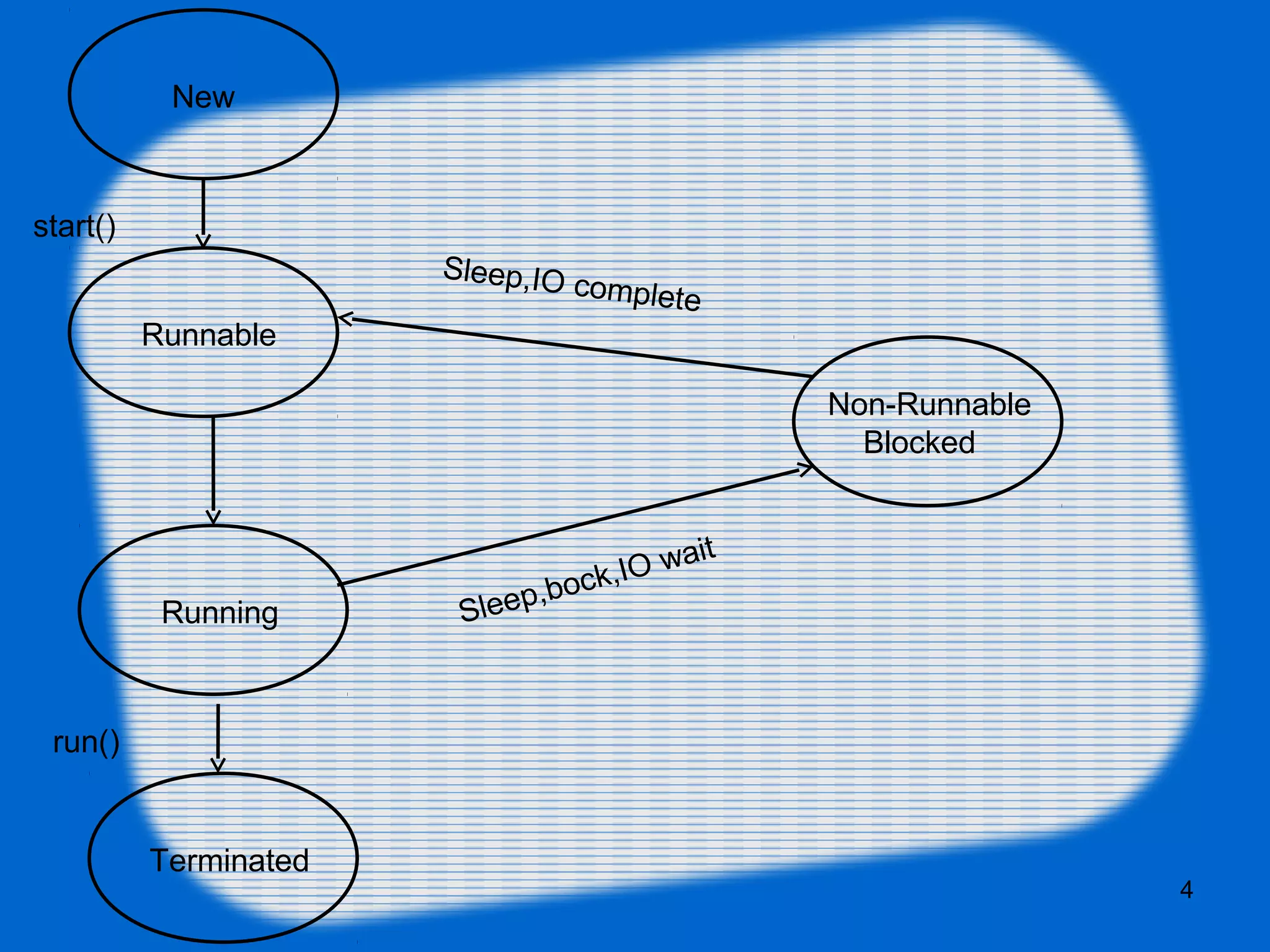
The document explains Java threading, describing two methods of creating threads: by extending the Thread class and implementing the Runnable interface. It outlines various thread states, key methods in the Thread class, and details about thread priority, synchronization, and interrupts. Examples of implementing threads using both methods are provided to illustrate their functionality.






![class Multi extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("thread is running...");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Multi t1=new Multi();
t1.start();
}
}
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-thread-151027134920-lva1-app6891/75/Java-thread-8-2048.jpg)
![class Multi implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
System.out.println("thread is running...");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Multi3 m1=new Multi3();
Thread t1 =new Thread(m1);
t1.start();
}
}
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-thread-151027134920-lva1-app6891/75/Java-thread-9-2048.jpg)





