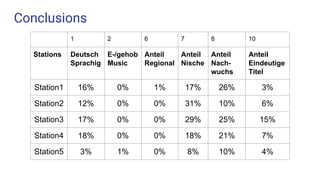
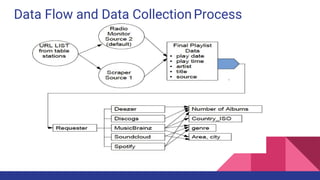
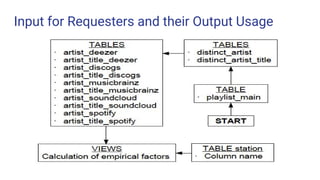
This document discusses music information retrieval and classifying German radio stations based on their content. It involves collecting music metadata from over 200 publicly accessible German radio stations using various data sources. The stations are then analyzed and classified based on empirical factors like the proportion of German artists played, newcomer artists, distinct song titles, etc. An experiment is also described to use audio fingerprinting to identify songs from radio broadcasts to reduce requests to music databases and help analyze broadcast monitoring. The results show classifications of 5 sample stations based on the empirical factors. Overall, the study aims to systematically classify radio stations in Germany based on their music content.

![What is Information Retrieval?
● It is a discipline that deals with retrieval of unstructured data
● Mainy textual documents
● This is in response to a query or topic statement
● Output may be unstructured or structured
● Example:
○ A sentence or even another document (Unstructured),
○ A boolean expression (Structured document) [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesisfinalpresentation-170901125914/85/Thesis-presentation-on-Music-Information-Retrieval-2-320.jpg)




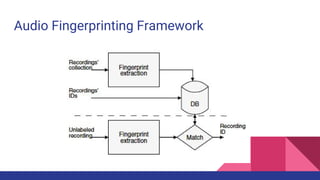
![Experiment on Audio Fingerprint
● What is audio fingerprinting?
○ It is a summary of an audio object using a limited number of bits [2].
● Audio fingerprint need
○ It is crucial to think resourceful ways to accelerate the process
○ To analyse how effectively audio fingerprinting can be used in broadcast monitoring
○ To reduce the number of repeated requests to music information services.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesisfinalpresentation-170901125914/85/Thesis-presentation-on-Music-Information-Retrieval-9-320.jpg)
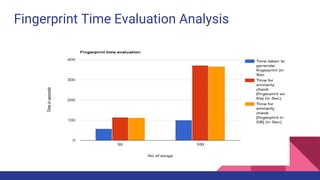
![Audio Fingerprint Realisation
● Various recent APIs were analysed
● Finally, musicg API was used which suited best to system requirements
● The system is prepared to take “.wav” file as input and generate fingerprints
● Use of the system:
○ Audio stream of 24 hrs is splitted to songs (.mp3)
○ “.mp3” are converted to “.wav” (ffmpeg)
○ This wave input generates fingerprint in byte stream
○ It give an opportunity to save it is as filetype or as byte[] in database
○ It also has an function to find similarity with other songs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesisfinalpresentation-170901125914/85/Thesis-presentation-on-Music-Information-Retrieval-10-320.jpg)