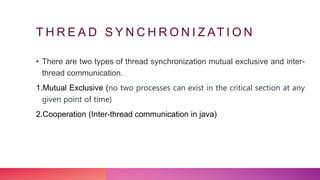
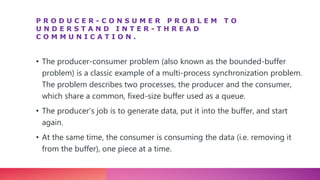
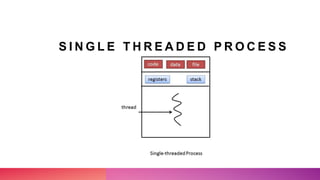
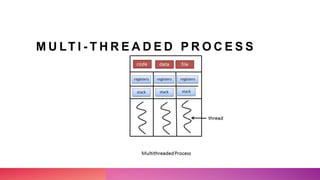
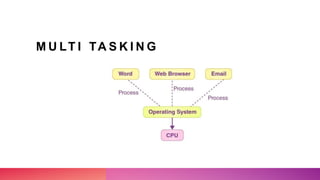
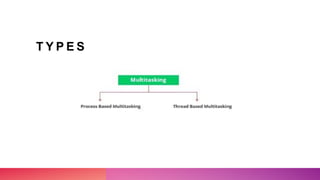
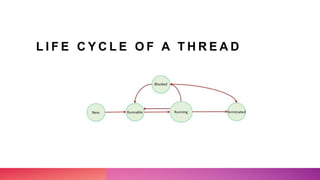
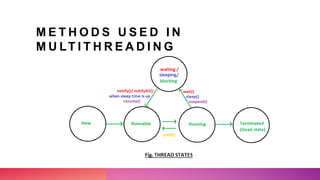
Multithreading allows a process to be split into multiple threads to allow parallel processing and faster execution. A thread is a sub-division of a process that can run concurrently with other threads. There are two main ways to create threads in Java: by extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface. Threads have lifecycles and states like new, runnable, running, blocked, waiting, and terminated. Synchronization is used to control access to shared resources and prevent interference between threads.











![class Multi extends Thread{
public void run(){
System.out.println("thread is running...");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Multi t1=new Multi();
t1.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-231025194714-76bc9787/85/multithreading-pptx-18-320.jpg)

![class Multi implements Runnable{
public void run(){
System.out.println("thread is running...");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Multi m1=new Multi();
Thread t1 =new Thread(m1); // Using the constructor Thread(Runnable r)
t1.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-231025194714-76bc9787/85/multithreading-pptx-20-320.jpg)