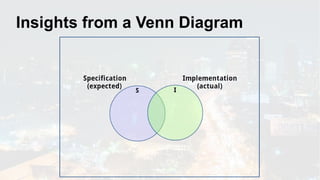
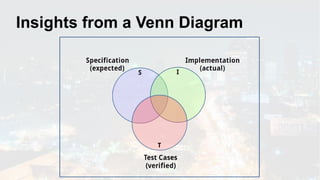
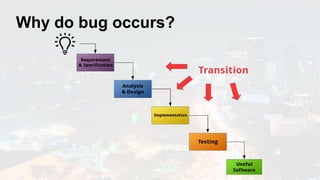
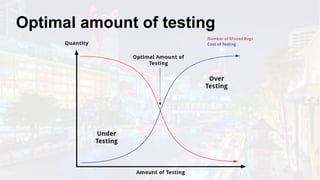
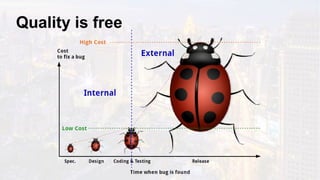
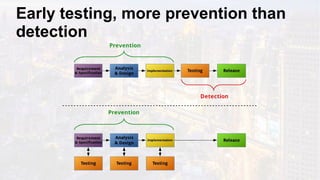
The document discusses the fundamentals of software testing, highlighting its role in demonstrating the absence of errors and ensuring programs function as intended. It emphasizes the definition of software bugs and the impracticality of exhaustive testing due to the vast number of potential test cases. Additionally, the document outlines the differences between testing and debugging, stressing that quality must be integrated into the development process rather than solely reinforced through testing.