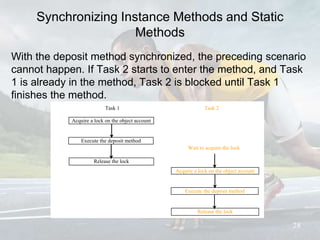
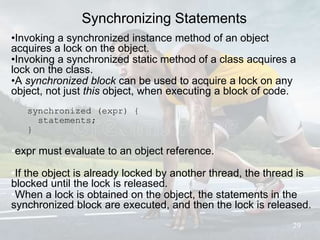
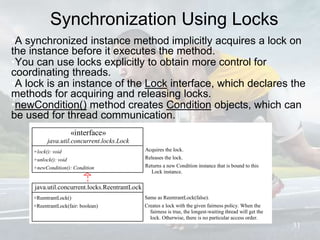
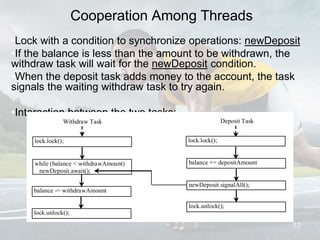
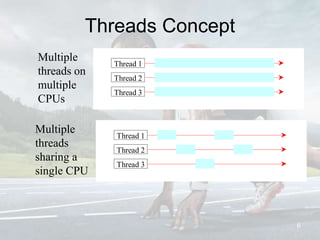
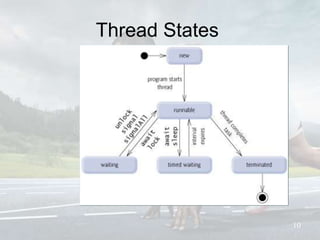
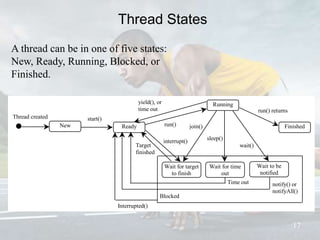
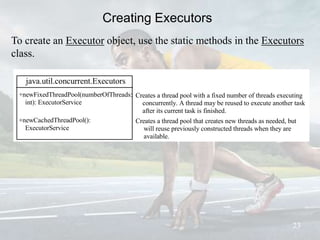
This document discusses multithreading and concurrency in Java. It defines a thread as a single sequential flow of control within a program. Multithreading allows a single processor to run multiple threads concurrently by rapidly switching between them. Creating threads in Java involves either extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface. The document outlines thread states like new, ready, running, blocked, and finished. It also discusses thread scheduling, priorities, synchronization to prevent race conditions, and thread pools for managing tasks.



















![Thread Synchronization
24
A shared resource may be corrupted if it is
accessed simultaneously by multiple threads.
Example: two unsynchronized threads accessing
the same bank account may cause conflict.
Step balance thread[i] thread[j]
1 0 newBalance = bank.getBalance() + 1;
2 0 newBalance = bank.getBalance() + 1;
3 1 bank.setBalance(newBalance);
4 1 bank.setBalance(newBalance);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ooplecture-week14-191111023820/85/Multi-Threading-24-320.jpg)