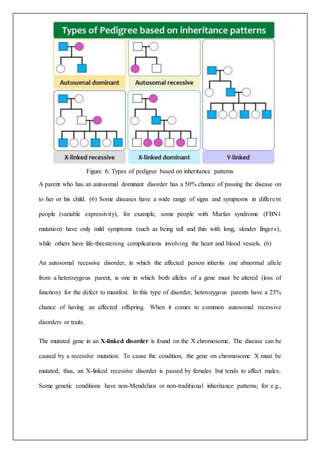
The document discusses using targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) panels to identify genetic causes of nephrotic diseases in individuals with unknown etiology. The study found rare pathogenic/likely pathogenic mutations in nephrotic disease-related genes in 12% of patients using the ACMG-AMP variant classification standards. NGS can improve diagnosis accuracy for nephrotic diseases by discovering uncommon pathogenic variations compatible with clinical diagnoses in 65% of samples. The document provides background on genetics, genetic variations, inheritance patterns, and NGS techniques for detecting mutations.