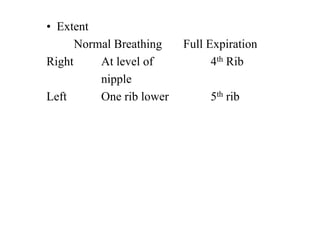
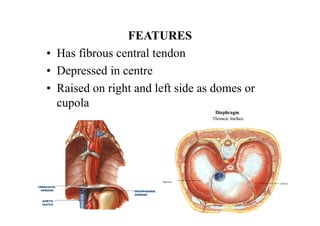
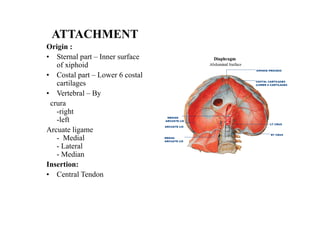
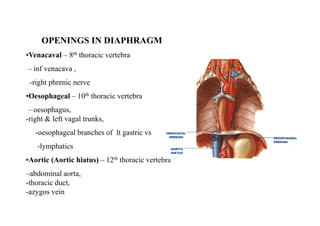
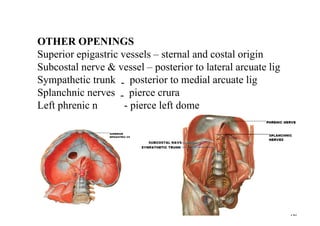
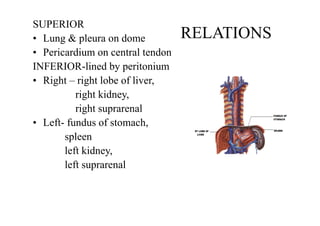
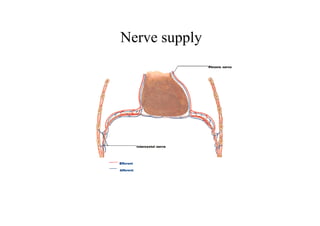
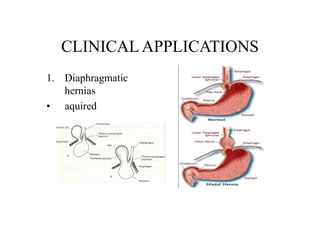
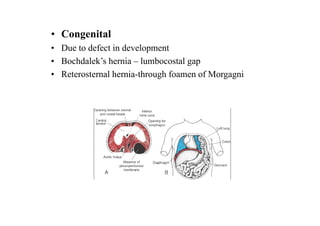
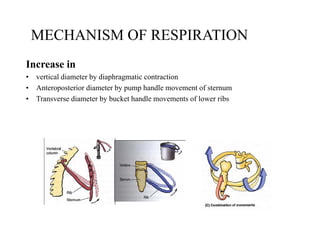
The diaphragm is a thin fibro muscular partition that separates the abdomen and thorax. It is the primary muscle of respiration and has a central tendon and domes on the right and left sides. It attaches to the sternum, lower ribs, and vertebrae. There are openings for structures like the vena cava, esophagus, and aorta. During breathing, the diaphragm contracts to increase the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity. It functions to inspire air into the lungs and acts as a thoracoabdominal pump to circulate blood. Clinical applications include diaphragmatic hernias and paralysis.