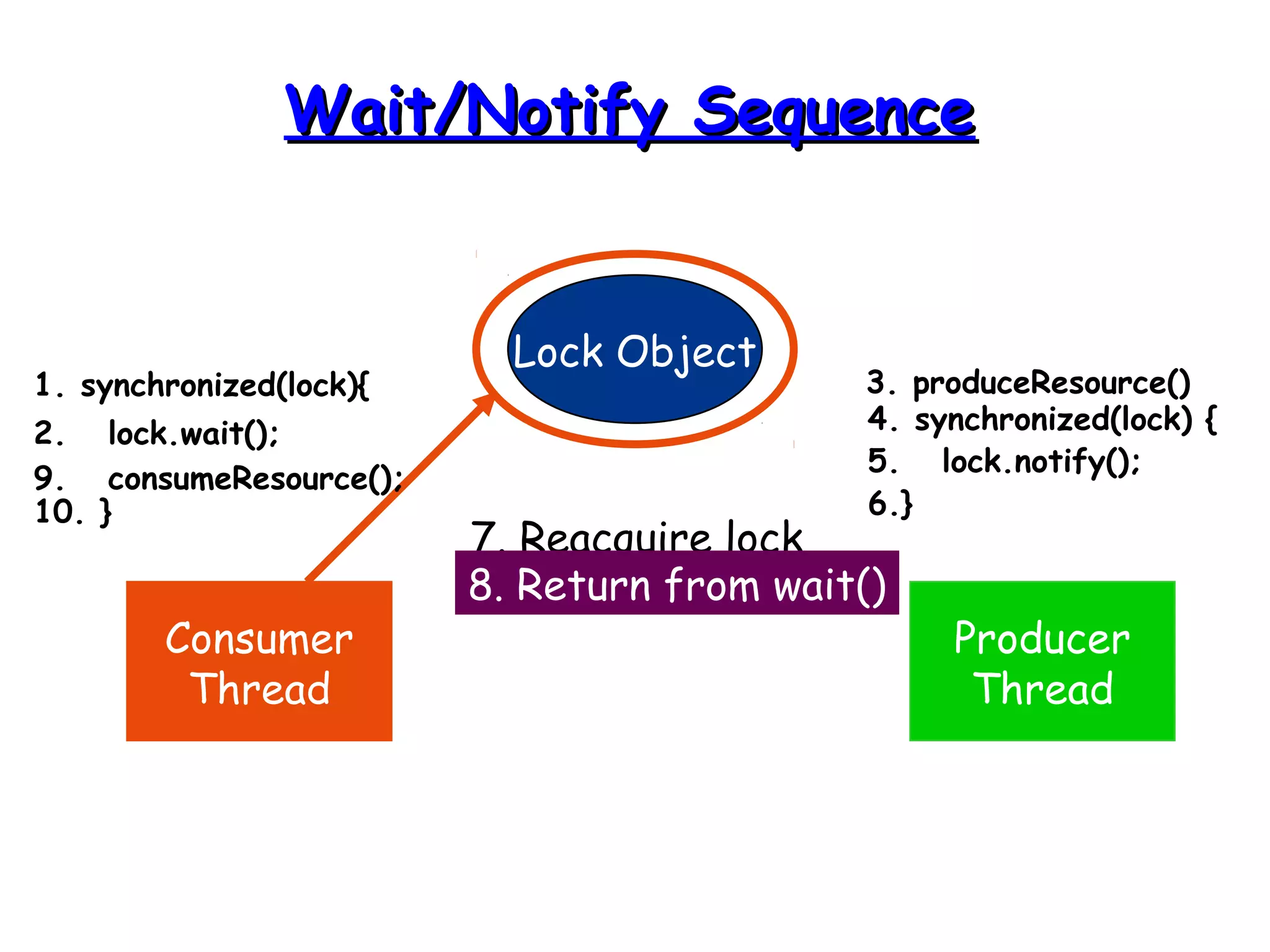
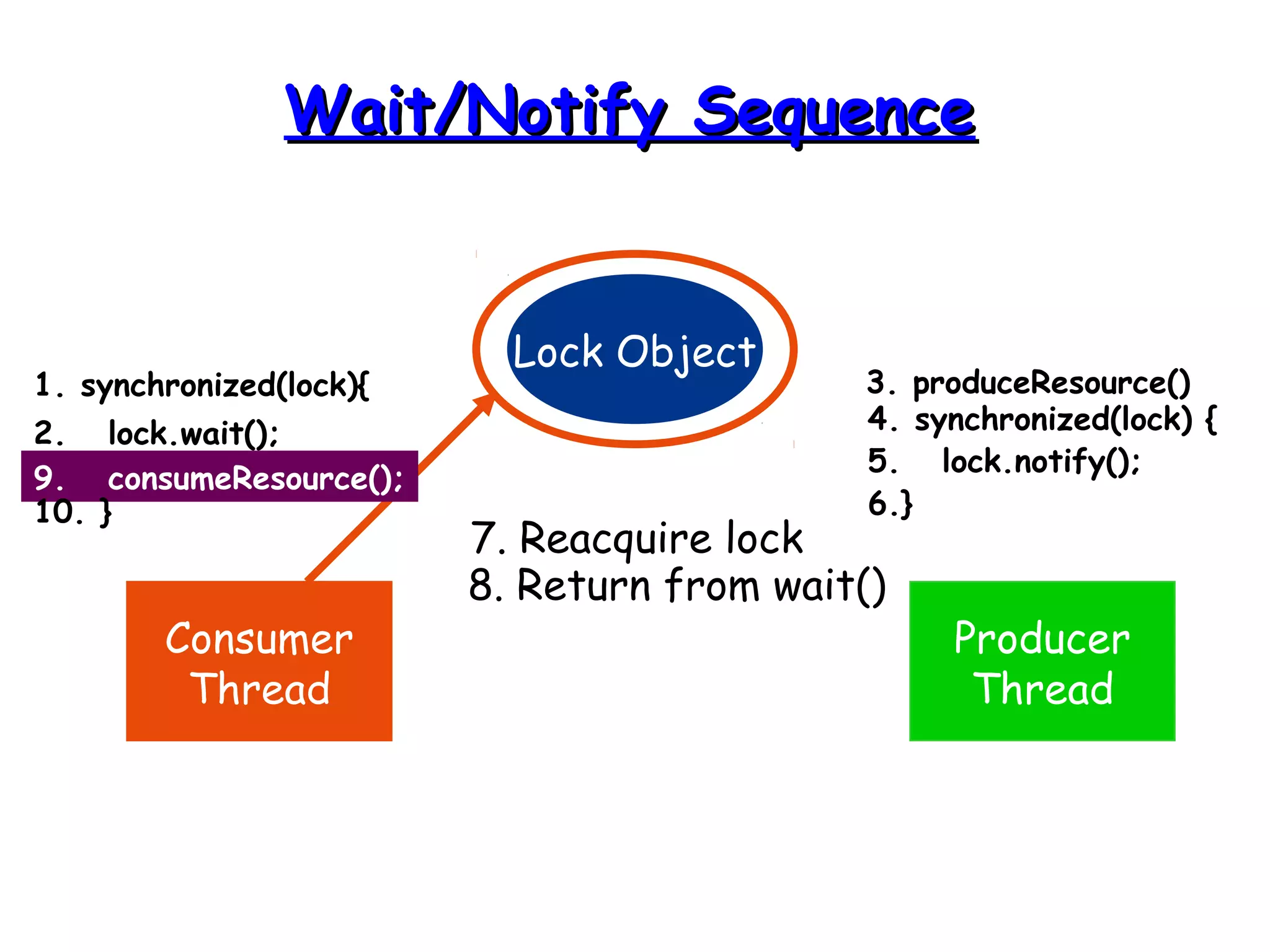
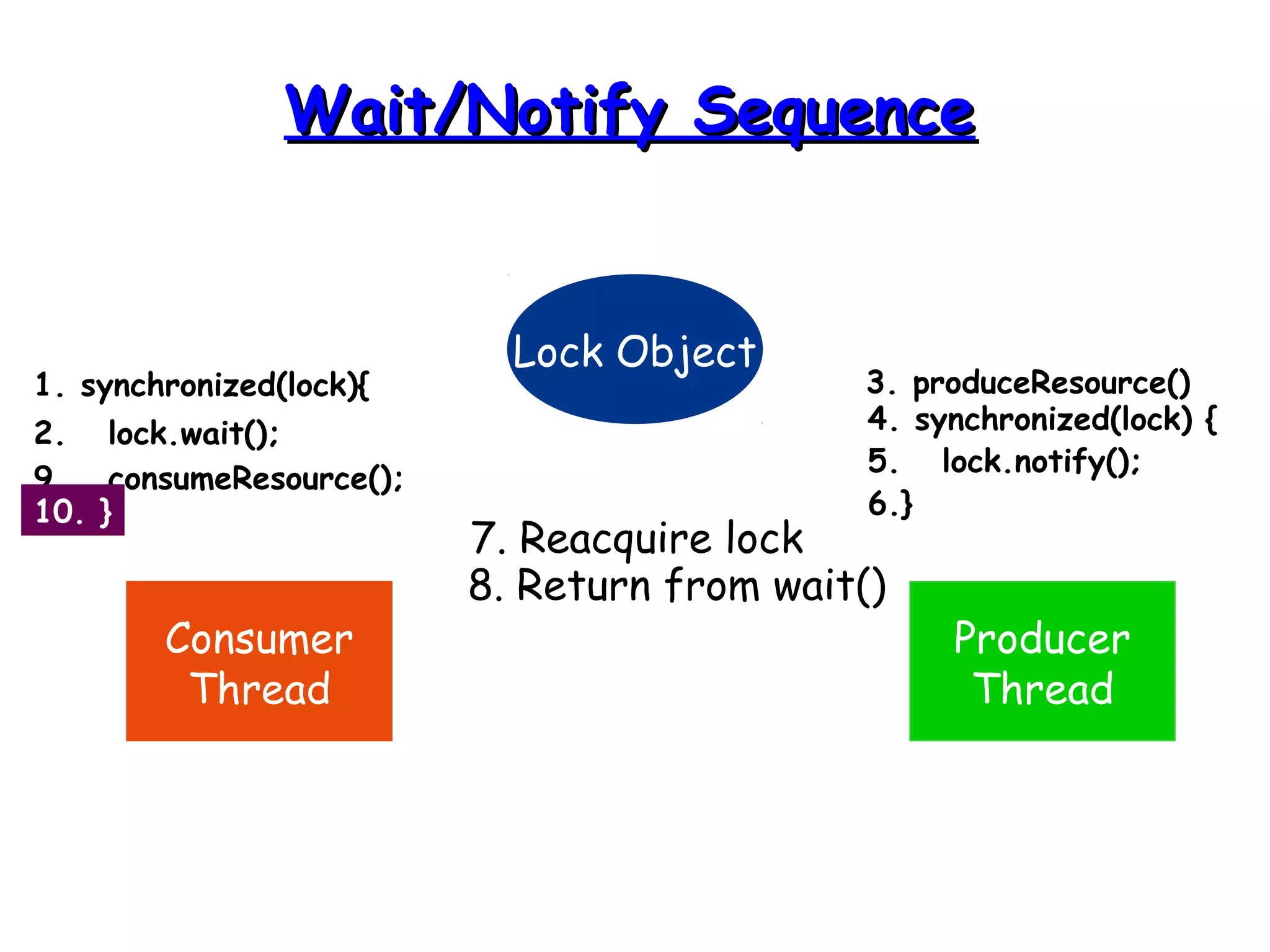
Threads allow programs to perform multiple tasks concurrently. A thread is a single sequence of execution within a program. Multithreading refers to multiple threads running within a single program. Threads share program resources but have their own call stack and local variables. Threads are created by extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface. Synchronization is needed when multiple threads access shared resources concurrently to prevent race conditions. The wait() and notify() methods enable threads to cooperate by pausing and resuming execution.






![SSttaarrttiinngg tthhee TThhrreeaaddss
public class ThreadsStartExample {
public static void main (String argv[]) {
new ThreadExample ().start ();
new Thread(new RunnableExample ()).start ();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threads-140911002055-phpapp02/75/Threads-in-Java-14-2048.jpg)
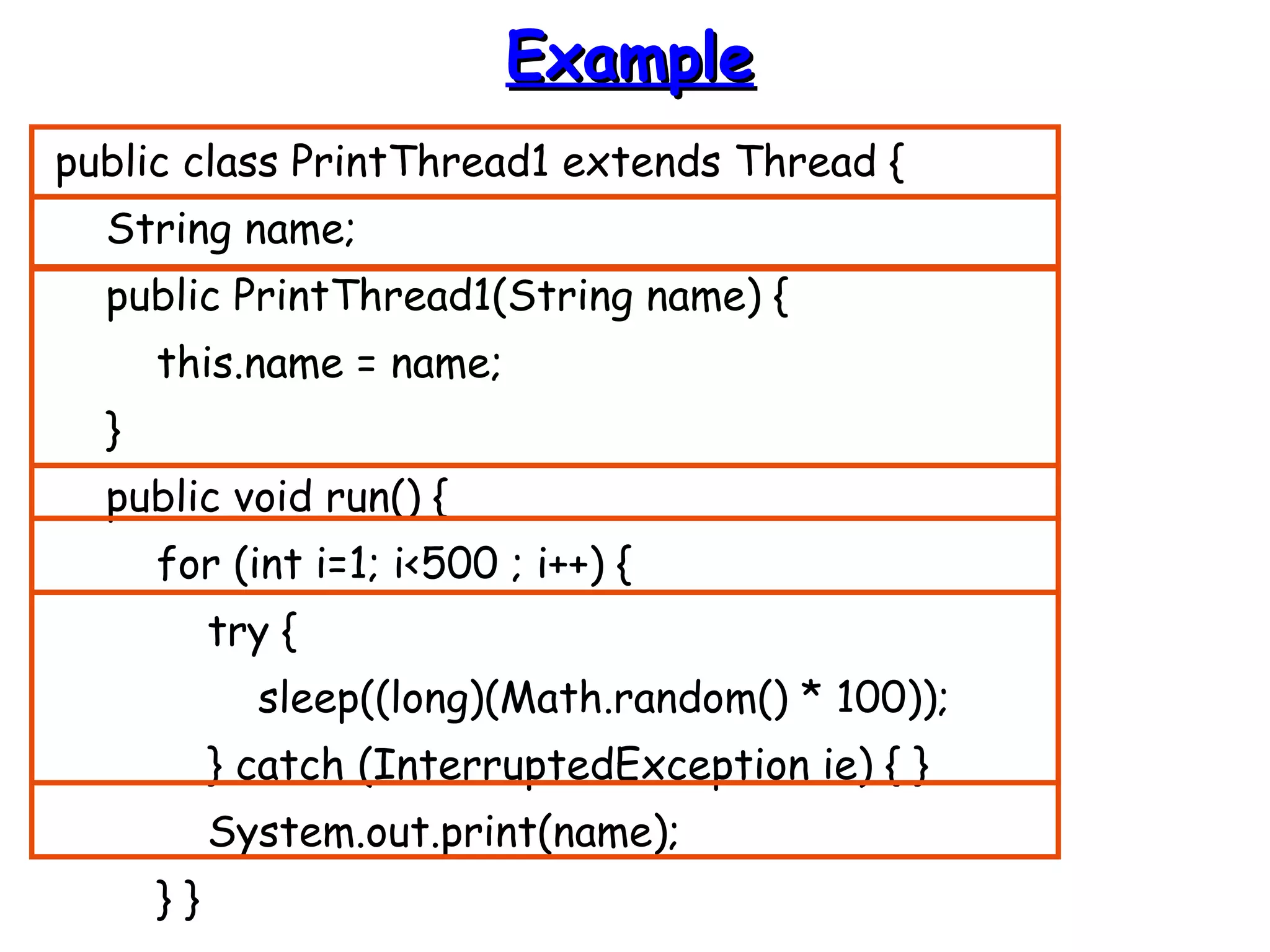
![EExxaammppllee ((ccoonntt))
public static void main(String args[]) {
PrintThread1 a = new PrintThread1("*");
PrintThread1 b = new PrintThread1("-");
PrintThread1 c = new PrintThread1("=");
a.start();
b.start();
c.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threads-140911002055-phpapp02/75/Threads-in-Java-18-2048.jpg)













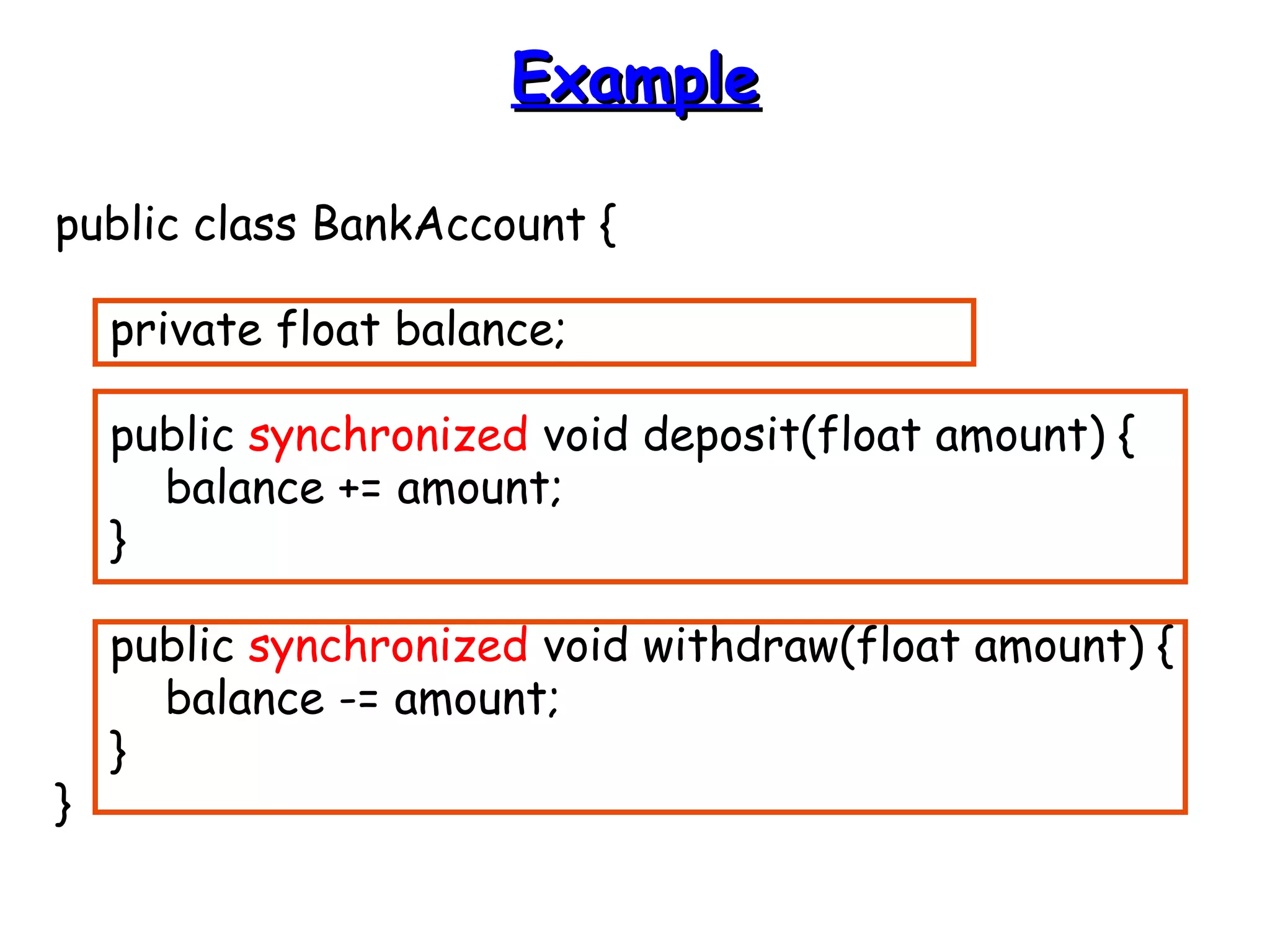

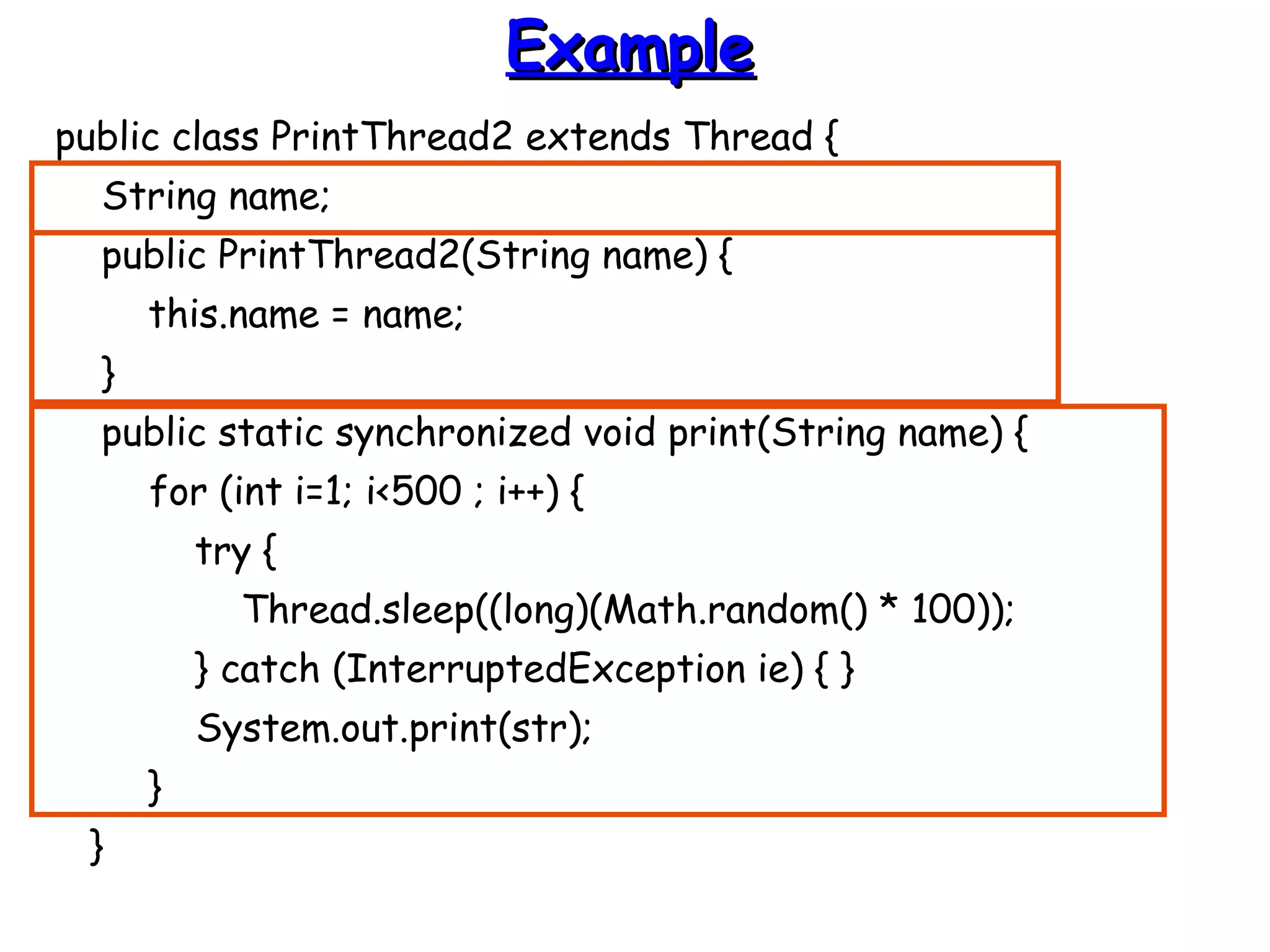
![EExxaammppllee ((ccoonntt))
public void run() {
print(name);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
PrintThread2 a = new PrintThread2("*“);
PrintThread2 b = new PrintThread2("-“);
PrintThread2 c = new PrintThread2("=“);
a.start();
b.start();
c.start();
}
}
RESULT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threads-140911002055-phpapp02/75/Threads-in-Java-37-2048.jpg)

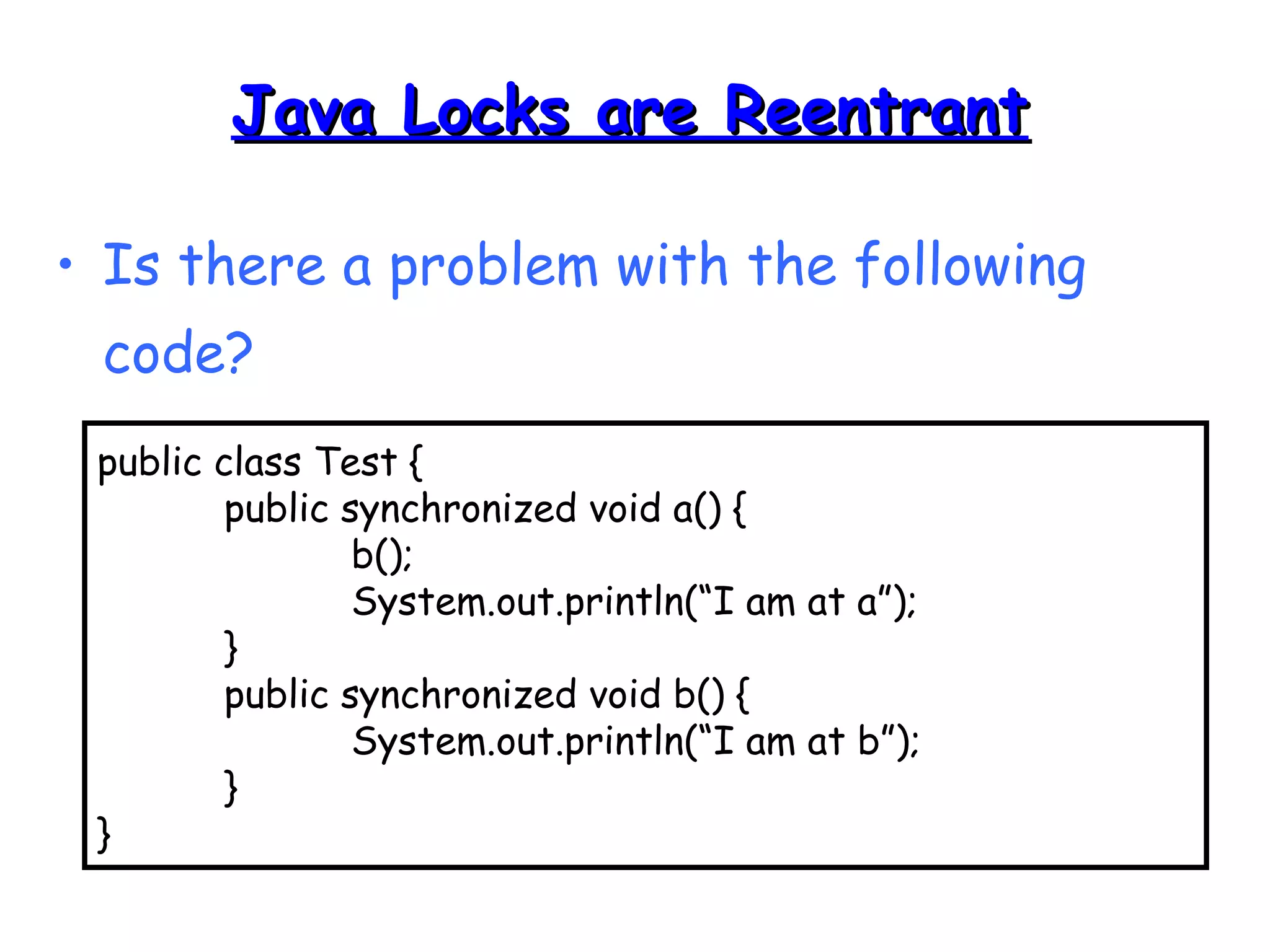





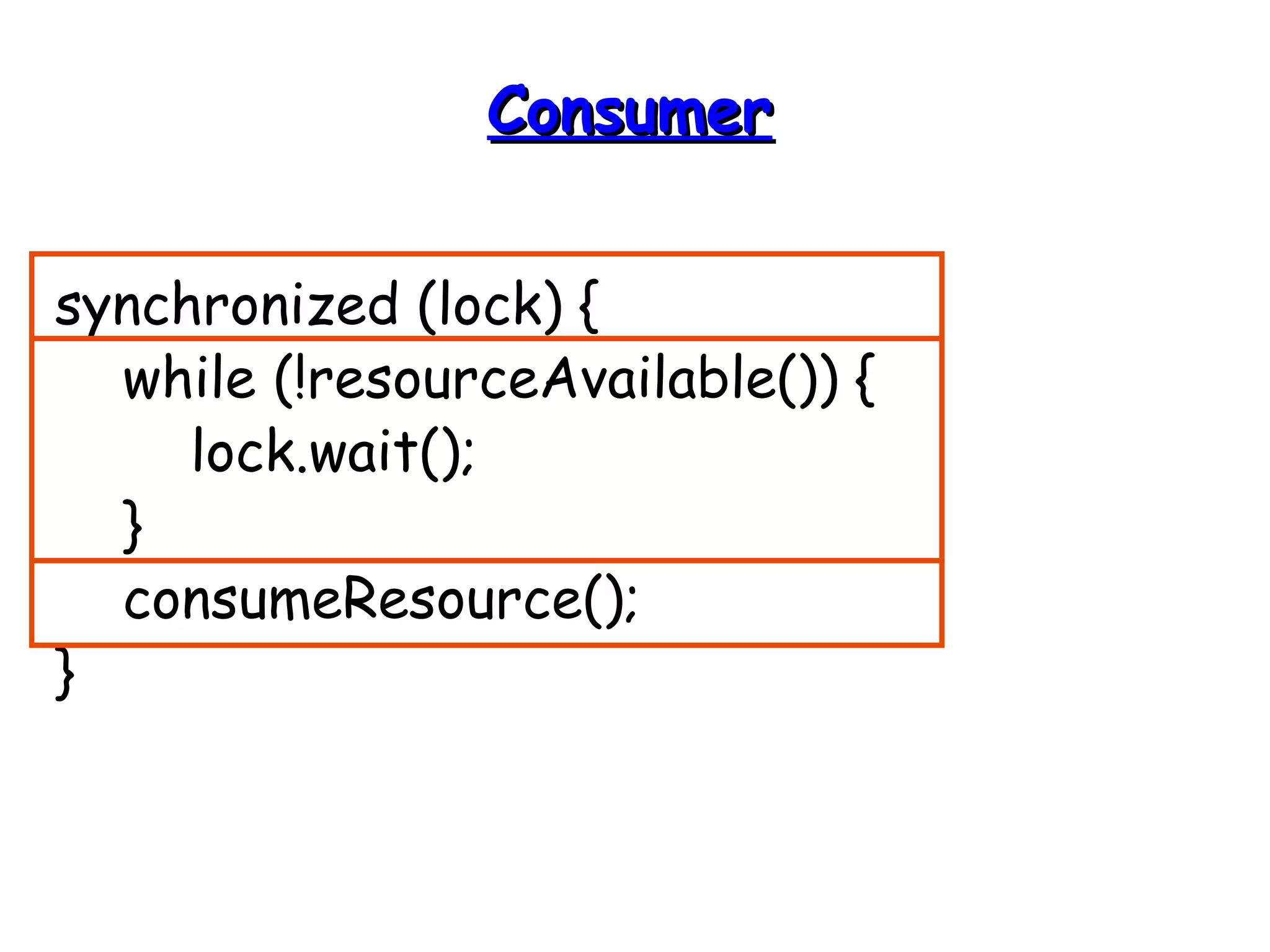






![import java.util.*;
public class MinchaTask extends TimerTask {
public void run() {
System.out.println(“Time for Mincha!!!!”);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
long day = 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24;
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new MinchaTask(),
new Date(), day);
}
}
TTiimmeerr EExxaammppllee](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threads-140911002055-phpapp02/75/Threads-in-Java-63-2048.jpg)
