1) The study aimed to determine the effect of music and noise elimination on sedative requirements in patients undergoing surgery under spinal anesthesia.
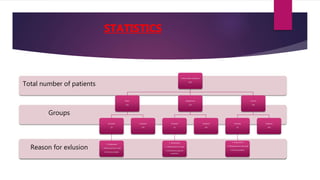
2) 87 patients were randomly assigned to three groups: a control group with no headphones exposed to ambient noise; a music group who listened to relaxing instrumental music; and a headphones only group.
3) Sedative requirements were assessed using Ramsay Sedation Scores and Bispectral Index monitoring. Patient satisfaction was also evaluated. The study found that listening to music significantly reduced intraoperative sedative requirements compared to the other groups.










![ In addition Bispectral index monitor [BIS] was connected, Baseline value noted and
injection midazolam 0.04mg per kg i.v will be given.
Further depending on group allotted
For,
• Group-C: Control group- No headphones, patients were exposed to operative room
ambient noise.
• Group M: Receive music through headphones, volume comfortable to the patient
[Instrumental relaxing music].
• Group H: Patients were given headphones with no music.
METHODOLOGY: Contd..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-220905105233-f42b78f4/85/thesis-presentation-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![ Type of music- Instrumental music (same music for all the patients allotted in group M).
All Haemodynamic parameters [Heart rate, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and
mean arterial pressure] noted along with BIS score and Ramsey sedation score(RSS).
Intra operatively baseline parameters, BIS index, Ramsey sedation score were noted as follows:
1. Every 5 minutes for the First 20 minutes of the procedure.
2. Every 10 minutes from 20 minutes to 1 hour of the procedure.
3. Every 20 minutes after 1 hour of surgery till the end of procedure.
METHODOLOGY: Contd..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-220905105233-f42b78f4/85/thesis-presentation-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![ Intra operative sedation requirement was be determined by Ramsey sedation score.
Intra operatively if patients Ramsey sedation score is less than 3, Injection Midaolam i.v 0.01mg per kg
given [Maximum dosage-0.1mg per kg].
SCORE RESPONSE
1 ANXIOUS OR RESTLESS OR BOTH
2 COOPERATIVE,ORIENTED AND TRANQUIL
3 RESPONDING TO VERBAL COMMANDS
4 BRISK RESPONSE TO STIMULUS
5 SLUGGISH RESPONSE TO STIMULUS
6 NO RESPONSE TO STIMULUS
METHODOLOGY Contd..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-220905105233-f42b78f4/85/thesis-presentation-pptx-13-320.jpg)